Question
Given a directed acyclic graph G=(V,E). For every node u and every directed edge (u, v) , we are also given the probability that the
Given a directed acyclic graph G=(V,E). For every node u and every directed edge (u, v), we are also given the probability that the system will go next to vertex v if it is in state u. The outgoing edges e needs to sum up to 1 (100%). If u is the final state (a sink), the vertex has no outgoing edges. The random decisions at different nodes u are assumed to be mutually independent.
There's exactly one source s and one sink t. Hence the possible behaviors of the system are exactly all directed st paths. This also defines a probability space whose elementary events are all these paths. Down below is an example of a DAG.
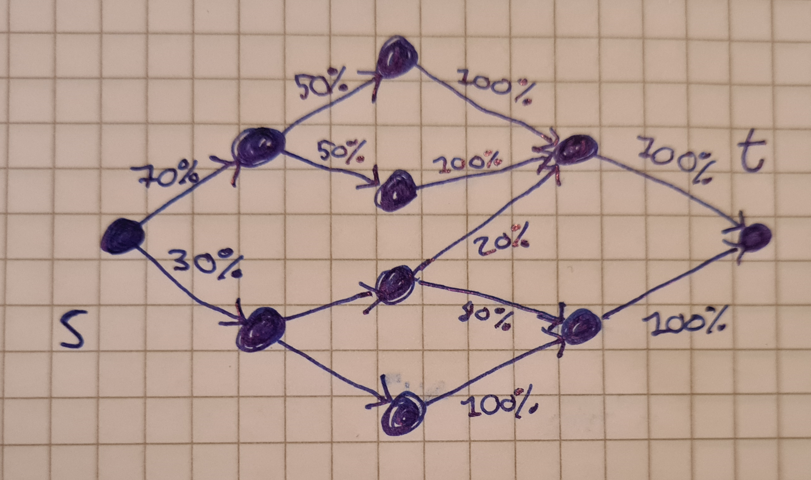
I want to figure out the probabilities of certain events in the system using efficient algorithms.
Given a certain subset of edges in E, how can I compute the probability of traversing all of them and how can I compute the probability of traversing at least one of them?
50%. 100% 50% 100% t 70% 200% 120% 30% % S 1007 100%Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


