Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
For most firms, the main source of funds is: debt. equity. cash generated by operations. government. Which equation expresses the external funds need? External funds
- For most firms, the main source of funds is:
- debt.
- equity.
- cash generated by operations.
- government.
- Which equation expresses the external funds need?
- External funds need = [ Cash + WCR + Fixed assets] [Retained earnings + Depreciation expense]
- External funds need = [ Cash + WCR + Fixed assets] + [Retained earnings + Depreciation expense]
- External funds need = [ Cash + WCR + Fixed assets] + [Retained earnings
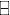 Depreciation expense]
Depreciation expense] - External funds need = [ Cash + WCR + Fixed assets] [Retained earnings
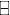 Depreciation expense]
Depreciation expense]
- Research conducted with nonfinancial US corporations, showed that:
- most of the total funds available are used to finance WCR, with the balance going to finance capital expenditures and cash holdings.
- most of the total funds available are used to finance capital expenditures, with the balance going to finance WCR and cash holdings.
- most of the total funds available are used to finance cash holdings, with the balance going to finance WCR and capital expenditures.
- the distribution of the funds available into capital expenditures, WCR and cash holdings varies over time, none of them are consistently predominant.
- The main supplier of capital is:
- the government.
- firms with temporary excess cash.
- household savings.
- venture capital firms.
- Which of the following statements is true for indirect financing?
- Commercial banks typically offer short- to medium-term loans with maturities of one day to five years.
- Commercial banks typically offer medium- to long-term loans with maturities from five to ten years.
- Commercial banks typically offer short- to medium-term loans with maturities of one day to ten years.
- Commercial banks typically offer medium- to long-term loans with maturities from 10 to 20 years.
- Which of the following institutions is specialized in supplying equity to recently established firms with limited track records?
- Insurance companies
- Venture capital firms
- Commercial banks
- Pension funds
- Which of the following is NOT true for the relative share of assets held by financial institutions?
- Decline in the share of financial assets held by banks
- Decline in the share of financial assets held by pension funds
- Increase in the share of financial assets held by investment funds
- Increase in the share of financial assets held by nonbanking institutions
- Which of the following is NOT an example of a covenant?
- Maintain a minimum amount of working capital
- Restrict the ability to sell assets
- Distribute dividends
- Issue new debt
- When a firm returns to the market for another public issue of equity, it is called:
- IPO.
- seasoned issue.
- secondary public offering.
- secondary distribution.
- Empirical studies show that IPOs are often:
- underpriced.
- overpriced.
- priced correctly.
- There is not a clear path.
- Which of the following statements is correct for the difference between dealers and brokers?
- Dealers trade shares that they own; brokers trade on behalf of a third party and do not own the traded shares.
- Dealers trade on behalf of a third party and do not own the traded shares; brokers trade shares that they own.
- Dealers and brokers are the same. Dealers as well as brokers trade shares that they own.
- Dealers and brokers are the same. Dealers as well as brokers trade on behalf of a third party and do not own the traded shares.
- Which of the following statements is correct for equity markets?
- Unlisted securities are shares of larger companies, traded in OTC markets.
- Unlisted securities are shares of larger companies, traded in organized stock exchanges.
- Unlisted securities are shares of smaller companies, traded in OTC markets.
- Unlisted securities are shares of smaller companies, traded in organized stock exchanges.
- For a firm to be listed at an organized stock exchange, the firm does NOT have to comply with which of the following requirements?
- Have a minimum acceptable number of publicly held shares
- A minimum ratio of EBT in relation to sales
- Have a minimum asset size
- Must publish financial reports
- Which of the following statements is correct for money market instruments?
- Certificates of deposits are issued by firms; commercial papers are issued by banks to raise short-term debt.
- Certificates of deposits are issued by firms; commercial papers are issued by banks to raise long-term debt.
- Certificates of deposits are issued by banks; commercial papers are issued by firms to raise long-term debt.
- Certificates of deposits are issued by banks; commercial papers are issued by firms to raise short-term debt.
- Most of securities issued in the US more recently are predominantly:
- common stocks.
- preferred stocks.
- debt instruments.
- convertible securities.
- Which of the following statements is correct for financial and capital markets?
- Financial markets can be divided into capital and bond markets, and capital markets can be divided into equity and money markets.
- Financial markets can be divided into capital and money markets, and capital markets can be divided into equity and bond markets.
- Financial markets can be divided into equity and money markets, and capital markets can be divided into capital and bond markets.
- Financial markets can be divided into equity and bond markets, and capital markets can be divided into capital and money markets.
- Which of the following statements is correct?
- Bonds denominated in yen are called Yankee bonds; bonds denominated in US dollars sold in the Japanese bond market are called Shogun bonds, and bonds issued by foreign firms in the United States are called Samurai bonds.
- Bonds denominated in yen are called Shogun bonds; bonds denominated in US dollars sold in the Japanese bond market are called Samurai bonds, and bonds issued by foreign firms in the United States are called Yankee bonds.
- Bonds denominated in yen are called Samurai bonds; bonds denominated in US dollars sold in the Japanese bond market are called Shogun bonds, and bonds issued by foreign firms in the United States are called Yankee bonds.
- Bonds denominated in yen are called Samurai bonds; bonds denominated in US dollars sold in the Japanese bond market are called Yankee bonds, and bonds issued by foreign firms in the United States are called Shogun bonds.
