Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
For a normal distribution, answer the questions below. Answer parts a and b Click here to view page 1 of the standard normal table.
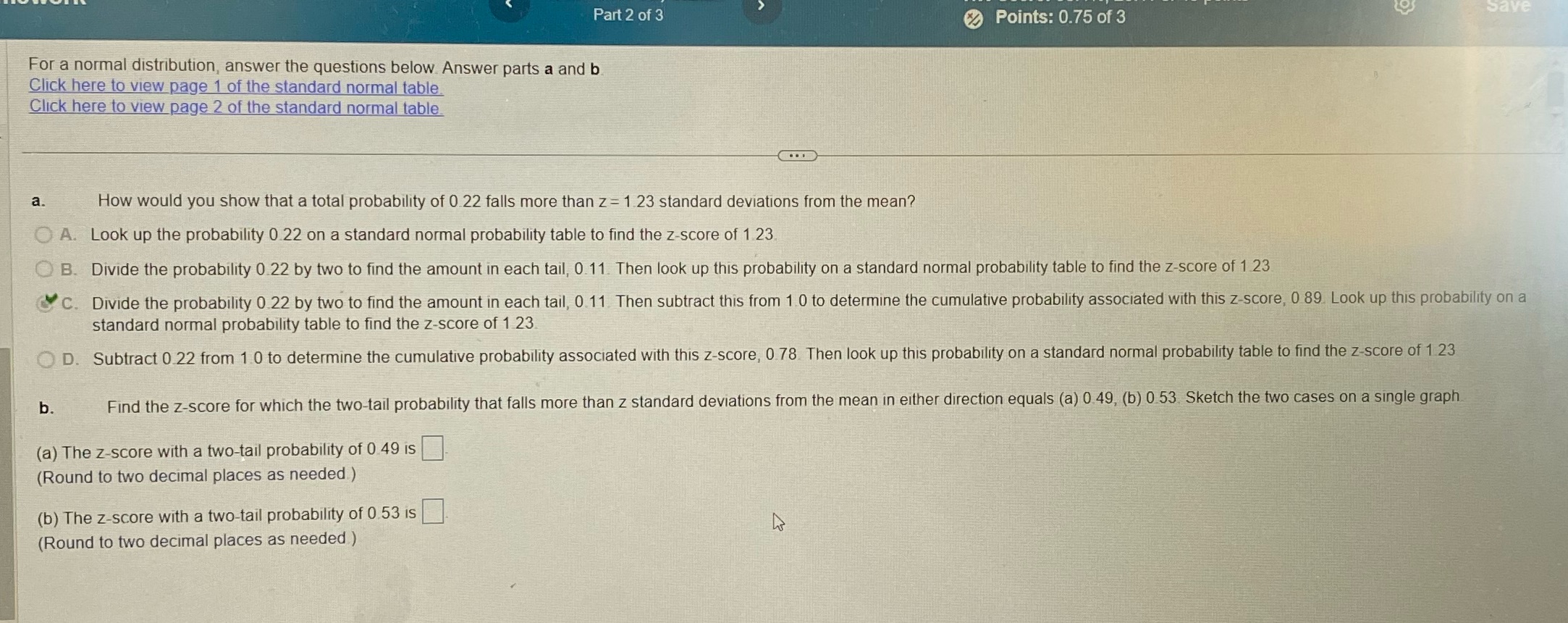
For a normal distribution, answer the questions below. Answer parts a and b Click here to view page 1 of the standard normal table. Click here to view page 2 of the standard normal table. Save Part 2 of 3 Points: 0.75 of 3 a. How would you show that a total probability of 0.22 falls more than z = 1.23 standard deviations from the mean? OA. Look up the probability 0.22 on a standard normal probability table to find the z-score of 1.23 b. B. Divide the probability 0.22 by two to find the amount in each tail, 0.11. Then look up this probability on a standard normal probability table to find the z-score of 1.23 C. Divide the probability 0.22 by two to find the amount in each tail, 0.11 Then subtract this from 1.0 to determine the cumulative probability associated with this z-score, 0.89. Look up this probability on a standard normal probability table to find the z-score of 1.23 D. Subtract 0.22 from 1.0 to determine the cumulative probability associated with this z-score, 0.78. Then look up this probability on a standard normal probability table to find the z-score of 1.23 Find the z-score for which the two-tail probability that falls more than z standard deviations from the mean in either direction equals (a) 0.49, (b) 0.53 Sketch the two cases on a single graph (a) The z-score with a two-tail probability of 0.49 is (Round to two decimal places as needed.) (b) The z-score with a two-tail probability of 0.53 is (Round to two decimal places as needed)
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


