Good Morning, I need help with this worksheet.
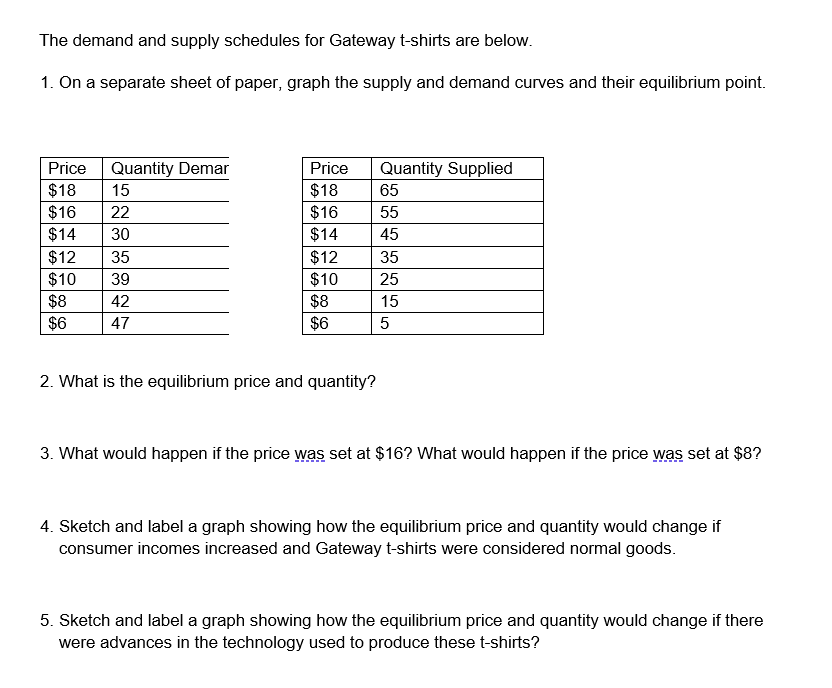
Unit 3 Markets, Equilibrium, & Prices Demand Supply curve curve Equilibrium Equilibrium quantity Quantity Equilibrium is the point where quantity demanded equals quantity supplied. In a free market, demand and supply automatically move towards this point in the market because it balances the desires of consumers with the desires of producers. On a graph, the equilibrium point is the point where the demand curve and supply curve intersect, or cross. While markets move to this point, sometimes they get out of balance - or enter disequilibrium. When that happens... Surplus: supply is greater than demand - there's too much product! o Usually caused by prices being too high. | . Shortage: demand is greater than supply - we've run out of product! o Usually caused by prices being too low. As our demand or supply shifters affect the market, the equilibrium point will move. For example, if Beyonce does a bunch of commercials for 7-up, demand will likely increase with consumer tastes and preferences. As the demand curve shifts right, the equilibrium point will also shift to the new intersection of supply and demand. In another example, if there is a massive drought killing most of the strawberry crops, the supply of Jamba Juice strawberry smoothies will decrease, shifting the curve left. The equilibrium point will move to the new intersection of supply and demand. Because most economies today are mixed economies, the intervention of government can affect prices and markets. Governments sometimes implement price controls when prices are considered unfairly high for consumers or unfairly low for producers. Price floors, such as minimum wage laws, prevent prices from going too low, but can lead to excess supply Price ceilings, such as rent control laws, prevent prices from going too high, but can lead to shortages.The demand and supply schedules for Gateway tshirts are below. 1. On a separate sheet of paper, graph the supply and demand curves and their equilibrium point. Price Quantity De mar Price Quantity 8 uppli ed $1 8 1 5 $1 8 65 $16 22 $1 6 55 $14 30 $1 4 45 $12 35 $1 2 35 $10 39 $1 C- 25 $8 42 $8 15 $6 47 $6 5 2. What is the equilibrium price and quantity? 3. What would happen if the pnoe was set at $16? What would happen if the price was set at $8? 4. Sketch and label a graph showing how the equilibrium price and quantity would change if consumer incomes increased and Gateway tshirts were considered normal goods. 5. Sketch and label a graph showing how the equilibrium price and quantity would change if there were advances in the technology used to produce these tshirts