Question
Hatfield Medical Supplies stock price had been lagging its industry averages, so its board of directors brought in a new CEO, Jaiden Lee. Lee had
Hatfield Medical Supplies’ stock price had been lagging its industry averages, so its board of directors brought in a new CEO, Jaiden Lee. Lee had brought in Ashley Novak, a finance MBA who had been working for a consulting company, to replace the old CFO, and Lee asked Ashley to develop the financial planning section of the strategic plan. In her previous job, Novak’s primary task had been to help clients develop financial forecasts, and that was one reason Lee hired her.
Novak began by comparing Hatfield’s financial ratios to the industry averages. If any ratio was substandard, she discussed it with the responsible manager to see what could be done to improve the situation. The following data show Hatfield’s latest financial statements plus some ratios and other data that Novak plans to use in her analysis.
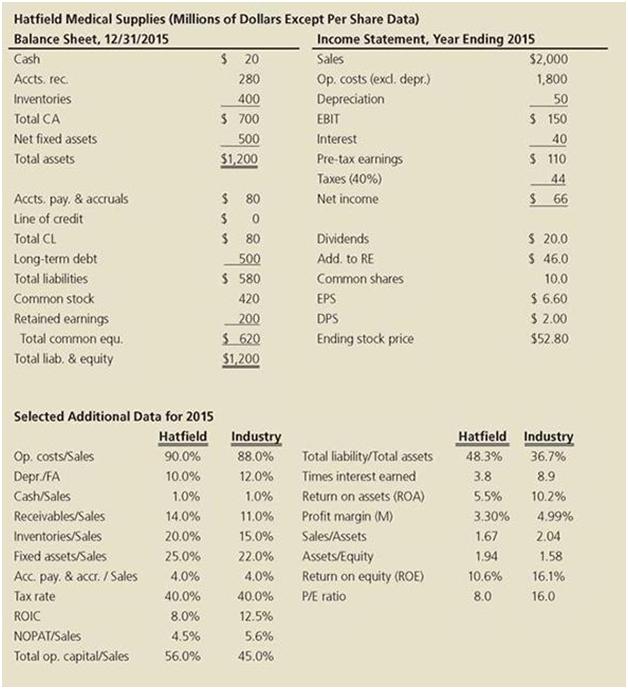
a. Using Hatfield’s data and its industry averages, how well run would you say Hatfield appears to be compared to other firms in its industry? What are its primary strengths and weaknesses? Be specific in your answer, and point to various ratios that support your position. Also, use the DuPont equation (see Chapter 7) as one part of your analysis.
b. Use the AFN equation to estimate Hatfield’s required new external capital for 2016 if the sales growth rate is 10%. Assume that the firm’s 2015 ratios will remain the same in 2016. (Hint: Hatfield was operating at full capacity in 2015.)
c. Define the term capital intensity. Explain how a decline in capital intensity would affect the AFN, other things held constant. Would economies of scale combined with rapid growth affect capital intensity, other things held constant? Also, explain how changes in each of the following would affect AFN, holding other things constant: the growth rate, the amount of accounts payable, the profit margin, and the payout ratio.
d. Define the term self-supporting growth rate. What is Hatfield’s self-supporting growth rate? Would the self-supporting growth rate be affected by a change in the capital intensity ratio or the other factors mentioned in the previous question? Other things held constant, would the calculated capital intensity ratio change over time if the company were growing and were also subject to economies of scale and/or lumpy assets?
e. Use the following assumptions to answer the questions below: (1) Operating ratios remain unchanged. (2) Sales will grow by 10%, 8%, 5%, and 5% for the next 4 years. (3) The target weighted average cost of capital (WACC) is 9%. This is the No Change scenario because operations remain unchanged.
(1) For each of the next 4 years, forecast the following items: sales, cash, accounts receivable, inventories, net fixed assets, accounts payable & accruals, operating costs (excluding depreciation), depreciation, and earnings before interest and taxes (EBIT).
