Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
first 4 pictures are source code for the Linked list. the Instructions are at the last two pages. please help! The list contains: CEF Removed:
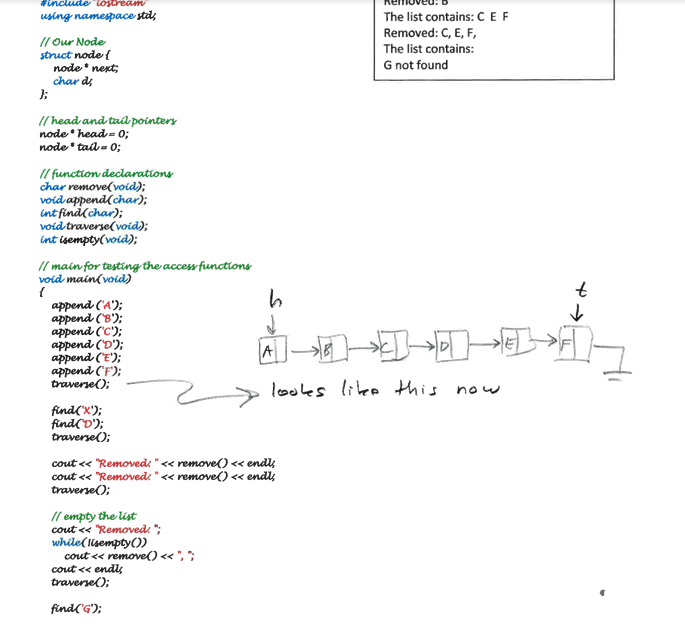
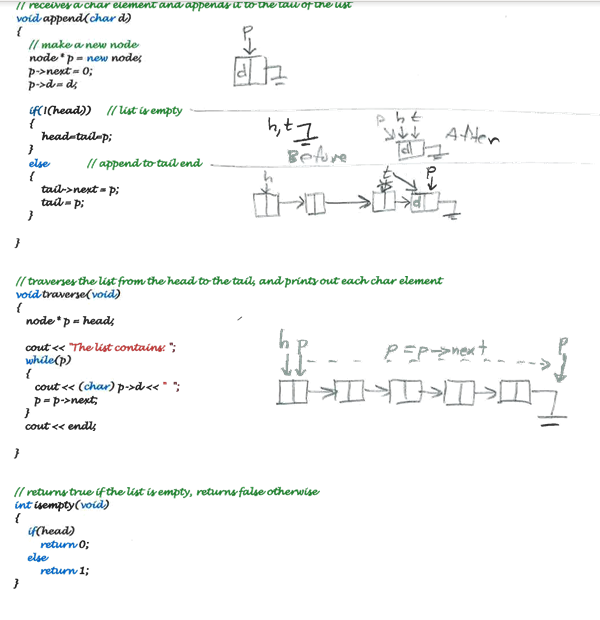
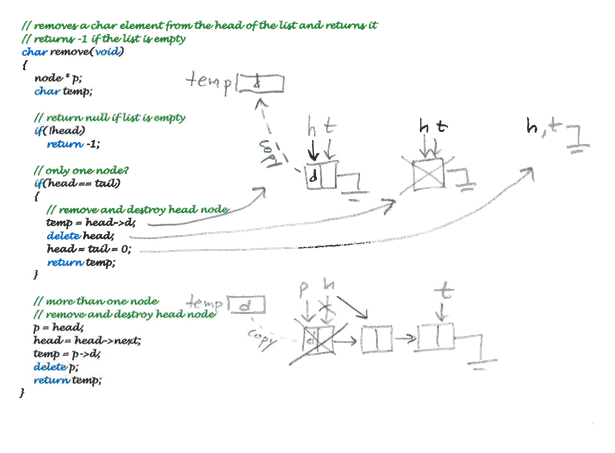
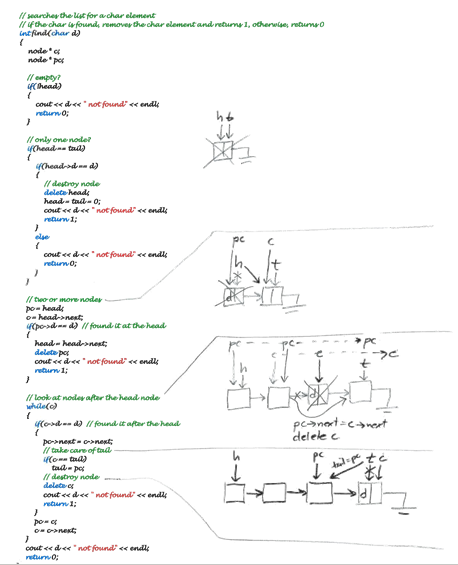

 first 4 pictures are source code for the Linked list. the Instructions are at the last two pages. please help!
first 4 pictures are source code for the Linked list. the Instructions are at the last two pages. please help!
