Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
For the words number 1) decrease/increase 2) lower/higher 4. Merger analysis - Adjusted present value (APV) approach Aa Aa BTR Warehousing, which is considering the
For the words number 1) decrease/increase 2) lower/higher
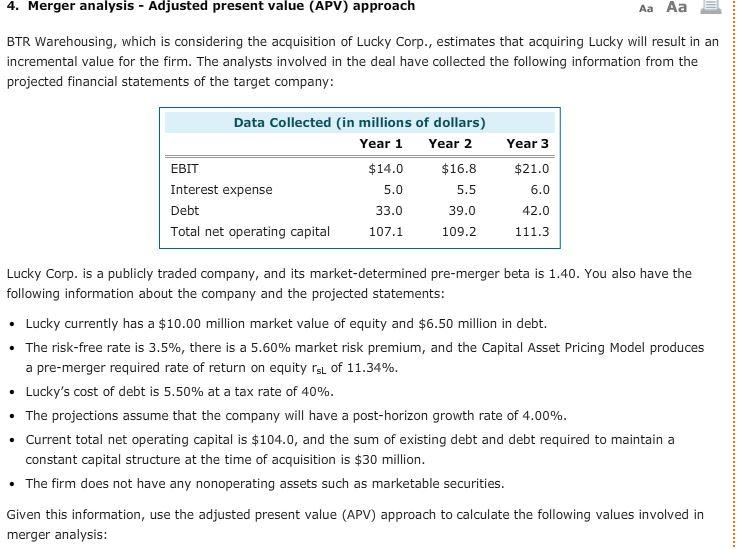
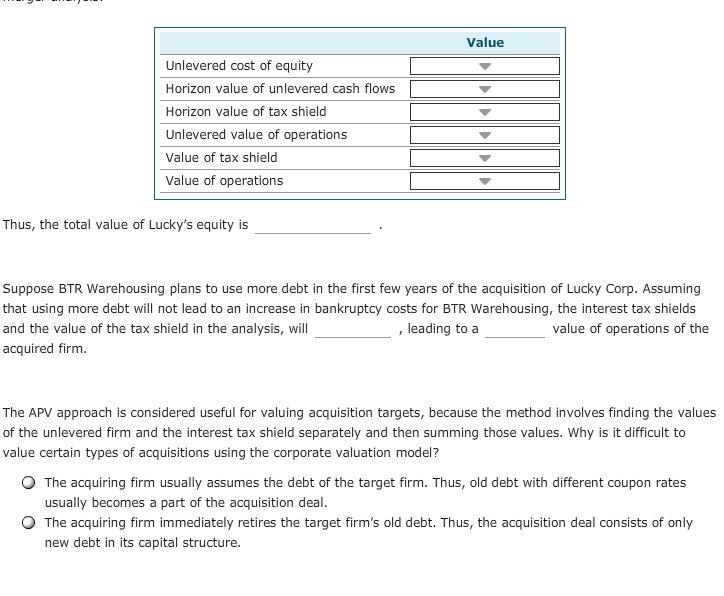
4. Merger analysis - Adjusted present value (APV) approach Aa Aa BTR Warehousing, which is considering the acquisition of Lucky Corp., estimates that acquiring Lucky will result in an incremental value for the firm. The analysts involved in the deal have collected the following information from the projected financial statements of the target company: Year 3 Data Collected in millions of dollars) Year 1 Year 2 EBIT $14.0 $16.8 Interest expense 5.0 5.5 Debt 33.0 39.0 Total net operating capital 107.1 109.2 $21.0 6.0 42.0 111.3 . Lucky Corp. is a publicly traded company, and its market-determined pre-merger beta is 1.40. You also have the following information about the company and the projected statements: Lucky currently has a $10.00 million market value of equity and $6.50 million in debt. The risk-free rate is 3.5%, there is a 5.60% market risk premium, and the Capital Asset Pricing Model produces a pre-merger required rate of return on equity rsl of 11.34%. Lucky's cost of debt is 5.50% at a tax rate of 40%. The projections assume that the company will have a post-horizon growth rate of 4.00%. Current total net operating capital is $104.0, and the sum of existing debt and debt required to maintain a constant capital structure at the time of acquisition is $30 million. The firm does not have any nonoperating assets such as marketable securities. Given this information, use the adjusted present value (APV) approach to calculate the following values involved in merger analysis: Value Unlevered cost of equity Horizon value of unlevered cash flows Horizon value of tax shield Unlevered value of operations Value of tax shield Value of operations Thus, the total value of Lucky's equity is Suppose BTR Warehousing plans to use more debt in the first few years of the acquisition of Lucky Corp. Assuming that using more debt will not lead to an increase in bankruptcy costs for BTR Warehousing, the interest tax shields and the value of the tax shield in the analysis, will leading to a value of operations of the acquired firm. The APV approach is considered useful for valuing acquisition targets, because the method involves finding the values of the unlevered firm and the interest tax shield separately and then summing those values. Why is it difficult to value certain types of acquisitions using the corporate valuation model? The acquiring firm usually assumes the debt of the target firm. Thus, old debt with different coupon rates usually becomes a part of the acquisition deal. The acquiring firm immediately retires the target firm's old debt. Thus, the acquisition deal consists of only new debt in its capital structure. 4. Merger analysis - Adjusted present value (APV) approach Aa Aa BTR Warehousing, which is considering the acquisition of Lucky Corp., estimates that acquiring Lucky will result in an incremental value for the firm. The analysts involved in the deal have collected the following information from the projected financial statements of the target company: Year 3 Data Collected in millions of dollars) Year 1 Year 2 EBIT $14.0 $16.8 Interest expense 5.0 5.5 Debt 33.0 39.0 Total net operating capital 107.1 109.2 $21.0 6.0 42.0 111.3 . Lucky Corp. is a publicly traded company, and its market-determined pre-merger beta is 1.40. You also have the following information about the company and the projected statements: Lucky currently has a $10.00 million market value of equity and $6.50 million in debt. The risk-free rate is 3.5%, there is a 5.60% market risk premium, and the Capital Asset Pricing Model produces a pre-merger required rate of return on equity rsl of 11.34%. Lucky's cost of debt is 5.50% at a tax rate of 40%. The projections assume that the company will have a post-horizon growth rate of 4.00%. Current total net operating capital is $104.0, and the sum of existing debt and debt required to maintain a constant capital structure at the time of acquisition is $30 million. The firm does not have any nonoperating assets such as marketable securities. Given this information, use the adjusted present value (APV) approach to calculate the following values involved in merger analysis: Value Unlevered cost of equity Horizon value of unlevered cash flows Horizon value of tax shield Unlevered value of operations Value of tax shield Value of operations Thus, the total value of Lucky's equity is Suppose BTR Warehousing plans to use more debt in the first few years of the acquisition of Lucky Corp. Assuming that using more debt will not lead to an increase in bankruptcy costs for BTR Warehousing, the interest tax shields and the value of the tax shield in the analysis, will leading to a value of operations of the acquired firm. The APV approach is considered useful for valuing acquisition targets, because the method involves finding the values of the unlevered firm and the interest tax shield separately and then summing those values. Why is it difficult to value certain types of acquisitions using the corporate valuation model? The acquiring firm usually assumes the debt of the target firm. Thus, old debt with different coupon rates usually becomes a part of the acquisition deal. The acquiring firm immediately retires the target firm's old debt. Thus, the acquisition deal consists of only new debt in its capital structure
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


