Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
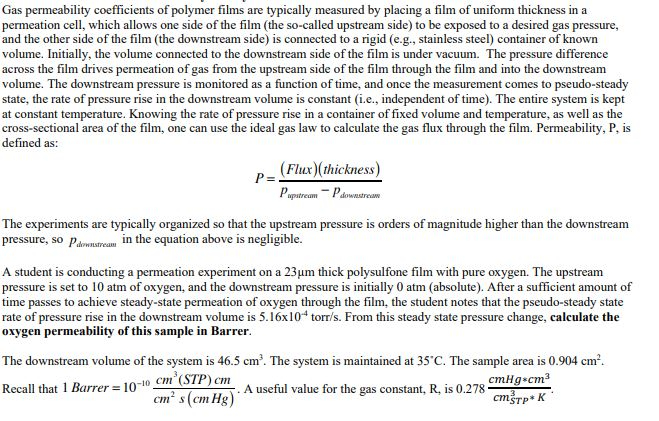
Gas permeability coefficients of polymer films are typically measured by placing a film of uniform thickness in a permeation cell, which allows one side of
Gas permeability coefficients of polymer films are typically measured by placing a film of uniform thickness in a
permeation cell, which allows one side of the film the socalled upstream side to be exposed to a desired gas pressure,
and the other side of the film the downstream side is connected to a rigid eg stainless steel container of known
volume. Initially, the volume connected to the downstream side of the film is under vacuum. The pressure difference
across the film drives permeation of gas from the upstream side of the film through the film and into the downstream
volume. The downstream pressure is monitored as a function of time, and once the measurement comes to pseudosteady
state, the rate of pressure rise in the downstream volume is constant ie independent of time The entire system is kept
at constant temperature. Knowing the rate of pressure rise in a container of fixed volume and temperature, as well as the
crosssectional area of the film, one can use the ideal gas law to calculate the gas flux through the film. Permeability, P is
defined as:
The experiments are typically organized so that the upstream pressure is orders of magnitude higher than the downstream
pressure, so
in the equation above is negligible.
A student is conducting a permeation experiment on a thick polysulfone film with pure oxygen. The upstream
pressure is set to atm of oxygen, and the downstream pressure is initially atm absolute After a sufficient amount of
time passes to achieve steadystate permeation of oxygen through the film, the student notes that the pseudosteady state
rate of pressure rise in the downstream volume is torrs From this steady state pressure change, calculate the
oxygen permeability of this sample in Barrer.
The downstream volume of the system is The system is maintained at The sample area is
Recall that Barrer A useful value for the gas constant, is
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


