Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
Formulate LP or NLP to minimize total cost of meeting the expected demand XYZ Manufacturing plans to distribute a new product, the Flugel and would
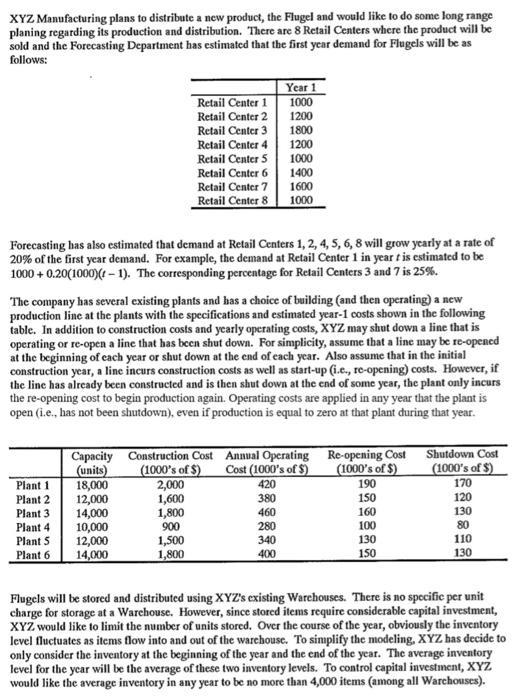
Formulate LP or NLP to minimize total cost of meeting the expected demand
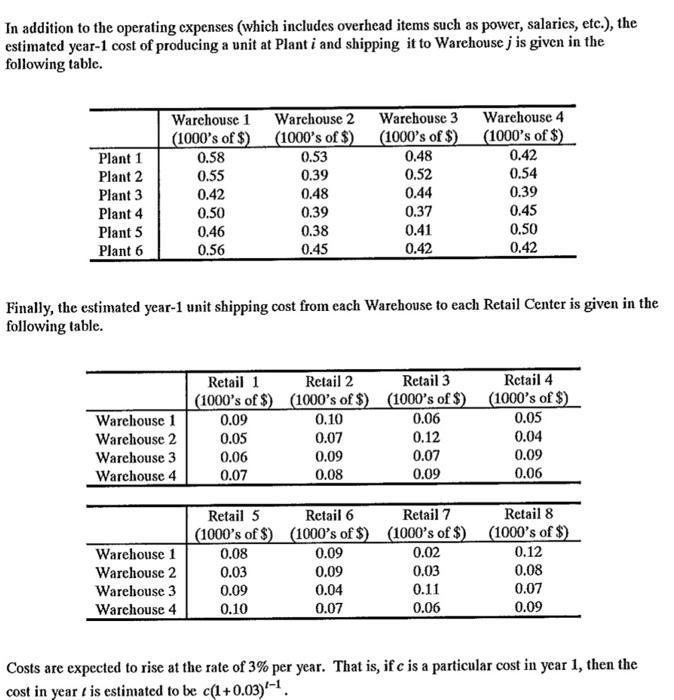
XYZ Manufacturing plans to distribute a new product, the Flugel and would like to do some long range planing regarding its production and distribution. There are 8 Retail Centers where the product will be sold and the Forecasting Department has estimated that the first year demand for Flugels will be as follows: Retail Center 1 Retail Center 2 Retail Center 3 Retail Center 4 Retail Center 5 Retail Center 6 Retail Center 7 Retail Center 8 Year 1 1000 1200 1800 1200 1000 1400 1600 1000 Forecasting has also estimated that demand at Retail Centers 1, 2, 4, 5, 6, 8 will grow yearly at a rate of 20% of the first year demand. For example, the demand at Retail Center 1 in year t is estimated to be 1000+ 0.20(1000)(1 - 1). The corresponding percentage for Retail Centers 3 and 7 is 25%. The company has several existing plants and has a choice of building (and then operating) a new production line at the plants with the specifications and estimated year-1 costs shown in the following table. In addition to construction costs and yearly operating costs, XYZ may shut down a line that is operating or re-open a line that has been shut down. For simplicity, assume that a line may be re-opened at the beginning of cach year or shut down at the end of each year. Also assume that in the initial construction year, a line incurs construction costs as well as start-up (i.c., re-opening) costs. However, if the line has already been constructed and is then shut down at the end of some year, the plant only incurs the re-opening cost to begin production again. Operating costs are applied in any year that the plant is open (i.e., has not been shutdown), even if production is equal to zero at that plant during that year. 420 Capacity Construction Cost Annual Operating Re-opening Cost (units) (1000's of $) Cost (1000's of 5) (1000's of $) 18,000 2,000 190 12,000 1,600 380 150 14,000 460 160 10,000 900 280 100 12,000 1,500 340 130 14,000 1,800 400 150 Shutdown Cost (1000's of $) 170 120 130 Plant 1 Plant 2 Plant 3 Plant 4 Plants Plant 6 1,800 80 110 130 Flugels will be stored and distributed using XYZ's existing Warehouses. There is no specific per unit charge for storage at a Warehouse. However, since stored items require considerable capital investment, XYZ would like to limit the number of units stored. Over the course of the year, obviously the inventory level fluctuates as items flow into and out of the warehouse. To simplify the modeling, XYZ has decide to only consider the inventory at the beginning of the year and the end of the year. The average inventory level for the year will be the average of these two inventory levels. To control capital investment, XYZ would like the average inventory in any year to be no more than 4,000 items (among all Warehouses). In addition to the operating expenses (which includes overhead items such as power, salaries, etc.), the estimated year-1 cost of producing a unit at Plant i and shipping it to Warehouse j is given in the following table. Plant 1 Plant 2 Plant 3 Plant 4 Plant 5 Plant 6 Warehouse 1 Warehouse 2 Warehouse 3 Warehouse 4 (1000's of $) (1000's of $) (1000's of $) (1000's of $) 0.58 0.53 0.48 0.42 0.55 0.39 0.52 0.54 0.42 0.48 0.44 0.39 0.50 0.39 0.37 0.45 0.46 0.38 0.41 0.50 0.56 0.45 0.42 0.42 Finally, the estimated year-1 unit shipping cost from each Warehouse to each Retail Center is given in the following table. Warehouse 1 Warehouse 2 Warehouse 3 Warehouse 4 Retail 1 Retail 2 Retail 3 Retail 4 (1000's of $) (1000's of $) (1000's of $) (1000's of $) 0.09 0.10 0.06 0.05 0.05 0.07 0.12 0.04 0.06 0.09 0.07 0.09 0.07 0.08 0.09 0.06 Warehouse 1 Warehouse 2 Warehouse 3 Warehouse 4 Retail 5 Retail 6 Retail 7 Retail 8 (1000's of $) (1000's of $) (1000's of $) (1000's of $) 0.08 0.09 0.02 0.12 0.03 0.09 0.03 0.08 0.09 0.04 0.11 0.07 0.10 0.07 0.06 0.09 Costs