Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
For the following 3 memory organizations 1)compute the time in cycles to load the cache and 2)compute the average memory latency Useful explanation to solve
For the following 3 memory organizations 1)compute the time in cycles to load the cache and 2)compute the average memory latency
Useful explanation to solve this problem:
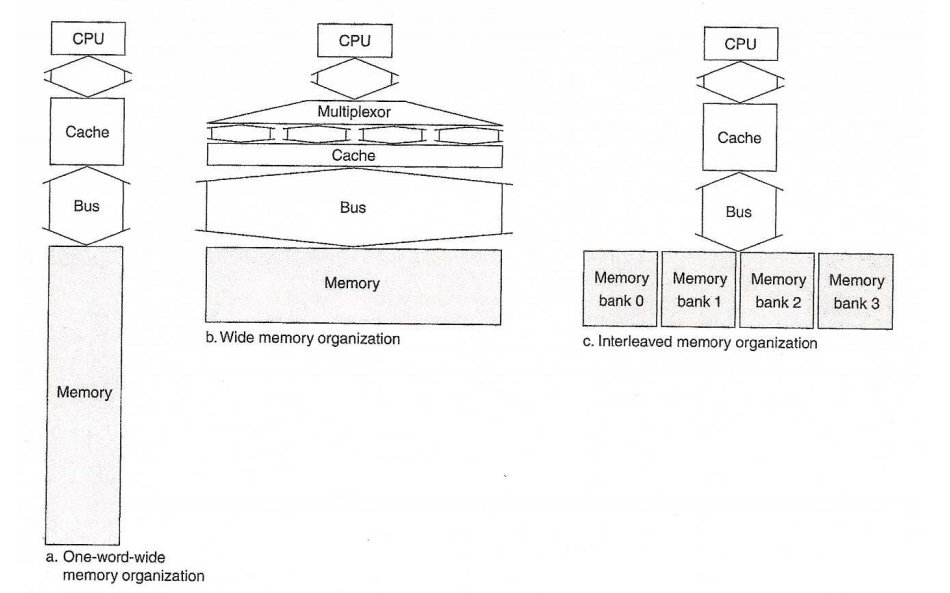
For figure a) Cache 16 words per block. bus one word wide. memory one word wide
Figure b) cache 16 words per block. bus four words wide. memory four word wide.
Figure c) cache 16 words per block. bus one word wide. memory four INDEPENDENT word wide.
Address incrementer inside the memory unit. For a) each address is one greater and 16 fetches occur. b) each address is four greater and 4 fetches occur. c) m0 gets addresses 0, 4, 8, 12, four fetches occur m1 gets addresses 1, 5, 9, 13, four fetches occur m2 gets addresses 2, 6, 10, 14, four fetches occur m3 gets addresses 3, 7, 11, 15, four fetches occur fetching is overlapped, concurrent, in m0, m1, m2, m3.
List each clock cycle (or range of clock cycles) and show what is happening or a formula for this specific case that you derive from looking at the clock cycles. "W0" stands for the word at the base address. The quote marks have the meaning 'ditto' which means same as above.
You may write out the full sequence or figure out a formula that works for this case. Include the formula if you use one.
Back to instructions:
1) For each memory organization give the total clock cycles to load the cache. The last word of the cache must be loaded thus count the last bus cycle. This number is called the "miss penalty". 2) The miss penalty would be divided by 16, the cache block size, to get the average increase in CPI for a cache miss, assuming instructions are executed sequentially. The miss penalty divided by 16 is called the average memory latency. Note that this is less than the 6 cycles for a single memory fetch for cases b) and c).CPU CPU CPU Multiplexor Cache Cache Cache Bus Bus Bus Memory Memory Memory Memory bank 0 ank bank 2bank 3 Memory b. Wide memory organization c. Interleaved memory organization Memory a. One-word-wide memory organization CPU CPU CPU Multiplexor Cache Cache Cache Bus Bus Bus Memory Memory Memory Memory bank 0 ank bank 2bank 3 Memory b. Wide memory organization c. Interleaved memory organization Memory a. One-word-wide memory organization
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started