(2) Using the previously forecasted items, calculate for each of the next 4 years the net operating profit after taxes (NOPAT), net operating working capital, total operating capital, free cash flow, (FCF), annual growth rate in FCF, and return on invested capital. What does the forecasted free cash flow in the first year imply about the need for external financing? Compare the forecasted ROIC with the WACC. What does this imply about how well the company is performing?
(3) Assume that FCF will continue to grow at the growth rate for the last year in the forecast horizon (Hint: gL = 5%). What is the horizon value at 2019? What is the present value of the horizon value? What is the present value of the forecasted FCF? (Hint: Use the free cash flows for 2016 through 2019.) What is the current value of operations? Using information from the 2015 financial statements, what is the current estimated intrinsic stock price?
f. Continue with the same assumptions for the No Change scenario from the previous question, but now forecast the balance sheet and income statements for 2016 (but not for the following 3 years) using the following preliminary financial policy. (1) Regular dividends will grow by 10%. (2) No additional long-term debt or common stock will be issued. (3) The interest rate on all debt is 8%. (4) Interest expense for longterm debt is based on the average balance during the year. (5) If the operating results and the preliminary financing plan cause a financing deficit, eliminate the deficit by drawing on a line of credit. The line of credit would be tapped on the last day of the year, so it would create no additional interest expenses for that year. (6) If there is a financing surplus, eliminate it by paying a special dividend. After forecasting the 2016 financial statements, answer the following questions.
(1) How much will Hatfield need to draw on the line of credit?
(2) What are some alternative ways than those in the preliminary financial policy that Hatfield might choose to eliminate the financing deficit?
g. Repeat the analysis performed the previous question, but now assume that Hatfield is able to improve the following inputs: (1) reduce operating costs (excluding depreciation)/sales to 89.5% at a cost of $40 million; and (2) reduce inventories/sales to 16% at a cost of $10 million. This is the Improve scenario.
(1) Should Hatfield implement the plans? How much value would they add to the company?
(2) How much can Hatfield pay as a special dividend in the Improve scenario? What else might Hatfield do with the financing surplus?
Hatfield Medical Supplies (Millions of Dollars Except Per Share Data) Balance Sheet, 12/31/2015 Cash Income Statement, Year Ending 2015 $ 20 Sales $2,000 Accts. rec. Op. costs (exd. depr.) Depreciation 280 1,800 Inventories 400 50 Total CA S 700 EBIT S 150 Net fixed assets 500 $1,200 Interest 40 Total assets Pre-tax earnings $ 110 Taxes (40%) 44 $ 80 $ 66 Accts. pay. & accruals Line of credit Net incorne S 20.0 $ 46.0 Total CL $ 80 Dividends Long-term debt 500 Add. to RE Total liabilities $ 580 Common shares 10.0 $ 6.60 $ 2.00 Common stock 420 EPS 200 $ 620 $1,200 Retained earnings DPS Total common equ. Ending stock price $52.80 Total liab, & equity Selected Additional Data for 2015 Hatfield Industry Hatfield Industry Op. costs/Sales Depr./FA 90.0% 88.0% Total liability/Total assets 48.3% 36.7% 10.0% 12.0% Times interest earned 3.8 8.9 Cash/Sales 1.0% 1.0% Return on assets (ROA) 5.5% 10.2% Receivables/Sales 14.0% 11.0% Profit margin (M) 3.30% 4.99% Inventories/Sales 20.0% 15.0% Sales/Assets 1.67 2.04 Fixed assets/Sales 25.0% 22.0% Assets/Equity 1.94 1.58 Acc. pay, & accr. / Sales 4.0% 4.0% Return on equity (ROE) 10.6% 16.1% Tax rate 40.0% 40.0% PE ratio 8.0 16.0 ROIC 8.0% 12.5% NOPATISales 4.5% 5.6% Total op. capital/Sales 56.0% 45.0%
Step by Step Solution
3.31 Rating (163 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1
Use spreadsheet for the ease in ...
Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