The list contains: CEF Removed: C, E, F, The list contains: G not found l/Our Node struct nodef node next, char d Thead and talpointer- node*head- 0; node tail0 char remove void): void append(char): intfind char): void traverse(void); int isempty(void) II main for testing the acceswfiunctions void main void) append CA) append C8): append ('C'); append CD) append CE) findcx); findcD) Il empty the list cout"Removed whde lisempty)) "; coutnest; coutd, delete heads head tail 0 return temp; l more thanone nodee Il removeand destroy head ps head head a head-> next; temp- p->d, deletep return temp; ff searchey the ut for a char element ifthe char foandk removey the char element and returna I, othenelse retum intfind char d) nodecg node por f empty? f head lf only one nole? tad) desbroy node head-td O po- head o- head-net head head net deleta po return 1 f loobat nodey after the head nade delele c take core of tad //destroy nod.nw.- turn O Basic Containers Implementations See the posted file "LinkedList.pdf" and "CircList.pdf" which contain source code to mplement a simple "list" container using 2 different implementations. Input and debug this source as given, then use that as a code base to implement the following. A) Old Programs Get LinkedList and CircList working, and include the source code and testing in your B) New Programs 1) Stack 2) Queue 3) Priority Queue Using a circular array implementation Using a circular array implementation Using a circular array implementation 4) Stack 5) Queue 6) Priority Queue 7) Double Linked List Using a linked node implementation Using a linked node implementation Using a linked node implementation Using a linked node implementation C) Analysis Analyze, state, and explain the TIME COMPLEXITY in Big Oh notation for every function. D) Interface Functions Both implementations will share the same set of interface functions below Stack must su push(data) char pop(vold) char peek void); bool isempty void): appends data to the head of the list removes the head node and returns data; returns-1 if empty returns a copy of data at the head but does not remove the head returns true if the stack is empty, returns false otherwise returns -1 if empty must the void q(char) char dq void) bool isempty void); appends data to the tail of the list removes the head node and returns data; returns-1 if empty returns true if the queue is empty, returns false otherwise void insert(data) data dq(void) data peek(void) bool isEmpty void); inserts data in sorted order removes the head node and returns data; returns-1 if empty returns a copy of data at the head but does not remove the head returns -1 if empty returns true if the Pqueue is empty, returns false otherwise Double Linked List must s void appendTal(char); void appendHead(char) char remoaod) char removeHead(void): void void traverseBWD(void): appends data to the tail of the list appends data to the head of the list removes the head node and returns data; returns -1 if the list is empty removes the head node and returns data; returns -1 if the list is empty traverses the list from the head to the tail, and prints out each data element traverses the list from the tal to the head, and prints out each data element returns true if the list is empty, returns false otherwise Testing Thoroughly test your code with a variety of data. Exercise a functionality Turn in: 1) Paper source code listings. 2) Paper output listings that demonstrate full testing of all program functionality. 3) Follow the formatting requirements for this class, as descnibed elsewhere. The list contains: CEF Removed: C, E, F, The list contains: G not found l/Our Node struct nodef node next, char d Thead and talpointer- node*head- 0; node tail0 char remove void): void append(char): intfind char): void traverse(void); int isempty(void) II main for testing the acceswfiunctions void main void) append CA) append C8): append ('C'); append CD) append CE) findcx); findcD) Il empty the list cout"Removed whde lisempty)) "; coutnest; coutd, delete heads head tail 0 return temp; l more thanone nodee Il removeand destroy head ps head head a head-> next; temp- p->d, deletep return temp; ff searchey the ut for a char element ifthe char foandk removey the char element and returna I, othenelse retum intfind char d) nodecg node por f empty? f head lf only one nole? tad) desbroy node head-td O po- head o- head-net head head net deleta po return 1 f loobat nodey after the head nade delele c take core of tad //destroy nod.nw.- turn O Basic Containers Implementations See the posted file "LinkedList.pdf" and "CircList.pdf" which contain source code to mplement a simple "list" container using 2 different implementations. Input and debug this source as given, then use that as a code base to implement the following. A) Old Programs Get LinkedList and CircList working, and include the source code and testing in your B) New Programs 1) Stack 2) Queue 3) Priority Queue Using a circular array implementation Using a circular array implementation Using a circular array implementation 4) Stack 5) Queue 6) Priority Queue 7) Double Linked List Using a linked node implementation Using a linked node implementation Using a linked node implementation Using a linked node implementation C) Analysis Analyze, state, and explain the TIME COMPLEXITY in Big Oh notation for every function. D) Interface Functions Both implementations will share the same set of interface functions below Stack must su push(data) char pop(vold) char peek void); bool isempty void): appends data to the head of the list removes the head node and returns data; returns-1 if empty returns a copy of data at the head but does not remove the head returns true if the stack is empty, returns false otherwise returns -1 if empty must the void q(char) char dq void) bool isempty void); appends data to the tail of the list removes the head node and returns data; returns-1 if empty returns true if the queue is empty, returns false otherwise void insert(data) data dq(void) data peek(void) bool isEmpty void); inserts data in sorted order removes the head node and returns data; returns-1 if empty returns a copy of data at the head but does not remove the head returns -1 if empty returns true if the Pqueue is empty, returns false otherwise Double Linked List must s void appendTal(char); void appendHead(char) char remoaod) char removeHead(void): void void traverseBWD(void): appends data to the tail of the list appends data to the head of the list removes the head node and returns data; returns -1 if the list is empty removes the head node and returns data; returns -1 if the list is empty traverses the list from the head to the tail, and prints out each data element traverses the list from the tal to the head, and prints out each data element returns true if the list is empty, returns false otherwise Testing Thoroughly test your code with a variety of data. Exercise a functionality Turn in: 1) Paper source code listings. 2) Paper output listings that demonstrate full testing of all program functionality. 3) Follow the formatting requirements for this class, as descnibed elsewhere
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


