Go through the attached case and answer the questions at the end on its basis.


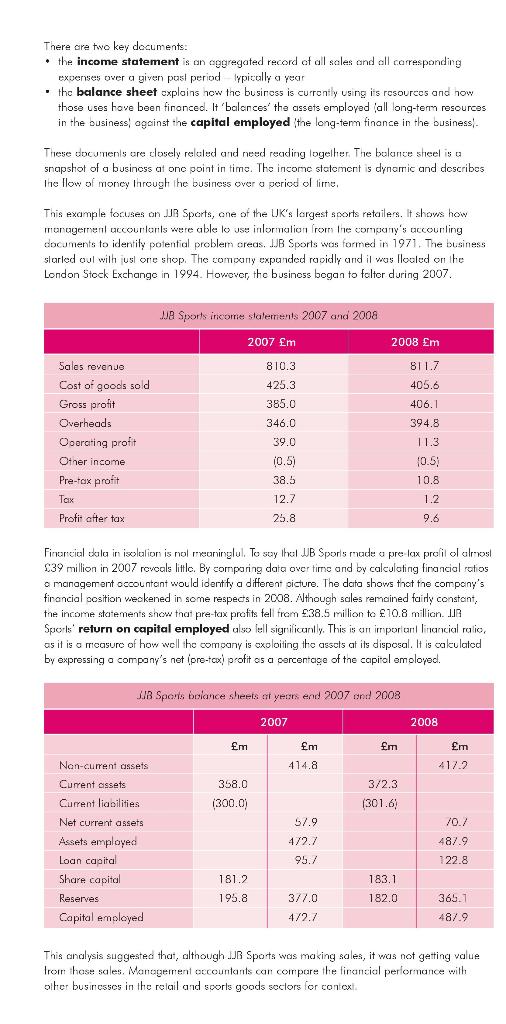
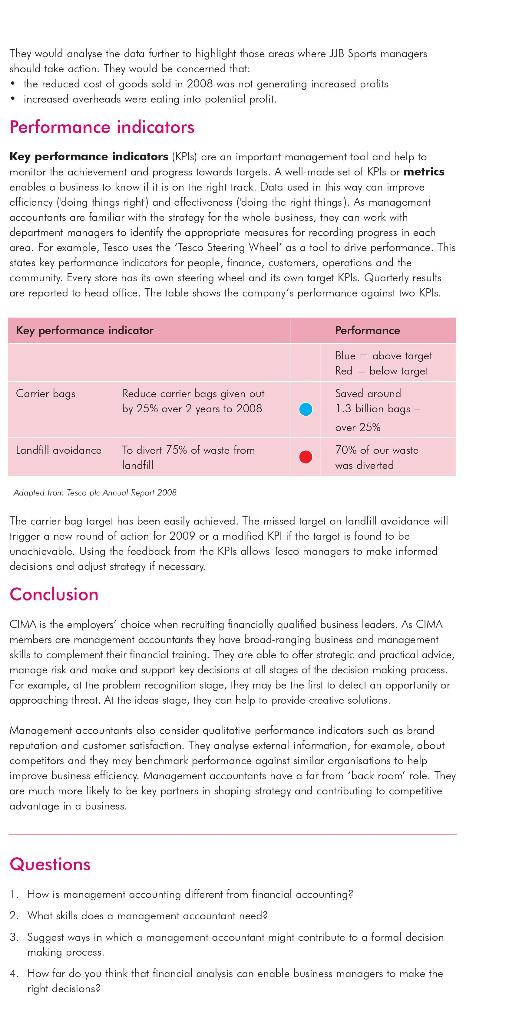
Improving strategic decision making Introduction Financial accountants keep records of business transactions such as sales invoices. They use these records to prepare a firm's accounting statements. Management accountants evaluate and interpret this financial data to advise the senior managers in the business. They play important roles in managing business performance and improving decision making. CIMA is the leading and largest professional body for management accountants with over 171,000 members and students operating at the heart of business in 165 countries. Its members work in financial and non-financial roles throughout organisations and carry out all their training and experience requirements in business itself. This provides them with a unique insight into how their organisations operate. CIMA's mission is to be the first choice for employers in the qualification and development of management accountants. Young people obtain the CIMA qualification and then membership for many reasons. Some want a career in accountancy but do not just want to work with numbers. They look for management and leadership roles where they can contribute to business performance. Others are already managers in business but want to improve their skills in financially-based decision making. CIMA people are financially qualified business leaders and are not limited to working in accountancy practices and finance departments. They are active across a range of management roles in retailing, manutacturing, property, energy and government services. The decision making process Elective strategic business decisions bring together the right resources for the right markets at the right time. Timing is crucial. For example, Tesco developed its online ordering and delivery service as internet shopping expanded. Virgin sold off its music stores as downloading music became more popular. The quality of a company's decision making helps it gain an advantage over competitors. Business decisions must reflect on organisation's aims (its purpose), such as to maximise returns for its shareholders. They should also relate to its objectives (its goals), such as to be the market leader in its field. To achieve its aims and objectives, a business puts in place strategies. This approach applies regardless of the size of the business. Feedback Recognition of the problem Consider a local bakery that operates a small cate business. The caf is open trom 9am to 4pm, Monday to Friday Competition from a nearby supermarket and fast food outlets is preventing the caf business from growing. What action could the caf take to increase sales? Implementation A systematic approach Information and intelligence The key issue to identity is why customers are choosing other outlets. Is it because of location, price or product quality Analysing a problem of this kind needs a systematic approach. Choice Alternatives Talking to customers about what they like, visiting other outlets to see the competition and cxamining in-house data on costs, pricing and service could provide valuable information Based on this research, alternative courses of action might include cuting costs in order to reduce prices or promoling the col in different ways. The business chooses actions based on evidence in support of its objectives. The decision may be a hard one. As a last resort, the bakery may need to cxil the cal markel altogether it it cannot combal Inc competition and increase sales. Monitoring the feedback from, or outcomes of, a decision allows the business to know whal working and what is not, which leads to a new decision making cycle. However, A rational decision making approach can help to reduce uncertainty. However, the external environment of a business adds varioble factors which can increase risk. For example, suppose an engineering business needs new cost saving technology to improve production and make it competitive. Justifying this expenditure becomes more dificult in a recession. what is the risk of not taking action? Will the business survive without the Technology il is also ir porlari to balance risk against the likely telurn on investment. The extent to which this happens may depend on the organisational culture. Some businesses encourage risk leiking some are more risk