Question
Hello, I need some help with writing a bit of code if possible. I am to write and complete code for part G of this
Hello, I need some help with writing a bit of code if possible. I am to write and complete code for part G of this assignment involving code for Python and a word ladder BFS format.
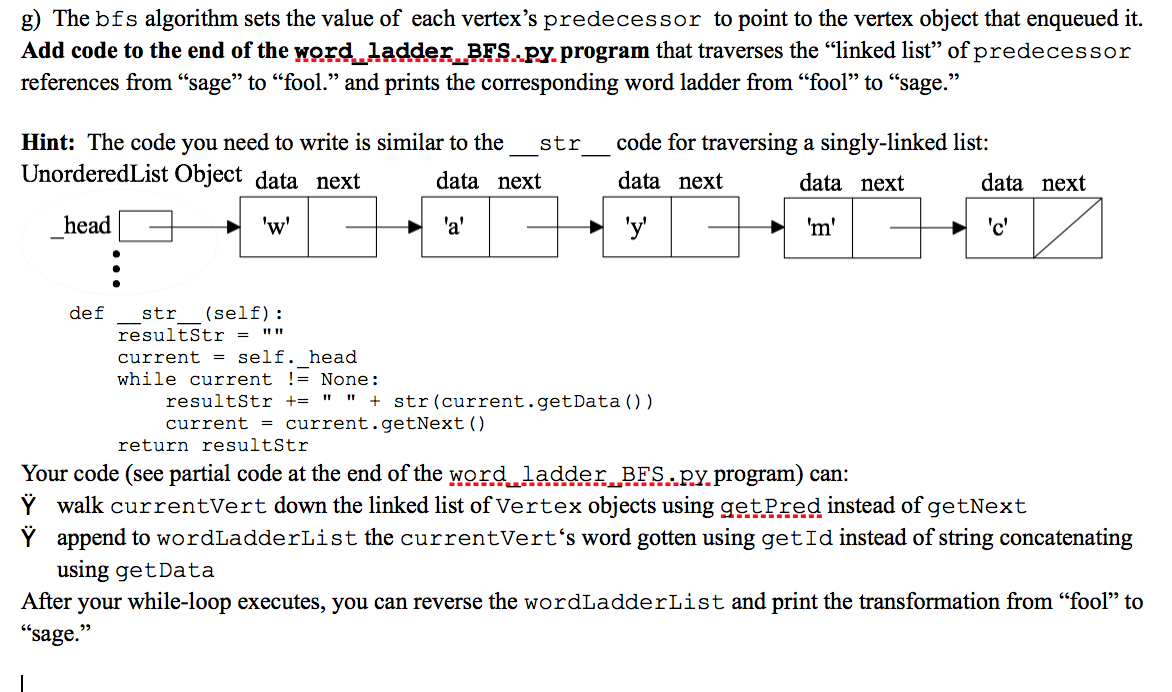
The bfs algorithm sets the value of each vertexs predecessor to point to the vertex object that enqueued it. Add code to the end of the word_ladder_BFS.py program that traverses the linked list of predecessor references from sage to fool. and prints the corresponding word ladder from fool to sage.
Your code (see partial code at the end of the word_ladder_BFS.py program) can:
- walk currentVert down the linked list of Vertex objects using getPred instead of getNext
- append to wordLadderList the currentVerts word gotten using getId instead of string concatenating using getData
After your while-loop executes, you can reverse the wordLadderList and print the transformation from fool to sage.
Included are images and code to help.
