Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
Given: A packet that has arrived at packet switch Q Perform: The next-hop forwarding step Method: Extract the destination address from the packet; Divide

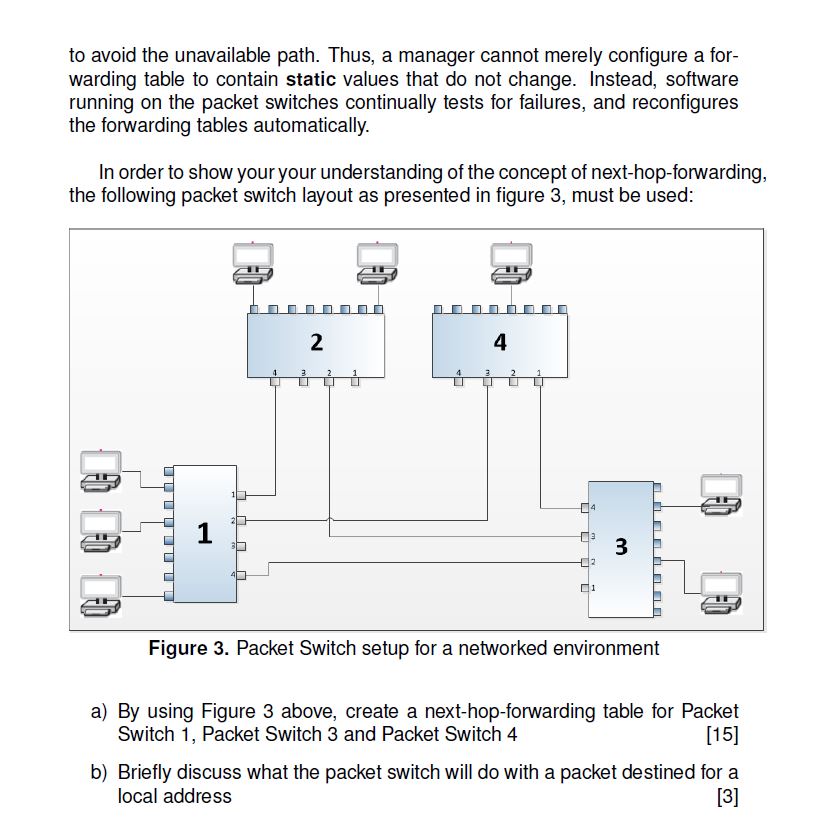
Given: A packet that has arrived at packet switch Q Perform: The next-hop forwarding step Method: Extract the destination address from the packet; Divide the address into a packet switch number, P, and a computer identification, C; if (P == Q) { /* the destination is local */ Forward the packet to local computer C; } else { ward Select a link that leads to another packet switch, and for- the packet over the link; } to avoid the unavailable path. Thus, a manager cannot merely configure a for- warding table to contain static values that do not change. Instead, software running on the packet switches continually tests for failures, and reconfigures the forwarding tables automatically. In order to show your your understanding of the concept of next-hop-forwarding, the following packet switch layout as presented in figure 3, must be used: 1 3 2 2 4 3 Figure 3. Packet Switch setup for a networked environment a) By using Figure 3 above, create a next-hop-forwarding table for Packet Switch 1, Packet Switch 3 and Packet Switch 4 [15] b) Briefly discuss what the packet switch will do with a packet destined for a local address [3]
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