coverse Virgin rellects ils owner, Richard Branson, an entrepreneur who thrives on risk toking both in business and in his personal lifel. The Nolionwide Building Sociely, which has a duly lo saleguard ils members' money, odools a more cautious approach. High-perfoming organisations use the skills of their people to ensure they make more effective decisions than poor ches. Levels of decision making Decisions are mode at different levels in on organisction's hierarchy: Strategic decisions are long-term in their impact. They attect and shape the direction of the whole business. They are generally made by senior managers. The managers cl the bakery need to take a strategic decision about whether to remain in the cate business. Long-term forecasts al business turnover sel against likely markel conditions will help lo determine if it should close the cot business. . Tactical decisions help to implement the strategy. They are usually made by middle management For the caf, a tactical decision would be whether to open earlier in the morning or en Saludoy lo allract new customers. Managers would want research data on likely customer numbers to holo them decide if opening hours should be extended. Operational decisions relate to the day-to-day running of the business. They cre mainly routine and may be taken by middle or junior managers. For examplo, a simple operational decision for the cont would be whether to order more coffee for next week. Stock and solos data will show when it needs to order moro supplies. As these exa moles show decisions at all levels noed dota. A business creates a trail of doto. This includes data on sales, employee costs and payments. In a large company, such as Tesco, milions oldala ilers are created every day against thousands el cost and sales headings. This dato can provide a picture of trends, which the business can use in its forword planning Financial accountants use recorded date to prepare the accounting statements for a business. Every company large and small) has a duty to keep accounting records and must prepere annual accounts that report on the cerformance and activities of the company during the year. Financial accountants must ensure these accounts are accurate and prepared in accordance with accounting rules and conventions. Management accountants nood understand these formal accounting documents. However, because their role involves the analysis ond application of data, they must also be familiar with business strategy and risk management Management accountants use internal data (like a balonce sheet and external data (such as market information to assess effects on the business and drive better intormed decision making Analysing accounts In practice the work of a management accountant is rather like that of a detective. The task is to sift through evidence and to extract meaningful messages that will help managers make ellective business decisions. The starting point is often the basic accounting documents that record the progress of any business. There are two key documents. the income statement is an aggregated record of all sales and all corresponding expenses over a given pasi period typically a year . the balance sheet explains how the business is currently using its resources and how those uses have been financeol. It 'balonces' the assets employed all long-term resources in the business against the capital employed the long-term finance in the business These documents are closely related and need reading together. The balance sheel is a snapshot of a business at one point in time. The income statement is dynamic and describes The llow of money through the business over a period of time, This example focuses on JB Sports, one of the UK's largest sports retailers. It shows how management accountants were able lo use inlormation from the company's accounting documents to identity potential problem creas. IJB Sports was formed in 1971. The business slarled oul with usl one shop. The company expanded rapidly and il vos looled on the London Stock Exchango in 1994. However, the business began to folter during 2007. JJ Sports income statements 2007 and 2008 2007 m 810.3 425.3 385.0 2008 m 8117 405.6 406.1 Sales revenue Cost of goods sold Gross profit Overheads Operating profit Other income Pre-tex profit 346.0 39.0 10.5) 38.5 12.7 394.8 11.3 10.5; 10.8 1.2 Tax Proti after tax 25.8 9.6 Firwarcial skila in isolution is no meaninglul. To say