Programs to get things running
""" File: graph.py """ from vertex import Vertex
class Graph: def __init__(self): self.vertList = {} self.numVertices = 0 def addVertex(self,key): self.numVertices = self.numVertices + 1 newVertex = Vertex(key) self.vertList[key] = newVertex return newVertex def getVertex(self,n): if n in self.vertList: return self.vertList[n] else: return None
def __contains__(self,n): return n in self.vertList def addEdge(self,f,t,cost=0): if f not in self.vertList: nv = self.addVertex(f) if t not in self.vertList: nv = self.addVertex(t) self.vertList[f].addNeighbor(self.vertList[t], cost) def getVertices(self): return self.vertList.keys() def __iter__(self): return iter(self.vertList.values())
### File: linked_queue.py from node import Node
class LinkedQueue: def __init__(self): self._front = None self._size = 0 self._rear = None
def isEmpty(self): return self._size == 0
def enqueue(self, item): temp = Node(item) if self._size == 0: self._front = temp else: self._rear.setNext(temp) self._rear = temp self._size += 1
def dequeue(self): temp = self._front self._front = temp.getNext() self._size -= 1 if self._size == 0: self._rear = None
return temp.getData()
def size(self): return self._size
def __str__(self): resultStr = "" temp = self._front while temp != None: resultStr = str(temp.getData()) + " " + resultStr temp = temp.getNext() resultStr = "(front) " + resultStr + "(rear)" return resultStr
""" File: vertex.py """ class Vertex: def __init__(self,key, color = 'white', dist = 0, pred = None): self.id = key self.connectedTo = {} self.color = color self.predecessor = pred self.distance = dist self.discovery = 0 self.finish = 0
def addNeighbor(self,nbr,weight=0): self.connectedTo[nbr] = weight
def __str__(self): return str(self.id) + ' connectedTo: ' + str([x.id for x in self.connectedTo])
def getConnections(self): return self.connectedTo.keys()
def getId(self): return self.id
def getWeight(self,nbr): return self.connectedTo[nbr]
def getColor(self): return self.color
def setColor(self, newColor): self.color = newColor
def getPred(self): return self.predecessor
def setPred(self, newPred): self.predecessor = newPred
def getDiscovery(self): return self.discovery
def setDiscovery(self, newDiscovery): self.discovery = newDiscovery
def getFinish(self): return self.finish
def setFinish(self, newFinish): self.finish = newFinish
def getDistance(self): return self.distance
def setDistance(self, newDistance): self.distance = newDistance
Build Graph File
from graph import Graph def buildGraph(wordFile): d = {} g = Graph() wfile = open(wordFile,'r') # create buckets of words that differ by one letter for line in wfile: word = line[:-1] for i in range(len(word)): bucket = word[:i] + '_' + word[i+1:] if bucket in d: d[bucket].append(word) else: d[bucket] = [word] # add vertices and edges for words in the same bucket for bucket in d.keys(): for word1 in d[bucket]: for word2 in d[bucket]: if word1 != word2: g.addEdge(word1,word2) return g
Graph_algorithms file
from graph import Graph from vertex import Vertex from linked_queue import LinkedQueue
def bfs(g,start): start.setDistance(0) start.setPred(None) vertQueue = LinkedQueue() print("enqueue:", start.getId()) vertQueue.enqueue(start) while (vertQueue.size() > 0): currentVert = vertQueue.dequeue() print(" dequeue:", currentVert.getId()) for nbr in currentVert.getConnections(): if (nbr.getColor() == 'white'): nbr.setColor('gray') nbr.setDistance(currentVert.getDistance() + 1) nbr.setPred(currentVert) vertQueue.enqueue(nbr) print("enqueue:", nbr.getId()) currentVert.setColor('black')
def dijkstra(aGraph,start): pq = PriorityQueue() start.setDistance(0) pq.buildHeap([(v.getDistance(),v) for v in aGraph]) while not pq.isEmpty(): currentVert = pq.delMin() for nextVert in currentVert.getConnections(): newDist = currentVert.getDistance() \ + currentVert.getWeight(nextVert) if newDist
Actual file to add code to
# File 'word_ladder_bfs'
from build_graph import buildGraph
from graph_algorithms import bfs
g = buildGraph("words.dat")
print("word ladder graph:") for v in g: print(v)
print(" ============ bfs prints ======================= ")
bfs(g, g.getVertex("fool"))
print(" ================================================ ")
wordLadderList = [] currentVert = g.getVertex("sage") # ADD CODE HERE for part B (g) of the Lab
g) The bfs algorithm sets the value of each vertex's predecessor to point to the vertex object that enqueued it. Add code to the end of the word_ladder_BES.py.program that traverses the linked list of predecessor references from "sage to fool. and prints the corresponding word ladder from fool to sage. str Hint: The code you need to write is similar to the Unordered List Object data next data next code for traversing a singly-linked list: data next data next data next head 'w 'a' 'y' 'm' 'c' : def str (self): resultStr = current = self. head while current != None: resultStr += " " + str(current.getData() ) current = current.getNext() return resultStr Your code (see partial code at the end of the word ladder_BFS.p.y. program) can: walk currentVert down the linked list of Vertex objects using getPred instead of getNext Y append to wordLadderList the currentVert's word gotten using getId instead of string concatenating using getData After your while-loop executes, you can reverse the wordLadderList and print the transformation from fool to sage." g) The bfs algorithm sets the value of each vertex's predecessor to point to the vertex object that enqueued it. Add code to the end of the word_ladder_BES.py.program that traverses the linked list of predecessor references from "sage to fool. and prints the corresponding word ladder from fool to sage. str Hint: The code you need to write is similar to the Unordered List Object data next data next code for traversing a singly-linked list: data next data next data next head 'w 'a' 'y' 'm' 'c' : def str (self): resultStr = current = self. head while current != None: resultStr += " " + str(current.getData() ) current = current.getNext() return resultStr Your code (see partial code at the end of the word ladder_BFS.p.y. program) can: walk currentVert down the linked list of Vertex objects using getPred instead of getNext Y append to wordLadderList the currentVert's word gotten using getId instead of string concatenating using getData After your while-loop executes, you can reverse the wordLadderList and print the transformation from fool to sageStep by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


