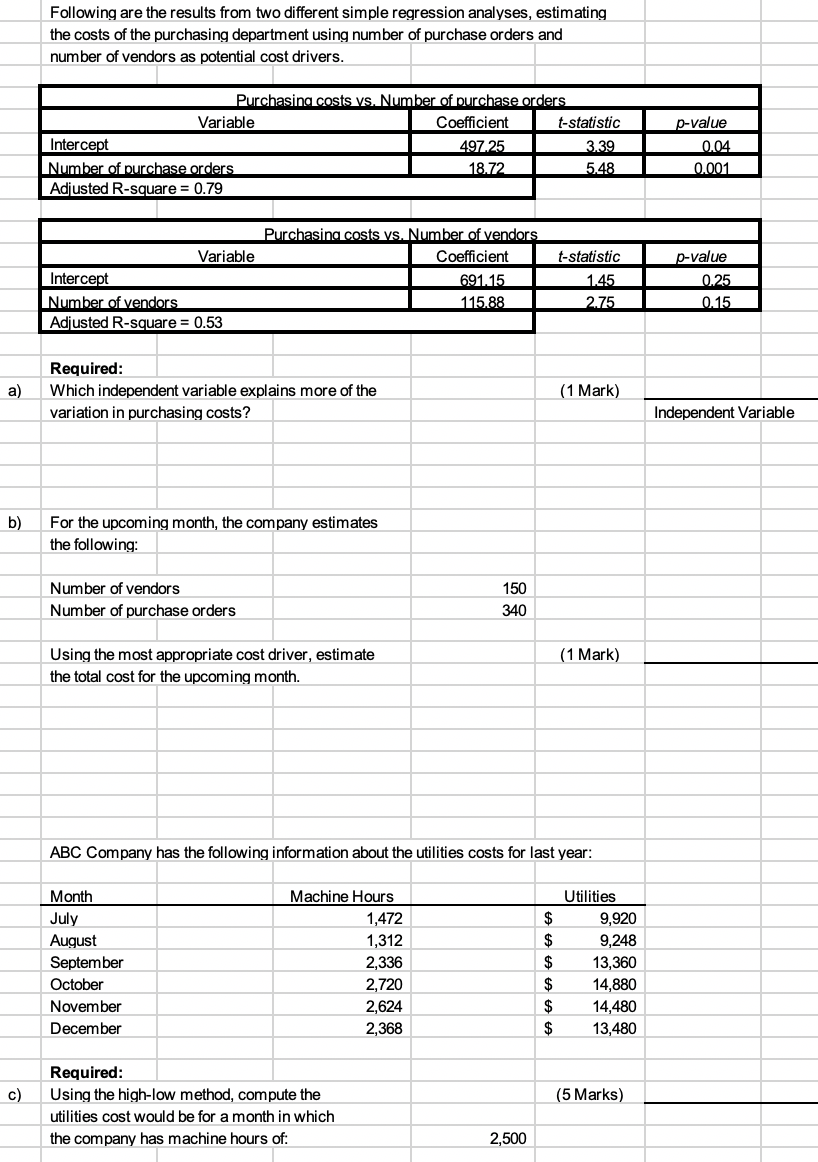
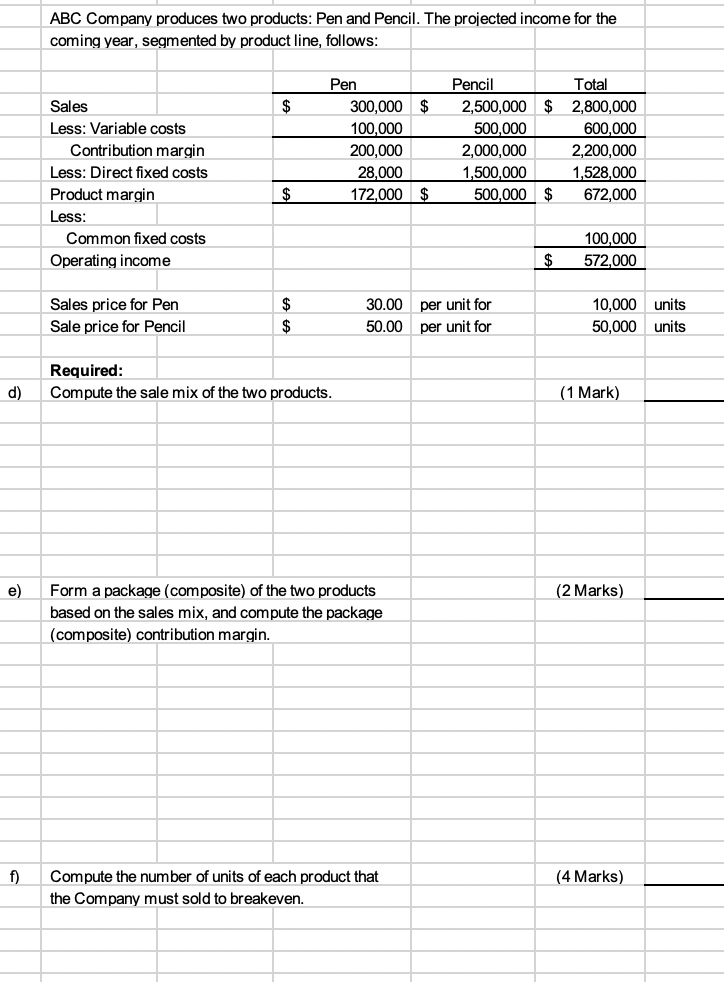
Following are the results from two different simple regression analyses, estimating the costs of the purchasing department using number of purchase orders and number of vendors as potential cost drivers. Purchasing costs vs. Number of purchase orders Variable Coefficient | t-statistic | Intercept 497.25 3 .39 Number of purchase orders 18.72 1 5.481 Adjusted R-square = 0.79 p-value 0.04 0.001 t-statistic | Purchasing costs vs. Number of vendors Coefficient 691.15 115.88 Variable Intercept Number of vendors Adjusted R-square = 0.53 1.45 p-value 0.25 0.15 2.75 a) Required: Which independent variable explains more of the variation in purchasing costs? (1 Mark) Independent Variable b) For the upcoming month, the company estimates the following: Number of vendors Number of purchase orders 150 340 (1 Mark) Using the most appropriate cost driver, estimate the total cost for the upcoming month. ABC Company has the following information about the utilities costs for last year: Month July August September October November December Machine Hours 1,472 1,312 2,336 2,720 2,624 2,368 Utilities 9,920 9,248 13,360 14,880 14,480 13,480 c) (5 Marks) Required: Using the high-low method, compute the utilities cost would be for a month in which the company has machine hours of: 2,500 ABC Company produces two products: Pen and Pencil. The projected income for the coming year, segmented by product line, follows: $ $ Sales Less: Variable costs Contribution margin Less: Direct fixed costs Product margin Less: Common fixed costs Operating income Pen 300,000 100,000 200,000 28,000 172,000 Pencil 2,500,000 500.000 2,000,000 1,500,000 500,000 Total 2,800,000 600.000 2,200,000 1,528,000 672,000 $ $ 100,000 572,000 $ Sales price for Pen Sale price for Pencil 30.00 50.00 per unit for per unit for 10,000 50,000 units units Required: Compute the sale mix of the two products. d) (1 Mark) e) (2 Marks) Form a package (composite) of the two products based on the sales mix, and compute the package (composite) contribution margin. f) (4 Marks) Compute the number of units of each product that