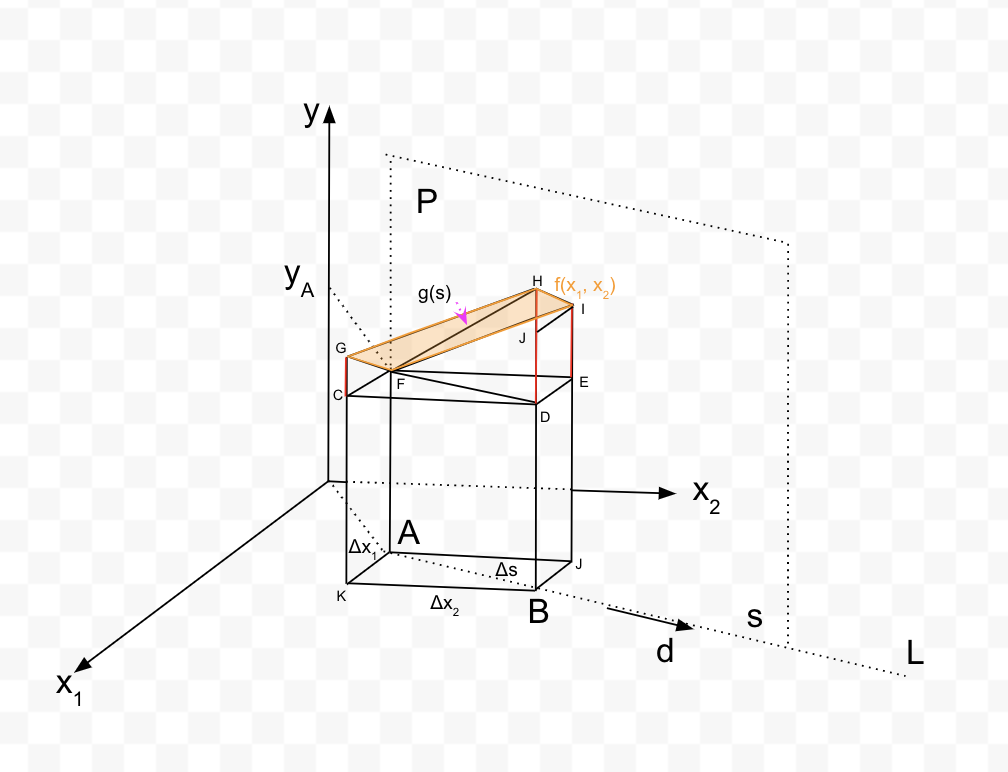


H f(x,x) g(s). .......s , 7. Q2 [4]. Functions, derivatives, gradients Consider a function of two variables y = f(x1, x2) = 4(x1 - 1)2 + 3(x2 - 2)2. The function represents a surface in the three-dimensional space (C1, 12,y). This diagram shows the local behaviour of f near a point A. The diagram shows a small step As from A to another point B, along the direction of unit vector d. The projections of As on the ri and 22 axes are Ac and Ac2 respectively. The "column" with footprint the rectangle AJBK, cuts off a piece of the 3D surface defined by f, shown as FGHI and highlighted in orange colour. If the step As is really small, and the surface f is reasonably smooth, then we can consider the surface piece to be planar, and FGHI is a parallelogram. Please refer to the diagram in the following questions, and your answers. a) Focus on point A = (1, 1) on the (21, 22) plane. What is the value of yA = f(1, 1)? What are the partial derivatives of f with respect to ri and X2, in closed form as functions of 21, 22? What is the value of the partial derivatives at point A? What are the lengths of segments GC and IE in terms of the partial derivatives at A and the small steps Ax and A.x2? Note: The vector formed by the partial derivatives (G T is the gradient of f. b) Consider the vertical plane P (perpendicular to the (21, 22) plane) such that (i) it contains point A = (xa, xb), (ii) it contains the unit vector d = (dj,d2) that originates at A, and lies on the (X1, 22) plane. Therefore it contains point B. P intersects the surface defined by f. The intersection contains line segment FH. The intersection between P and the surface is a function g(s) of a single variable, s, the distance from point A along vector d on the plane P. The intersection between P and the (X1, 22) plane is a straight line L. What is the position vector on the (x1, x2) plane of a point B on line L at distance s from A, as a function of s? What is the value of g(s) at point B? Apply the general forms you derive above, to compute the position vector B and g(s) at B, for d = d2 = 1/V2 and s=0.1. c) Explain why the derivative of g(s) at point A is the projection of the gradient of f on the direction defined by vector (d, d2). Express in terms of vector d and the partial derivatives of f. Hint: Identify Ag and As in the diagram based on your understanding of the geometric meaning of the derivative of one variable, s, on plane P. Compute the value of Agat A for d = d2 = 1/V2. Ang is the notion of directional derivative of f along a given direction d. An introduction to the directional derivative and the gradient is available here. Examples are presented here. d) Based on your answer of part (c), what is the directional derivative along the direction of the gradient? Why is this the maximum value of the directional derivative along all possible directions out of point A? H f(x,x) g(s). .......s , 7. Q2 [4]. Functions, derivatives, gradients Consider a function of two variables y = f(x1, x2) = 4(x1 - 1)2 + 3(x2 - 2)2. The function represents a surface in the three-dimensional space (C1, 12,y). This diagram shows the local behaviour of f near a point A. The diagram shows a small step As from A to another point B, along the direction of unit vector d. The projections of As on the ri and 22 axes are Ac and Ac2 respectively. The "column" with footprint the rectangle AJBK, cuts off a piece of the 3D surface defined by f, shown as FGHI and highlighted in orange colour. If the step As is really small, and the surface f is reasonably smooth, then we can consider the surface piece to be planar, and FGHI is a parallelogram. Please refer to the diagram in the following questions, and your answers. a) Focus on point A = (1, 1) on the (21, 22) plane. What is the value of yA = f(1, 1)? What are the partial derivatives of f with respect to ri and X2, in closed form as functions of 21, 22? What is the value of the partial derivatives at point A? What are the lengths of segments GC and IE in terms of the partial derivatives at A and the small steps Ax and A.x2? Note: The vector formed by the partial derivatives (G T is the gradient of f. b) Consider the vertical plane P (perpendicular to the (21, 22) plane) such that (i) it contains point A = (xa, xb), (ii) it contains the unit vector d = (dj,d2) that originates at A, and lies on the (X1, 22) plane. Therefore it contains point B. P intersects the surface defined by f. The intersection contains line segment FH. The intersection between P and the surface is a function g(s) of a single variable, s, the distance from point A along vector d on the plane P. The intersection between P and the (X1, 22) plane is a straight line L. What is the position vector on the (x1, x2) plane of a point B on line L at distance s from A, as a function of s? What is the value of g(s) at point B? Apply the general forms you derive above, to compute the position vector B and g(s) at B, for d = d2 = 1/V2 and s=0.1. c) Explain why the derivative of g(s) at point A is the projection of the gradient of f on the direction defined by vector (d, d2). Express in terms of vector d and the partial derivatives of f. Hint: Identify Ag and As in the diagram based on your understanding of the geometric meaning of the derivative of one variable, s, on plane P. Compute the value of Agat A for d = d2 = 1/V2. Ang is the notion of directional derivative of f along a given direction d. An introduction to the directional derivative and the gradient is available here. Examples are presented here. d) Based on your answer of part (c), what is the directional derivative along the direction of the gradient? Why is this the maximum value of the directional derivative along all possible directions out of point A