- Which of the following is NOT a feature of private placement for securities?
- The issue is tailored to meet specific needs.
- It needs to be registered with a government agency.
- It is a flexible and speedy method to raise funds.
- It is difficult for investors to resell the securities.
- If a firm wants to offer its share exclusively to its existing shareholders, this is called:
- private placement.
- general cash offering.
- rights offering.
- public offering.
- Which of the following is the most important function of an investment bank in a public offering?
- Advise on type and amount of security to issue
- Approval from supervising government agencies
- Determination of appropriate selling price
- Marketing and distribution of securities to the public
- Which of the following alternatives best represents how the spread is shared among the various intermediaries in selling securities?
- The originating house receives 15 to 20% of the spread; the members of the underwriting syndicate receive 20 to 30% and the balance is paid to members of the selling group.
- The originating house receives 20 to 30% of the spread; the members of the underwriting syndicate receive 10 to 20% and the balance is paid to members of the selling group.
- The originating house receives 15 to 20% of the spread; the members of the underwriting syndicate receive 10 to 20% and the balance is paid to members of the selling group.
- The originating house receives 20 to 30% of the spread; the members of the underwriting syndicate receive 15 to 20% and the balance is paid to members of the selling group.
- In a rights issue, shareholders do NOT have which of these possibilities?
- They can exercise their rights and subscribe the issue.
- They can sell their rights to interested investors.
- They can wait for a better time to sell their rights.
- They can do nothing and let the right expire.
- Which of the following equations represents the value of one right?
- Value of one right = (Subscription price
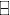 Rights-on price)/(N
Rights-on price)/(N 1)
1) - Value of one right = (Rights-on price Subscription price)/(N
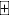 1)
1) - Value of one right = (Rights-on price Subscription price)/ (N
 1)
1) - Value of one right = (Subscription price
 Rights-on price)/ (N
Rights-on price)/ (N  1)
1)
- Value of one right = (Subscription price
- Which of the following is NOT an example of unsecured loans?
- Transaction loan
- Medium-term loan
- Line of credit
- Revolving credit agreement
- Which of the following is NOT a feature of an operating lease?
- It is a short-term lease.
- The contract is shorter than the useful life of the asset.
- The lessor is responsible for the maintenance and insurance cost of the asset.
- The lessor has the right to cancel the contract before it expires.
- Which of the following is NOT a feature of a financial lease?
- It is a long-term lease.
- The lessor pays for the maintenance and insurance cost of the asset.
- It cannot be cancelled.
- It usually extends over most of the useful life of the asset.
- Which of the following is NOT true for firms issuing CP (commercial paper)?
- Issued by large firms with high-credit standings
- Short-term funds
- Usually unsecured
- It can only be issued in the domestic money market.
- Which of the following statements is NOT true for corporate bonds?
- Corporate bonds can be issued over periods from 5 to 100 years.
- Corporate bonds denominated in US dollars are usually issued at a par value of $100.
- Flotation costs are the cost of issuing the bonds.
- Corporate bonds pay a fixed annual or semi-annually coupon payment over the bonds life.
- Which of the following is a NOT a feature of preferred stocks?
- They may have contingent voting rights.
- They cannot have sinking funds.
- They are priced as perpetual bonds.
- They can be callable.
- Which of the following is NOT a feature of common stocks?
- Dividends are paid only after payment of preferred stockholders.
- They are cumulative.
- They cannot be called.
- They cannot be converted.
- Which of the following statements is true for dividend payout ratios?
- Firms operating in sectors with stable and more predictable cash flow have average payout ratios exceeding 50%, whereas firms operating in unstable and less predictable cash flow sectors have average payout ratios not exceeding 10%.
- Firms operating in sectors with stable and more predictable cash flow have average payout ratios exceeding 40%, whereas firms operating in unstable and less predictable cash flow sectors have average payout ratios not exceeding 10%.
- Firms operating in sectors with stable and more predictable cash flow have average payout ratios exceeding 30%, whereas firms operating in unstable and less predictable cash flow sectors have average payout ratios not exceeding 5%.
- Firms operating in sectors with stable and more predictable cash flow have average payout ratios exceeding 20%, whereas firms operating in unstable and less predictable cash flow sectors have average payout ratios not exceeding 5%.
- Which of the following dates follows the right timeline when declaring and paying dividends?
- Declaration date, Record date, Ex-dividend date, and Payment date
- Declaration date, Ex-dividend date, Record date, and Payment date
- Record date, Declaration date, Ex- dividend date, and Payment date
- Record date, Declaration date, Payment date and Ex-dividend date
- Which of the following statements is NOT true for share repurchase and dividend payment?
- Share repurchases do not send as strong a signal as dividend payments.
- Share repurchases are more flexible than dividend payments.
- Share repurchases do not allow firms to neutralize the impact of dilution from granting stocks to employees.
- Share repurchases allow the firm to support its share price when shares are temporary undervalued.
- Considering an imperfect market, under which circumstances is a firm indifferent between paying of dividends or buying back shares?
- When capital gains and income are taxed.
- Investor preference
- Flotation costs
- Transaction costs
- Considering an imperfect market, under which circumstances would a firm pay dividends instead of buying back shares?
- Transaction costs
- Agency costs
- Taxation if some institutional investors are tax-exempt
- Taxation when capital gains are taxed at a lower rate than income
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


