First, save the file I sent to you with your last name and first initial at the start of the file name, with the six-digit original file name after your name. So, if my file was 123456.xlsx, I would save it as MannyW123456.xlsx. (Or whatever the Excel naming convention is, I think I had it wrong in my announcement.) Thats important so that I know whose file Im looking at.
2. The file has one tab, labeled with a letter or two (A or AD for example). Do not alter that worksheet, keep it exactly as you received it. It should be either the first or the last tab in your workbook, but it must be there and intact.
3. Note that I use the convention positive numbers are debits and negative numbers, shown in parentheses, are credits. You should use that same convention in making adjustments.
4. On a new worksheet, you will consolidate Parent and Subsidiary.
Set up a consolidation worksheet with parent, subsidiary and columns for adjustments, and consolidated amounts.
At the bottom of your worksheet is an amount of Intercompany Sales, from Subsidiary to Parent. Those sales were made to generate a gross profit at the percentage indicated with the intercompany sales amount. Just to be clear, the Intercompany Sales amount is at the selling price from Subsidiary to Parent.
Of the intercompany sales, one-half of the sales remain in Parent Companys inventory (part of Current Assets). Round if you must, do everything in whole dollars. Make appropriate adjustments for the inventory.
Parent Company charges a management fee to Subsidiary Company (related to services that Parent Company performs for Subsidiary). The fee is 1.5% of Subsidiarys sales. Subsidiary records the expense in Administrative expense. Parent Company records the income in Other Expense (since its income, it reduces the Other expense amount).
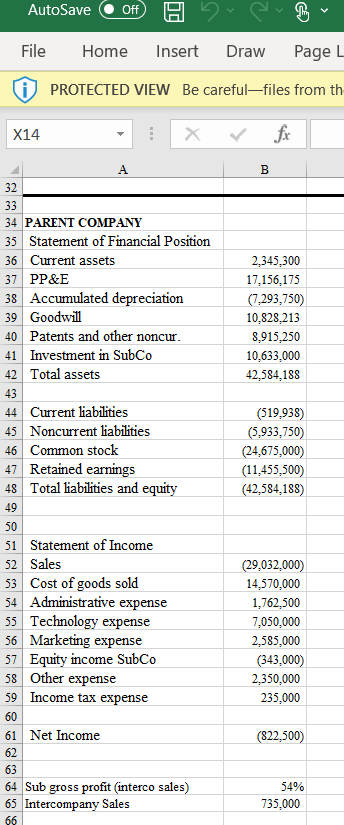
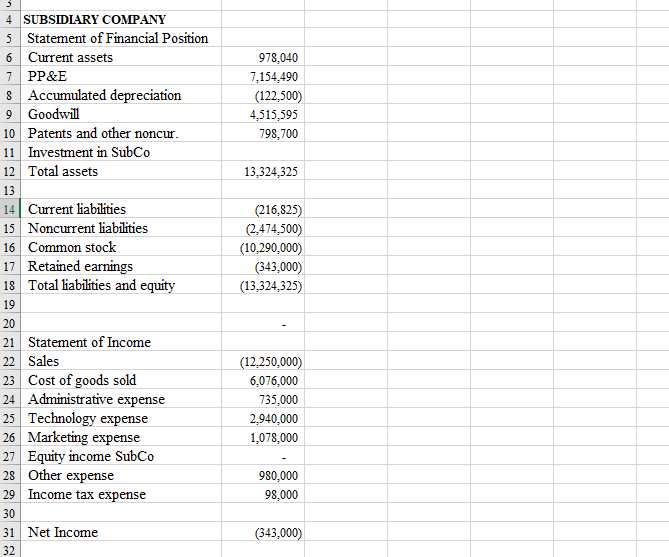
AutoSave Off Hov File Home Insert Draw Page 2 PROTECTED VIEW Be carefulfiles from th X14 fx B 2,345,300 17,156,175 (7.293,750) 10,828,213 8,915,250 10,633,000 42,584,188 A 32 33 34 PARENT COMPANY 35 Statement of Financial Position 36 Current assets 37 PP&E 38 Accumulated depreciation 39 Goodwill 40 Patents and other noncur. 