Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
GAP has a $600,000 line-of-credit with Texas Investment Bank. The limit could be extended, but only if the bank has sufficient loanable funds and
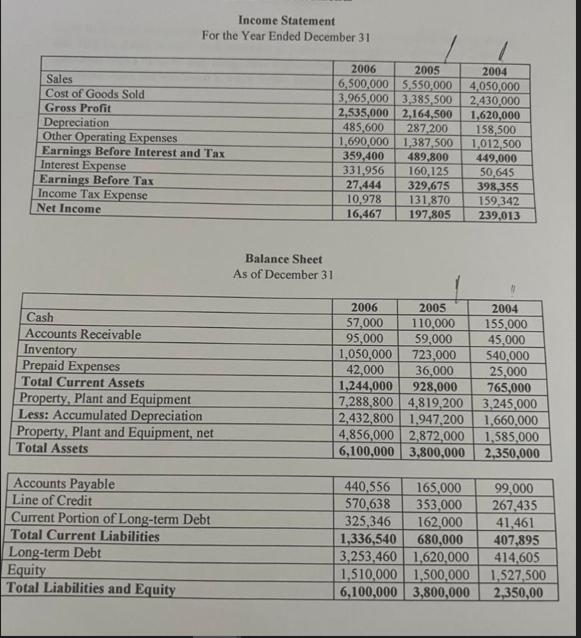
GAP has a $600,000 line-of-credit with Texas Investment Bank. The limit could be extended, but only if the bank has sufficient loanable funds and the company is in a good financial condition. The company must maintain a current ratio of 1.5, a times interest earned ratio of 5.0, and can only borrow up to 50 per cent of the value of its accounts receivable and inventory. The company negotiates separate term loans and mortgages to finance its capital purchases Under Jack's leadership, GAP had an excellent relationship with its bank, but John's poor management and interpersonal skills had put this relationship in jeopardy. Retail sales were paid for in cash or by credit card so there were no accounts receivable. Sales to businesses made up to 40 per cent of sales and were on terms 2/10, net 30 with negligible bad debts. GAP bought its auto parts from the manufacturers on terms 2/15, net 30, which was the norm in the industry. Interest was charged on overdue accounts at 12 per cent per annum and many retailers who got too far in arrears were put on a cash-and-carry basis. A slowdown was forecasted in the local economy in 2007 due to the corn fields fires that took place in the summer of 2006 and the collapse of the beef industry caused by the discovery of mad cow decease in more than half of the farms in Texas. The following industry average ratios (based on year-end figures) were available for companies that sold both tires and automotive maintenance services: Current Ratio Quick Ratio Inventory Turnover in Days Account Receivable turnover in Days Accounts Payable Turnover in Days Fixed Assets Turnover Total Assets Turnover Debt Ratio Times Interest Earned Cost of Borrowing Gross Profit Margin Operating Profit Margin Net Profit Margin Return on Assets Return on Equity GAP's marginal tax rate was 40 percent. 1.90 0.51 60 days 30 days 15 days 3.19 2.00 30.00% 14.63 6.50% 42.00% 12.00% 6.71% 13.42% 19.17% Sales Cost of Goods Sold Gross Profit Depreciation Other Operating Expenses Earnings Before Interest and Tax Interest Expense Earnings Before Tax Income Tax Expense Net Income Income Statement For the Year Ended December 31 Cash Accounts Receivable Inventory Prepaid Expenses Total Current Assets Property, Plant and Equipment Less: Accumulated Depreciation Property, Plant and Equipment, net Total Assets Accounts Payable Line of Credit Current Portion of Long-term Debt Total Current Liabilities Long-term Debt Equity Total Liabilities and Equity Balance Sheet As of December 31 2005 2004 2006 6,500,000 5,550,000 4,050,000 3,965,000 3,385,500 2,430,000 2,535,000 2,164,500 1,620,000 287,200 485,600 158,500 1,012,500 1,690,000 1,387,500 449,000 50,645 27,444 329,675 398,355 10,978 131,870 16,467 197,805 359,400 489,800 331,956 160,125 2005 110,000 59,000 723,000 42,000 36,000 1,244,000 928,000 7,288,800 4,819,200 2,432,800 1,947,200 4,856,000 2,872,000 6,100,000 3,800,000 2006 $7,000 95,000 1,050,000 159,342 239,013 2004 155,000 45,000 540,000 25,000 765,000 3,245,000 1,660,000 1,585,000 2,350,000 440,556 165,000 99,000 570,638 353,000 267,435 325,346 162,000 41,461 1,336,540 680,000 407,895 3,253,460 1,620,000 414,605 1,510,000 1,500,000 1,527,500 6,100,000 3,800,000 2,350,00 S You are to prepare the following ratio analysis calculations for the two years 2006 AND 2005 based on the following ratios listed below: Current Ratio Quick Ratio Inventory Turnover in Days Account Receivable turnover in Days Accounts Payable Turnover in Days Fixed Assets Turnover Total Assets Turnover Debt Ratio Times Interest Earned Cost of Borrowing (do your best on this one!) Gross Profit Margin Operating Profit Margin Net Profit Margin Return on Assets Return on Equity
Step by Step Solution
★★★★★
3.48 Rating (151 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1
To calculate the requested ratios well use the given financial data for the years 2006 and 2005 Lets go through each ratio calculation step by step 1 Current Ratio Current Ratio Current Assets Current ...
Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started