Question
// graph.h // #ifndef GRAPH_H #define GRAPH_H #include #include #include #include #include // For STL stack #include // For STL queue #include using namespace std;


// graph.h
//
#ifndef GRAPH_H
#define GRAPH_H
#include
class GraphPathNotFound { }; // Exception class represents path-not-found condition
class GraphEdgeNotFound { }; // Exception class represents edge-not-found condition
class GraphVertexNotFound { }; // Exception class represents vertex-not-found condition
class GraphFull { }; // Exception class represents graph-full condition
struct VertexNode; // Forward declaration of VertexNode type
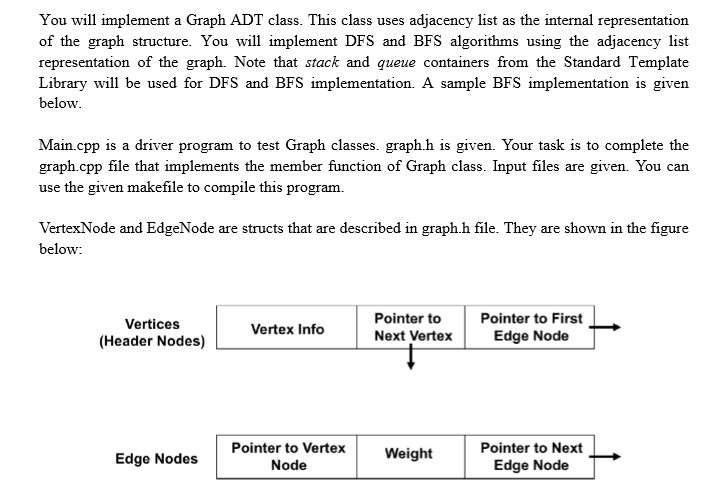
struct EdgeNode // Structure representing an edge { VertexNode* destination; // Pointer to destination vertex int weight; // Edge weight EdgeNode* nextEdge; // Pointer to next edge };
struct VertexNode // Structure representing a vertex { string vname; // Name of vertex bool mark; // Marked flag EdgeNode* edgePtr; // Pointer to list of outgoing edges VertexNode* nextVertex; // Pointer to next vertex in vertices list };
class Graph // Graph ADT using adjacency list representation { private: //***** Private class members below *****// VertexNode* vertices; // Linked list of vertex nodes
public: //***** Public members below *****// Graph(); // Graph() // Constructor initializes vertices linked list to empty ~Graph(); // ~Graph() // For each VertexNode in the vertices list, Destructor deallocates all EdgeNodes before // deallocating the VertexNode itself void AddVertex(string v); // AddVertex() // Adds vertex to graph assuming vertex not already present
void AddEdge(string s, string d, int w); // AddEdge() // Adds edge from source S to destination D with specified weight W. // If there is not enough memory to add the edge, throw the GraphFull exception VertexNode* VertexExists(string v) const; // VertexExists() // Returns pointer to corresponding VertexNode if vertex V in graph // Returns NULL otherwise
EdgeNode* EdgeExists(string s, string d) const; // EdgeExists() // Returns pointer to edge node if edge from vertex s to vertex d exists in graph // Returns NULL otherwise int WeightIs(string s, string d); // WeightIs() // Returns weight of edge (s,d). Throws GraphEdgeNotFound if edge not present. void ClearMarks(); // ClearMarks() // Clears all vertex marks void MarkVertex(string v); // MarkVertex() // Marks vertex V as visited // Throws GraphVertexNotFound if not present bool IsMarked(string v); // IsMarked() // Returns true if vertex V is marked, false if not marked // Throws GraphVertexNotFound if not present
void GetToVertices(string V, queue
void BreadthFirstSearch(string startVertex, string endVertex, queue #endif // main.cpp // #include using namespace std; int main(int argc, char* argv[]) { ifstream inputs; // Input file for commands char op, ch; // Hold operation and optional char input Graph* gPtr = NULL; // Will point to Graph object int num; // Holds number of graph nodes string v1, v2; // Vertex names input from file int w; // Edge weight input from file queue case '!': // EdgeExists() try { inputs >> v1 >> v2; if (gPtr->EdgeExists(v1, v2) != NULL) cout > v1 >> v2; cout WeightIs(v1, v2); cout case 'm': // MarkVertex() try { inputs >> v1; cout MarkVertex(v1); cout case 'e': // ClearMarks() try { cout ClearMarks(); cout case 'i': // IsMarked() try { inputs >> v1; cout IsMarked(v1)) cout > v1 >> v2; // Input v1-start and v2-end vertices cout DepthFirstSearch(v1, v2, visitedq); if (visitedq.empty()) cout case 'g': // GetToVertices try { inputs >> v1; cout GetToVertices(v1, adjq); if (adjq.empty()) cout case 'b': // Perform Breadth-First Search try { inputs >> v1 >> v2; // Input v1-start and v2-end vertices cout BreadthFirstSearch(v1, v2, visitedq); if (visitedq.empty()) cout Print(); break; case '~': // Destructor try { delete gPtr; gPtr = NULL; cout > op; // Attempt to input next command } return 0; } Test Graph(), ~Graph(), AddVertex(), AddEdge() with undirected graph # Test with undirected graph c v A v B v C v D u A B 5 u A C 10 u B C 15 u B D 25 u C D 20 p ~ # Test with larger undirected graph c v A v B v C v D v E v F v G v H u A B 25 u A C 10 u A E 60 u B G 75 u B H 15 u C E 15 u D F 25 u D H 80 u E G 35 u E F 5 u F H 40 p ~ # Test with small directed graph c v A v B v C v D d A B 5 d A C 10 d B C 15 d B D 25 d C D 20 p ~ # Test with larger directed graph c v A v B v C v D v E v F v G v H d A B 25 d A C 10 d A E 60 d B G 75 d B H 15 d C E 15 d D F 25 d D H 80 d E G 35 d E F 5 d F H 40 p ~ - Test VertexExists(), EdgeExists(), WeightIs() # Test VertexExists() and its error handling c v A v B v C v D v E v F v G v H u A B 25 u A C 10 u A E 60 u B G 75 u B H 15 u C E 15 u D F 25 u D H 80 u E G 35 u E F 5 u F H 40 p ? A ? B ? G ? H ? K ? Z ~ # Test EdgeExists() and its error handling c v A v B v C v D v E v F v G v H u A B 25 u A C 10 u A E 60 u B G 75 u B H 15 u C E 15 u D F 25 u D H 80 u E G 35 u E F 5 u F H 40 p ! A B ! B H ! G E ! H F ! K A ! C D ~ # Test WeightIs() and its error handling c v A v B v C v D v E v F v G v H u A B 25 u A C 10 u A E 60 u B G 75 u B H 15 u C E 15 u D F 25 u D H 80 u E G 35 u E F 5 u F H 40 p w E F w F H w A K w A H ~ - Test MarkVertex(), IsMarked(), and ClearMarks() # Test MarkVertex(), IsMarked(), ClearMarks() using small undirected graph c v A v B v C v D u A B 5 u A C 10 u B C 15 u B D 25 u C D 20 p m A m C m H m K i A i B i C i D i J e i A i B i C i D i J ~ Test GetToVertices() # Test GetToVertices() using larger directed graph c v A v B v C v D v E v F v G v H d A B 25 d A C 10 d A E 60 d B G 75 d B H 15 d C E 15 d D F 25 d D H 80 d E G 35 d E F 5 d F H 40 p g A g B g C g D g E g F g G g H g K ~
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


