Question
Hello tutor, using the instructions/data set below could you assist me in answering question 9-16. Use questions 1-8, as a reference point if needed. Thank
Hello tutor, using the instructions/data set below could you assist me in answering question 9-16. Use questions 1-8, as a reference point if needed. Thank you
Instructions
An experiment was conducted on randomly selected Fraser students: each student sees a photo of an object (visual) and then identifies the object, and each student hears a sound (auditory) and then identifies the sound.
The following are instructions to conduct two different hypothesis tests; the first (#s 1-8) is about the population mean difference (??) between visual and auditory response time, and the second (#s 9-16) is about the population proportion (?) of Student students who have jobs.
For Problems 1 - 8: A researcher claims that the response time for visual stimuli, in milliseconds, is greater than the response time for auditory stimuli, on average. Use the sample information to test if there is evidence, at ? = 0.1, that supports the researcher's claim.
1. Define the parameter
2. State the hypotheses for this test.
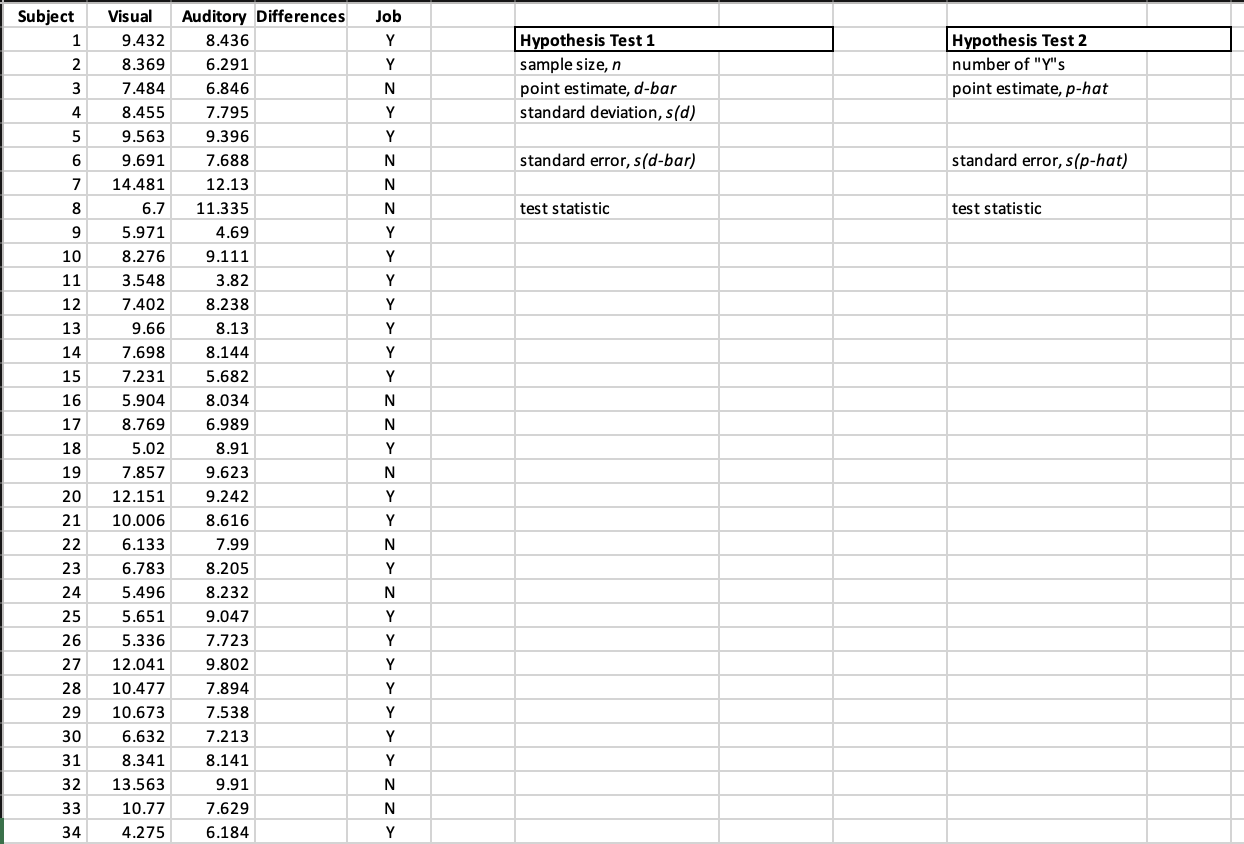
- In Column D, Revise a new data set for the differences in response times: Differences = Visual - Auditory In Cell D2 type: =B2-C2 to calculate the difference of Visual and Auditory response times for Subject 1. Use the fill handle to calculate the remaining differences for all n subjects.
