Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
// funcs.cpp #include using namespace std; template struct BinaryNode { T element; BinaryNode* left; BinaryNode* right; BinaryNode(const T & d = T()): element(d) { left

// funcs.cpp #include using namespace std; template struct BinaryNode { T element; BinaryNode* left; BinaryNode* right; BinaryNode(const T & d = T()): element(d) { left = nullptr; right = nullptr; } }; //print the elements of binary tree in preorder template void preorder(const BinaryNode* root) { // add your code } //print the elements of binary tree in inorder template void inorder(const BinaryNode* root) { // add your code } //print the elements of binary tree in postorder template void postorder(const BinaryNode* root) { // add your code } =============================================
/ lab06.cpp #include "funcs.cpp" BinaryNode* create_binary_tree() { BinaryNode* node_A = new BinaryNode('A'); BinaryNode* node_B = new BinaryNode('B'); BinaryNode* node_C = new BinaryNode('C'); BinaryNode* node_D = new BinaryNode('D'); BinaryNode* node_E = new BinaryNode('E'); node_A->left = node_B; node_A->right = node_C; node_B->left = node_D; node_B->right = node_E; return node_A; } int main() { BinaryNode* root = create_binary_tree(); // add your code // call traversal functions to print elements }

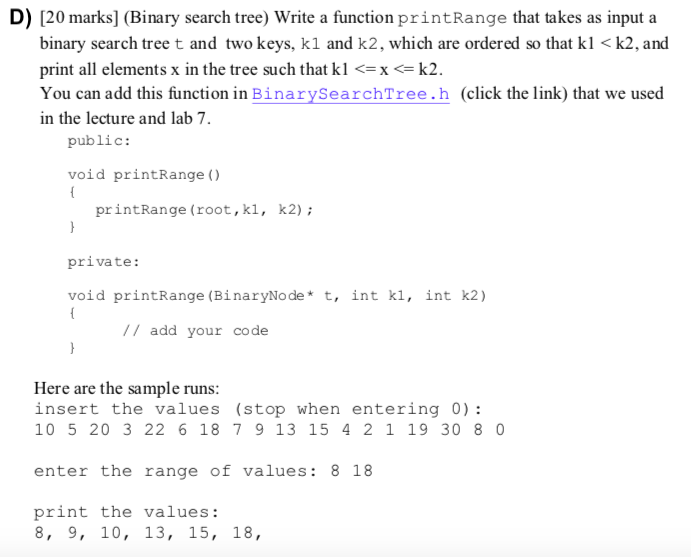
public:
void printRange() { printRange(root,k1, k2); }
private:
void printRange(BinaryNode* t, int k1, int k2) {
// add your code
}
=============================================
//BinarySearchTree.h // after Mark A. Weiss, Chapter 4, Dr. Kerstin Voigt #ifndef BINARY_SEARCH_TREE_H #define BINARY_SEARCH_TREE_H #include #include using namespace std; template class BinarySearchTree { public: BinarySearchTree( ) : root{ nullptr } { } ~BinarySearchTree( ) { makeEmpty(); } bool isEmpty( ) const { return root == nullptr; } const C & findMin( ) const { assert(!isEmpty()); return findMin( root )->element; } const C & findMax( ) const { assert(!isEmpty()); return findMax( root )->element; } bool contains( const C & x ) const { return contains( x, root ); } void printTree( ) const { if( isEmpty( ) ) out left == nullptr ) return t; return findMin( t->left ); } // Internal method to find the largest item in a subtree t. // Return node containing the largest item. BinaryNode* findMax( BinaryNode* t ) const { if( t != nullptr ) while( t->right != nullptr ) t = t->right; return t; } // Internal method to test if an item is in a subtree. // x is item to search for. // t is the node that roots the subtree. bool contains( const C & x, BinaryNode* t ) const { if( t == nullptr ) return false; else if( x element ) return contains( x, t->left ); else if( t->element right ); else return true; // Match } void printTree( BinaryNode* t) const { if( t != nullptr ) { printTree( t->left); cout element right); } } void makeEmpty( BinaryNode* & t ) { if( t != nullptr ) { makeEmpty( t->left ); makeEmpty( t->right ); delete t; } t = nullptr; } // Internal method to insert into a subtree. // x is the item to insert. // t is the node that roots the subtree. // Set the new root of the subtree. void insert( const C & x, BinaryNode* & t ) { if( t == nullptr ) t = new BinaryNode{ x, nullptr, nullptr }; else if( x element ) insert( x, t->left ); else if( t->element right ); else ; // Duplicate; do nothing } // Internal method to remove from a subtree. // x is the item to remove. // t is the node that roots the subtree. // Set the new root of the subtree. void remove( const C & x, BinaryNode* & t ) { if( t == nullptr ) return; // Item not found; do nothing if( x element ) remove( x, t->left ); else if( t->element right ); else if( t->left != nullptr && t->right != nullptr ) // Two children { t->element = findMin( t->right )->element; remove( t->element, t->right ); } else { BinaryNode* oldNode = t; if ( t->left == nullptr ) t = t->right; else t = t->left; delete oldNode; } } }; #endif =============================================
Please answer all these questions to receive credit.
Thank you.
=============================================
Write an application pro gram a3q4.cpp thiat contains a create_binary tree ( finction which create the following binary tree (refer to PartAclick the link). contains main() function which call create binary_tree ) function to create a binary tree, and then call preorder and breadth first functions to print the nodes in preor der and level order, respectively Five files should be su bmitted for this proram question. l) e stack and queue class templates Stack.h and Queue.h, 2) the file funcs.cpp which contains the implementation offunctions, 3) the application file a3q4.cpp containing main ) function, 4) a script file a3q4result containing result Here are the sample runs The preorder: A B DGICEHJKF The level order: A BCDEFGHI JK Hint: The non-recursive preorder traversal uses a stack to store the nodes of the tree. First push the root of the tree in the stack. Then use a while loop: if the stack of nodes is not empty, visit the element of the node at the top position, pop the node, and push the right child and left child of the node. Repeat until the stack is empty The level-order traversal uses a queue to store the nodes of the tree. First enqueue the root of the tree in the queue. Then use a while loop: if the queue of nodes is not empty visit the element of the node at the queue front, enqueue the left child and right child of the node. And then dequeue the node. Repeat until the queue is empty D) [20 marks] (Binary search tree) Write a function printRange that takes as input a binary search tree t and two keys, k1 and k2, which are ordered so that klStep by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


