Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
Gregson Foundries Ltd. (GFL) has a fiscal year end of September 30 and its statements for 2019 and 2020 are below. The firm is

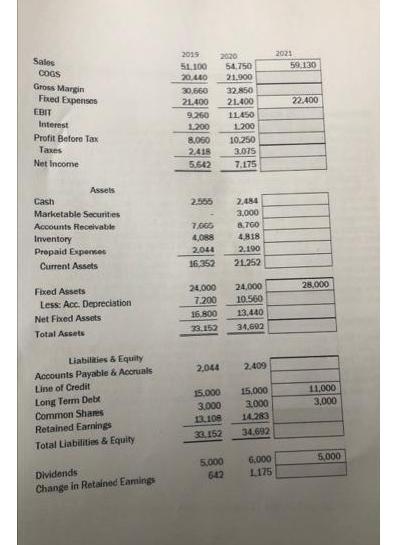
Gregson Foundries Ltd. (GFL) has a fiscal year end of September 30 and its statements for 2019 and 2020 are below. The firm is anticipating an excellent year for 2021, forecasting sales to increase by 8% in 2021 to $59.13 million As the firm only has sufficient capacity for sales of up to $60 million, CAPEX for 2021 is expected to be $4 million, Fixed expenses are expected to increase by $1.000.000. Tobias Gregson, Founder and CEO, is planning to withdraw $5 million in dividends in 2021. Interest is 8% of the previous year's long term debt and Gregson has an option to make a principal payment on the debt of $4 million at the end of 2021, which they intend to exercise. The rate earned on marketable securities is so low at this time that it is being forecast at 0%. The marketable securities can only be bought and sold in multiples of $1 million and the line of credit is drawn in multiples of $1 million as well. As the firm is growing rapidly, Tobias has decided to change the target range for the cash balance to between $3 million and 54 million, and adjusting the marketable securities balance or drawing on their unused line of credit, as necessary. Depreciation, which is included in Fixed Expenses on the Income Statement, is 20% of the preceding year's Net Fixed Assets value plus 10% of the current year CAPEX Required: Using the percentage of sales method, forecast GFL's working capital needs for 2021. Use "Cash", (and if necessary to keep cash within the specified target range, "Marketable Securities and "Line of Credit") as the plug variable(s). For your convenience, if needed, you are provided the entire set of financial statements are provided, but only the unshaded working capital items will be marked. Place your forecast values in the boxes. Sales COGS Gross Margin Fixed Expenses EBIT Interest Profit Before Tax Taxes Net Income Assets Cash Marketable Securities Accounts Receivable Inventory Prepaid Expenses Current Assets Fixed Assets Less: Acc. Depreciation Net Fixed Assets Total Assets Liabilities & Equity Accounts Payable & Accruals Line of Credit Long Term Debt Common Shares Retained Earnings Total Liabilities & Equity Dividends Change in Retained Eamings 2019 51.100 20,440 30.660 21.400 9,260 1,200 8,060 2,418 5.642 2.555 7,065 4,088 2,044 16.352 2020 2,044 54,750 21,900 32,850 21,400 5.000 642 11,450 1.200 10,250 3.075 7.175 2,484 3,000 24,000 24,000 7.200 10.560 16.800 13,440 33.152 34,602 8.700 4,818 2,190 21,252 2,409 15.000 15,000 3.000 13,108 33,152 3,000 14,283 34.692 6.000 1.175 2021 59,130 22.400 28,000 11,000 3,000 5,000
Step by Step Solution
★★★★★
3.52 Rating (166 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1
4 Depreciation current year 3088 Accumulated depreciation 13648 Ne...
Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


