| Forecast Zeiber's 2020 income statement and balance sheets. Use the following assumptions: (1) Sales grow by 6%. (2) The ratios of expenses to sales, depreciation to fixed assets, cash to sales, accounts receivable to sales, and inventories to sales will be the same in 2020 as in 2019. (3) Zeiber will not issue any new stock or new long-term bonds. (4) The interest rate is 11% for long-term debt and the interest expense on long-term debt is based on the average balance during the year. (5) No interest is earned on cash. (6) Regular dividends grow at an 8% rate. (7) The tax rate is 25%. Calculate the additional funds needed (AFN). If new financing is required, assume it will be raised by drawing on a line of credit with an interest rate of 12%. | Key Input Data: | | Used in the | | | | | forecast | | Tax rate | | | 25% | | Dividend growth rate | | 8% | | Rate on notes payable-term debt, rstd | 9% | | Rate on long-term debt, rd | | 11% | | Rate on line of credit, rLOC | | 12% | Answer down below - 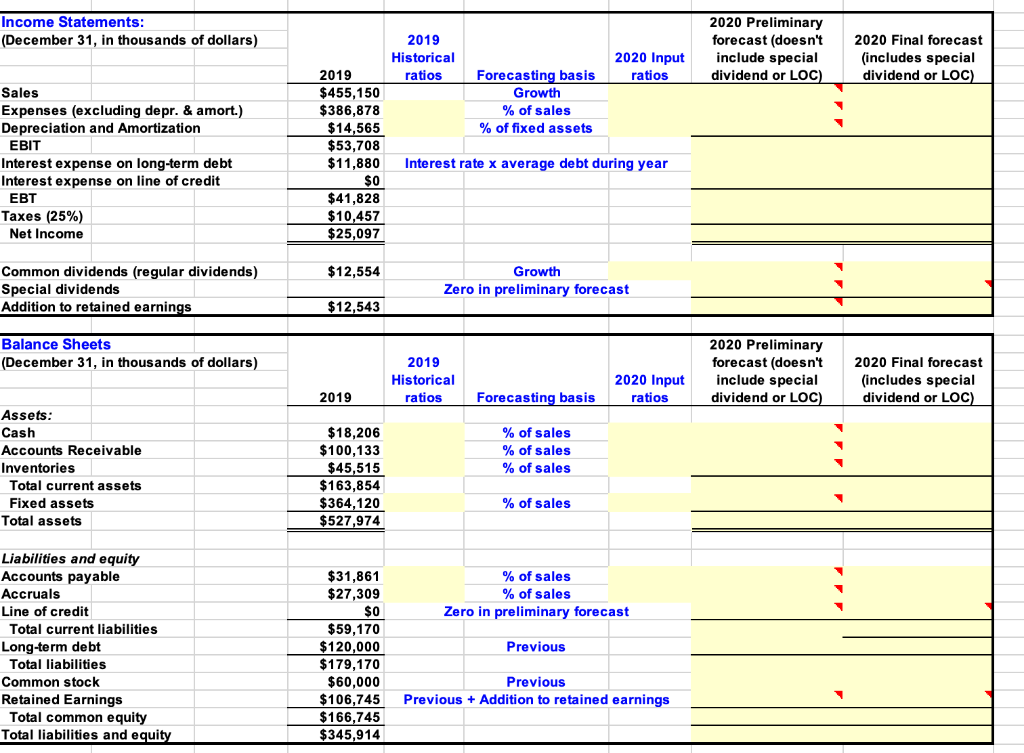 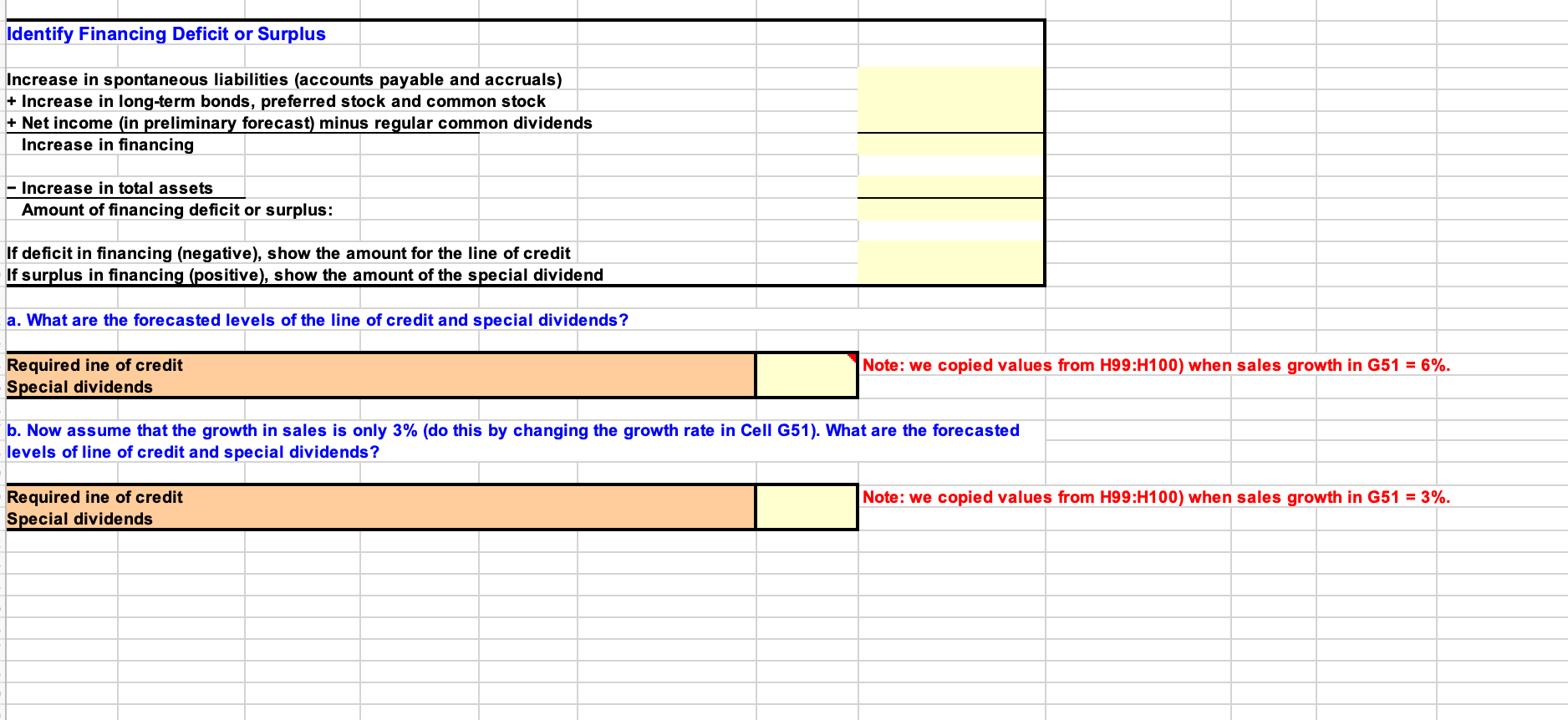
|
Income Statements: (December 31, in thousands of dollars) 2019 Historical ratios 2020 Input ratios 2020 Preliminary forecast (doesn't include special dividend or LOC) 2020 Final forecast (includes special dividend or LOC) Forecasting basis Growth % of sales % of fixed assets Sales Expenses (excluding depr. & amort.) Depreciation and Amortization EBIT Interest expense on long-term debt Interest expense on line of credit EBT Taxes (25%) Net Income 2019 $455,150 $386,878 $14,565 $53,708 $11,880 $0 $41,828 $10,457 $25,097 Interest rate x average debt during year $12,554 Common dividends (regular dividends) Special dividends Addition to retained earnings Growth Zero in preliminary forecast $12,543 Balance Sheets (December 31, in thousands of dollars) 2019 Historical ratios 2020 Preliminary forecast (doesn't include special dividend or LOC) 2020 Input ratios 2020 Final forecast (includes special dividend or LOC) 2019 