Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
Genetics Activity Fill the Punnett square below. Let's say that T = tall plants and t = plant and a homozygous recessive short plant.
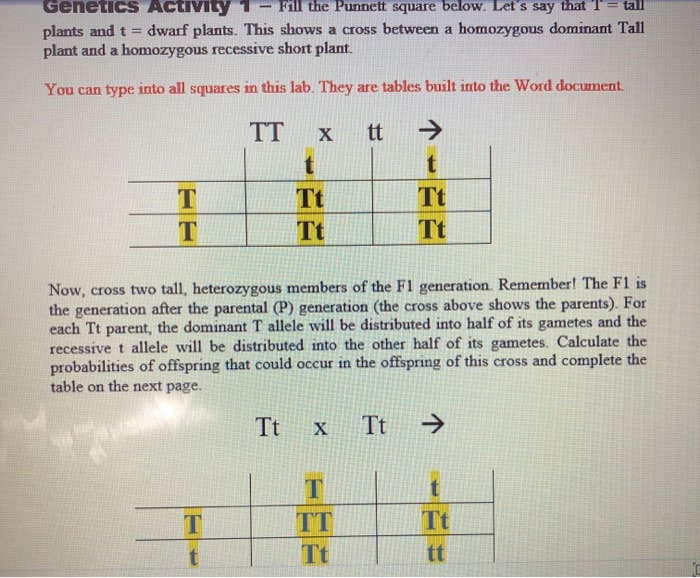
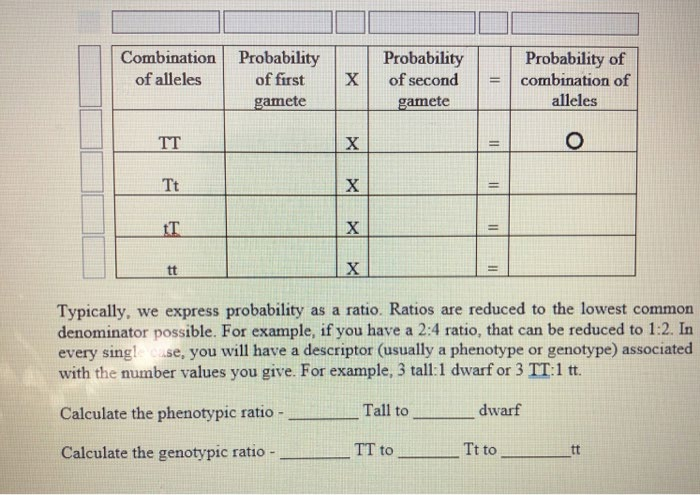
Genetics Activity Fill the Punnett square below. Let's say that T = tall plants and t = plant and a homozygous recessive short plant. dwarf plants. This shows a cross between a homozygous dominant Tall You can type into all squares in this lab. They are tables built into the Word document. TT Xt -> t Tt Tt Tt Tt Now, cross two tall, heterozygous members of the F1 generation. Remember! The F1 is the generation after the parental (P) generation (the cross above shows the parents). For each Tt parent, the dominant T allele will be distributed into half of its gametes and the recessive t allele will be distributed into the other half of its gametes. Calculate the probabilities of offspring that could occur in the offspring of this cross and complete the table on the next page. Tt x Tt -> T TT Tt Tt tt Probability Probability of combination of alleles Combination Probability X of second of alleles of first %3D gamete gamete TT X %3D Tt X IT tt Typically, we express probability as a ratio. Ratios are reduced to the lowest common denominator possible. For example, if you have a 2:4 ratio, that can be reduced to 1:2. In every sing! cse, you will have a descriptor (usually a phenotype or genotype) associated with the number values you give. For example, 3 tall:1 dwarf or 3 TT:1 tt. Calculate the phenotypic ratio - Tall to dwarf Calculate the genotypic ratio - TT to Tt to tt Genetics Activity Fill the Punnett square below. Let's say that T = tall plants and t = plant and a homozygous recessive short plant. dwarf plants. This shows a cross between a homozygous dominant Tall You can type into all squares in this lab. They are tables built into the Word document. TT Xt -> t Tt Tt Tt Tt Now, cross two tall, heterozygous members of the F1 generation. Remember! The F1 is the generation after the parental (P) generation (the cross above shows the parents). For each Tt parent, the dominant T allele will be distributed into half of its gametes and the recessive t allele will be distributed into the other half of its gametes. Calculate the probabilities of offspring that could occur in the offspring of this cross and complete the table on the next page. Tt x Tt -> T TT Tt Tt tt Probability Probability of combination of alleles Combination Probability X of second of alleles of first %3D gamete gamete TT X %3D Tt X IT tt Typically, we express probability as a ratio. Ratios are reduced to the lowest common denominator possible. For example, if you have a 2:4 ratio, that can be reduced to 1:2. In every sing! cse, you will have a descriptor (usually a phenotype or genotype) associated with the number values you give. For example, 3 tall:1 dwarf or 3 TT:1 tt. Calculate the phenotypic ratio - Tall to dwarf Calculate the genotypic ratio - TT to Tt to tt Genetics Activity Fill the Punnett square below. Let's say that T = tall plants and t = plant and a homozygous recessive short plant. dwarf plants. This shows a cross between a homozygous dominant Tall You can type into all squares in this lab. They are tables built into the Word document. TT Xt -> t Tt Tt Tt Tt Now, cross two tall, heterozygous members of the F1 generation. Remember! The F1 is the generation after the parental (P) generation (the cross above shows the parents). For each Tt parent, the dominant T allele will be distributed into half of its gametes and the recessive t allele will be distributed into the other half of its gametes. Calculate the probabilities of offspring that could occur in the offspring of this cross and complete the table on the next page. Tt x Tt -> T TT Tt Tt tt Probability Probability of combination of alleles Combination Probability X of second of alleles of first %3D gamete gamete TT X %3D Tt X IT tt Typically, we express probability as a ratio. Ratios are reduced to the lowest common denominator possible. For example, if you have a 2:4 ratio, that can be reduced to 1:2. In every sing! cse, you will have a descriptor (usually a phenotype or genotype) associated with the number values you give. For example, 3 tall:1 dwarf or 3 TT:1 tt. Calculate the phenotypic ratio - Tall to dwarf Calculate the genotypic ratio - TT to Tt to tt
Step by Step Solution
★★★★★
3.48 Rating (145 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1
Tt X Tt T iy2 TT Tt Tt CY2 tt Parent T 2 50 ...
Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