41 Investment in SubCo 42 Total assets 43 44 Current liabilities 45 Noncurrent liabilities 46 Common stock 47 Retained earnings 48 Total liabilities and equity 49 50 51 Statement of Income 52 Sales 53 Cost of goods sold 54 Administrative expense 55 Technology expense 56 Marketing expense 57 Equity income SubCo 58 Other expense 59 Income tax expense 60 61 Net Income 62 63 64 Sub gross profit (interco sales) 65 Intercompany Sales 66 (519,938) (5,933,750) (24,675,000) (11,455,500) (42,584,188) (29,032,000) 14,570,000 1,762,500 7,050,000 2,585,000 (343,000) 2,350,000 235,000 (822,500) 54% 735,000 978,040 7,154.490 (122,500) 4,515,595 798,700 13,324,325 4 SUBSIDIARY COMPANY 5 Statement of Financial Position 6 Current assets 7 PP&E 8 Accumulated depreciation 9 Goodwill 10 Patents and other noncur. 11 Investment in SubCo 12 Total assets 13 14 Current liabilities 15 Noncurrent liabilities 16 Common stock 17 Retained earnings 18 Total liabilities and equity 19 20 21 Statement of Income 22 Sales 23 Cost of goods sold 24 Administrative expense 25 Technology expense 26 Marketing expense 27 Equity income SubCo 28 Other expense 29 Income tax expense 30 31 Net Income 32 (216,825) (2,474,500) (10,290,000) (343,000) (13,324,325) (12,250,000) 6,076,000 735,000 2.940,000 1,078,000 980,000 98,000 (343,000) AutoSave Off Hov File Home Insert Draw Page 2 PROTECTED VIEW Be carefulfiles from th X14 fx B 2,345,300 17,156,175 (7.293,750) 10,828,213 8,915,250 10,633,000 42,584,188 A 32 33 34 PARENT COMPANY 35 Statement of Financial Position 36 Current assets 37 PP&E 38 Accumulated depreciation 39 Goodwill 40 Patents and other noncur. 41 Investment in SubCo 42 Total assets 43 44 Current liabilities 45 Noncurrent liabilities 46 Common stock 47 Retained earnings 48 Total liabilities and equity 49 50 51 Statement of Income 52 Sales 53 Cost of goods sold 54 Administrative expense 55 Technology expense 56 Marketing expense 57 Equity income SubCo 58 Other expense 59 Income tax expense 60 61 Net Income 62 63 64 Sub gross profit (interco sales) 65 Intercompany Sales 66 (519,938) (5,933,750) (24,675,000) (11,455,500) (42,584,188) (29,032,000) 14,570,000 1,762,500 7,050,000 2,585,000 (343,000) 2,350,000 235,000 (822,500) 54% 735,000 978,040 7,154.490 (122,500) 4,515,595 798,700 13,324,325 4 SUBSIDIARY COMPANY 5 Statement of Financial Position 6 Current assets 7 PP&E 8 Accumulated depreciation 9 Goodwill 10 Patents and other noncur. 11 Investment in SubCo 12 Total assets 13 14 Current liabilities 15 Noncurrent liabilities 16 Common stock 17 Retained earnings 18 Total liabilities and equity 19 20 21 Statement of Income 22 Sales 23 Cost of goods sold 24 Administrative expense 25 Technology expense 26 Marketing expense 27 Equity income SubCo 28 Other expense 29 Income tax expense 30 31 Net Income 32 (216,825) (2,474,500) (10,290,000) (343,000) (13,324,325) (12,250,000) 6,076,000 735,000 2.940,000 1,078,000 980,000 98,000 (343,000)