that JB Sports made o pre lcx prolil ol almost $39 million in 2007 reveals little. By comparing data over time and by calculating financial ratios o management occountant would identify a different picture. The data shows that the company's financial position veckened in some respects in 2008. Although sales remained fairly constant, the income statements show that pre-tax profits fell from 38.5 million to 10.8 million. IIB Sporls' return on capital employed also lell significantly. This is an important linancial ratio, as it is a measure of how well the company is excloiting the assets at its disposal. It is calculated by expressing a company's not (pro-tox) profitos a percentage of the capital omoloyoc. JIB Sports balance sheets at yeurs end 2007 and 2008 2007 2008 m m fm m 417.2 Nan-current assets 414.8 3/2.3 358,0 (300.0) (301.6) 57.9 /0.7 487.9 Current assets Current liabilities Net current assets Assets employed Loan capital Share capital Reserves Capital Amployed 472.7 95.7 122.8 181.2 183.1 195.8 182.0 3/7.0 4/2.7 365.7 487.9 This analysis suggested that, although JB Sports was making sales, it was not getting value from those sales. Management accountants can compare the financial performance with other businesses in the relail and sporls goods scclors for context They would analyse the data furtner to highlight those areas where JJB Sports managers should take action. They would be concerned that: the reduced cost of goods sold in 2008 was not generating increased prolits increased overheads were eating inlo solential prolil. Performance indicators Key performance indicators (KPIs are an important management tool and help to monitor the achievement and progress towards largels. A well-nede set of KPIs or metrics enables a business lo know il it is on the right track. Dals used in this way can improve cfficiency (doing things right) and effectiveness I'doing the right things). As management accountonts are familiar with the strategy for the whole business, they can work with department managers to identify the appropriate measures for recording progress in each area. For example, Tesco uses the 'Tesco Steering Wheel' as a tool to drive perfomance. This states key performance indicators for people, finance, customers, operations and the community. Every store nas its own steering wheel and its own target KPIs. Quarterly results ure reported to head office. The loble shows the comixiny's performance against wo> KPIs. Key performance indicator Performance Carier bags Reduce carrier begs given out by 25% over 2 years to 2008 Blue above target Red below largel Saved around 1.3 billion bags over 25% 70% of our wasto was diverted Landfill avoidance To divert 75% of waste from landfill Acqua from Texo ok All Ceport 2009 The carrier bag largel has been easily achieved. The missed largel on lardill avoidance will trigger a now round of action for 2009 or a modificd KPI if the target is found to be unacnicvadlo. Using the foodback from the KPIs allows losco managers to make informed decisions and adjust strategy if necessary. Conclusion CIMA is the employers' choice when recruiting financially oualified business leaders. As CIMA members are management accountants they have broad-ranging business and management skils to complement their financial training. They are able to offer strategis and practical advice, morage risk and make and suppor key decisions at all stages of the decision making process. For example, al te problem recognition stage, they may be the first to delect an opportunity or approaching throal. At the ideas slage, they can help to provide creative solutions. Management accountants also consider qualitative performance indicators such as brand reputation and customer satisfaction. They analyse external information, for example, obout competitors and they may benchmark performance against similar organisations to help improve business efficiency Management accountents have a far from 'back room' role. They are much more likely to be key partners in shaping strategy and contributing to competitive advanlage in a business, Questions 1. How is management occounting differont from financial accounting? 2. What skills does a management accountant need? 3. Suggest ways in which a monagement accountant might contribute to a formal decision making process 4. How far do you think that financial analysis con encble business managers to make the right decisions