the Company must sold to breakeven. Following are the results from two different simple regression analyses, estimating the costs of the purchasing department using number of purchase orders and number of vendors as potential cost drivers. Purchasing costs vs. Number of purchase orders Variable Coefficient | t-statistic | Intercept 497.25 3 .39 Number of purchase orders 18.72 1 5.481 Adjusted R-square = 0.79 p-value 0.04 0.001 t-statistic | Purchasing costs vs. Number of vendors Coefficient 691.15 115.88 Variable Intercept Number of vendors Adjusted R-square = 0.53 1.45 p-value 0.25 0.15 2.75 a) Required: Which independent variable explains more of the variation in purchasing costs? (1 Mark) Independent Variable b) For the upcoming month, the company estimates the following: Number of vendors Number of purchase orders 150 340 (1 Mark) Using the most appropriate cost driver, estimate the total cost for the upcoming month. ABC Company has the following information about the utilities costs for last year: Month July August September October November December Machine Hours 1,472 1,312 2,336 2,720 2,624 2,368 Utilities 9,920 9,248 13,360 14,880 14,480 13,480 c) (5 Marks) Required: Using the high-low method, compute the utilities cost would be for a month in which the company has machine hours of: 2,500 ABC Company produces two products: Pen and Pencil. The projected income for the coming year, segmented by product line, follows: $ $ Sales Less: Variable costs Contribution margin Less: Direct fixed costs Product margin Less: Common fixed costs Operating income Pen 300,000 100,000 200,000 28,000 172,000 Pencil 2,500,000 500.000 2,000,000 1,500,000 500,000 Total 2,800,000 600.000 2,200,000 1,528,000 672,000 $ $ 100,000 572,000 $ Sales price for Pen Sale price for Pencil 30.00 50.00 per unit for per unit for 10,000 50,000 units units Required: Compute the sale mix of the two products. d) (1 Mark) e) (2 Marks) Form a package (composite) of the two products based on the sales mix, and compute the package (composite) contribution margin. f) (4 Marks) Compute the number of units of each product that the Company must sold to breakeven