Forecasting basis Assets: Cash Accounts Receivable Inventories Total current assets Fixed assets Total assets % of sales % of sales % of sales $18,206 $100,133 $45,515 $163,854 $364,120 $527,974 % of sales % of sales % of sales Zero in preliminary forecast Liabilities and equity Accounts payable Accruals Line of credit Total current liabilities Long-term debt Total liabilities Common stock Retained Earnings Total common equity Total liabilities and equity Previous $31,861 $27,309 $0 $59,170 $120,000 $179, 170 $60,000 $106,745 $166,745 $345,914 Previous Previous + Addition to retained earnings Identify Financing Deficit or Surplus Increase in spontaneous liabilities (accounts payable and accruals) + Increase in long-term bonds, preferred stock and common stock + Net income (in preliminary forecast) minus regular common dividends Increase in financing - Increase in total assets Amount of financing deficit or surplus: If deficit in financing (negative), show the amount for the line of credit If surplus in financing (positive), show the amount of the special dividend a. What are the forecasted levels of the line of credit and special dividends? Note: we copied values from H99:H100) when sales growth in G51 = 6%. Required ine of credit Special dividends b. Now assume that the growth in sales is only 3% (do this by changing the growth rate in Cell G51). What are the forecasted levels of line of credit and special dividends? Note: we copied values from H99:H100) when sales growth in G51 = 3%. Required ine of credit Special dividends Income Statements: (December 31, in thousands of dollars) 2019 Historical ratios 2020 Input ratios 2020 Preliminary forecast (doesn't include special dividend or LOC) 2020 Final forecast (includes special dividend or LOC) Forecasting basis Growth % of sales % of fixed assets Sales Expenses (excluding depr. & amort.) Depreciation and Amortization EBIT Interest expense on long-term debt Interest expense on line of credit EBT Taxes (25%) Net Income 2019 $455,150 $386,878 $14,565 $53,708 $11,880 $0 $41,828 $10,457 $25,097 Interest rate x average debt during year $12,554 Common dividends (regular dividends) Special dividends Addition to retained earnings Growth Zero in preliminary forecast $12,543 Balance Sheets (December 31, in thousands of dollars) 2019 Historical ratios 2020 Preliminary forecast (doesn't include special dividend or LOC) 2020 Input ratios 2020 Final forecast (includes special dividend or LOC) 2019 Forecasting basis Assets: Cash Accounts Receivable Inventories Total current assets Fixed assets Total assets % of sales % of sales % of sales $18,206 $100,133 $45,515 $163,854 $364,120 $527,974 % of sales % of sales % of sales Zero in preliminary forecast Liabilities and equity Accounts payable Accruals Line of credit Total current liabilities Long-term debt Total liabilities Common stock Retained Earnings Total common equity Total liabilities and equity Previous $31,861 $27,309 $0 $59,170 $120,000 $179, 170 $60,000 $106,745 $166,745 $345,914 Previous Previous + Addition to retained earnings Identify Financing Deficit or Surplus Increase in spontaneous liabilities (accounts payable and accruals) + Increase in long-term bonds, preferred stock and common stock + Net income (in preliminary forecast) minus regular common dividends Increase in financing - Increase in total assets Amount of financing deficit or surplus: If deficit in financing (negative), show the amount for the line of credit If surplus in financing (positive), show the amount of the special dividend a. What are the forecasted levels of the line of credit and special dividends? Note: we copied values from H99:H100) when sales growth in G51 = 6%. Required ine of credit Special dividends b. Now assume that the growth in sales is only 3% (do this by changing the growth rate in Cell G51). What are the forecasted levels of line of credit and special dividends? Note: we copied values from H99:H100) when sales growth in G51 = 3%. Required ine of credit Special dividends