are expected to rise at the rate of 3% per year. That is, if c is a particular cost in year 1, then the cost in year t is estimated to be c(1+0.03)-1. XYZ Manufacturing plans to distribute a new product, the Flugel and would like to do some long range planing regarding its production and distribution. There are 8 Retail Centers where the product will be sold and the Forecasting Department has estimated that the first year demand for Flugels will be as follows: Retail Center 1 Retail Center 2 Retail Center 3 Retail Center 4 Retail Center 5 Retail Center 6 Retail Center 7 Retail Center 8 Year 1 1000 1200 1800 1200 1000 1400 1600 1000 Forecasting has also estimated that demand at Retail Centers 1, 2, 4, 5, 6, 8 will grow yearly at a rate of 20% of the first year demand. For example, the demand at Retail Center 1 in year t is estimated to be 1000+ 0.20(1000)(1 - 1). The corresponding percentage for Retail Centers 3 and 7 is 25%. The company has several existing plants and has a choice of building (and then operating) a new production line at the plants with the specifications and estimated year-1 costs shown in the following table. In addition to construction costs and yearly operating costs, XYZ may shut down a line that is operating or re-open a line that has been shut down. For simplicity, assume that a line may be re-opened at the beginning of cach year or shut down at the end of each year. Also assume that in the initial construction year, a line incurs construction costs as well as start-up (i.c., re-opening) costs. However, if the line has already been constructed and is then shut down at the end of some year, the plant only incurs the re-opening cost to begin production again. Operating costs are applied in any year that the plant is open (i.e., has not been shutdown), even if production is equal to zero at that plant during that year. 420 Capacity Construction Cost Annual Operating Re-opening Cost (units) (1000's of $) Cost (1000's of 5) (1000's of $) 18,000 2,000 190 12,000 1,600 380 150 14,000 460 160 10,000 900 280 100 12,000 1,500 340 130 14,000 1,800 400 150 Shutdown Cost (1000's of $) 170 120 130 Plant 1 Plant 2 Plant 3 Plant 4 Plants Plant 6 1,800 80 110 130 Flugels will be stored and distributed using XYZ's existing Warehouses. There is no specific per unit charge for storage at a Warehouse. However, since stored items require considerable capital investment, XYZ would like to limit the number of units stored. Over the course of the year, obviously the inventory level fluctuates as items flow into and out of the warehouse. To simplify the modeling, XYZ has decide to only consider the inventory at the beginning of the year and the end of the year. The average inventory level for the year will be the average of these two inventory levels. To control capital investment, XYZ would like the average inventory in any year to be no more than 4,000 items (among all Warehouses). In addition to the operating expenses (which includes overhead items such as power, salaries, etc.), the estimated year-1 cost of producing a unit at Plant i and shipping it to Warehouse j is given in the following table. Plant 1 Plant 2 Plant 3 Plant 4 Plant 5 Plant 6 Warehouse 1 Warehouse 2 Warehouse 3 Warehouse 4 (1000's of $) (1000's of $) (1000's of $) (1000's of $) 0.58 0.53 0.48 0.42 0.55 0.39 0.52 0.54 0.42 0.48 0.44 0.39 0.50 0.39 0.37 0.45 0.46 0.38 0.41 0.50 0.56 0.45 0.42 0.42 Finally, the estimated year-1 unit shipping cost from each Warehouse to each Retail Center is given in the following table. Warehouse 1 Warehouse 2 Warehouse 3 Warehouse 4 Retail 1 Retail 2 Retail 3 Retail 4 (1000's of $) (1000's of $) (1000's of $) (1000's of $) 0.09 0.10 0.06 0.05 0.05 0.07 0.12 0.04 0.06 0.09 0.07 0.09 0.07 0.08 0.09 0.06 Warehouse 1 Warehouse 2 Warehouse 3 Warehouse 4 Retail 5 Retail 6 Retail 7 Retail 8 (1000's of $) (1000's of $) (1000's of $) (1000's of $) 0.08 0.09 0.02 0.12 0.03 0.09 0.03 0.08 0.09 0.04 0.11 0.07 0.10 0.07 0.06 0.09 Costs are expected to rise at the rate of 3% per year. That is, if c is a particular cost in year 1, then the cost in year t is estimated to be c(1+0.03)-1Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