3. Compute the test statistic using Excel. To compute the test statistic, you need the following descriptive statistics for Column D (Difference = Visual - Auditory): n (sample size), ??, (the point estimate for the mean difference of Visual and Auditory), ?(?) (the sample standard deviation of the differences), and ?? (estimated standard error for the mean difference of Visual and Auditory).
- State the name of the test statistic and type the work (using values rounded to 3 decimals and parentheses to show order of operations); then give the computed value to 2 decimals.(2 points)
4. Find the p-value from a table using the test statistic.
- Type the probability statement for the p-value and the probability, or range of probability, found using the table (z or t table). (1 point) Hint: for one-tailed tests, the sign in your probability statement should match the sign in ??; for two-tailed tests the probability statement includes the probability of less than the negative test statistic value OR greater than the positive test statistic value.
5. The Data Analysis ToolPak in Excel has a paired t-test.
- Go to the "Data" Tab and click "Data Analysis". Select "t-Test: Paired Two Sample for Means". In the Variable 1 Range field: select the Visual data - including the "Visual" label In the Variable 2 Range field: select the Auditory data - including the "Auditory" label Enter the hypothesized value for the mean (from #2); Check the Labels box; Enter alpha of 0.1; Select "Output Range" and enter M12 in the field Click OK. Double click on the vertical line between M & N to resize the table for easier reading
- Copy and paste the output from M2:O15
6. Type the p-value exactly as provided in the output for "t-Test: Paired Two Sample for Means"; there are two p-values (probabilities) provided: one-tailed and two-tailed, select the one that is for your hypothesis from #2.
- Hint: the value should agree with the p-value you found in #4.
7. Type the critical value(s) for the rejection region for this test
8. After comparing the p-value to ?, or the test statistic to the critical value, type the conclusion.
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
For Problems 9 - 16: The variable "Job" indicates whether a student has a job or not. "Y" means the student has a job where they are required to work more than 5 hours per week, and "N" means the student does not have this type of job. A researcher wants to see if the population proportion of students with jobs at Purdue is different from 0.59. Use ? = 0.05.
Question 9. Define the parameter using context
Question 10. State the hypotheses for this test, using the correct parameter, signs, and hypothesized value
Question 11. Compute ??, the point estimate for the population proportion
- To estimate the proportion of students with jobs, divide the number of observed "Y"s by the sample size.
- Type the name and value of the point estimate, rounded to 4 decimals.
Question 12. . Is the Normality condition in place for your data?
- Type the correct values to confirm that this condition is valid: ? ?0 ? 5 and ? (1 ? ?0) ? 5
Question 13. Compute the test statistic.
- Round ??and standard error to 3 decimals
- State the name of the test statistic, type the work and state the computed value, rounded to 2 decimals.
Question 14. Find the p-value using a table: Type the probability statement for the p-value for the computed test statistic and the approximate probability found using the appropriate table. Refer to #4.
Question 15. Type the critical value(s) for the rejection region for this test.
Question 16. After comparing the p-value to ?, or the test statistic to the critical value, type the conclusion.
Data set:
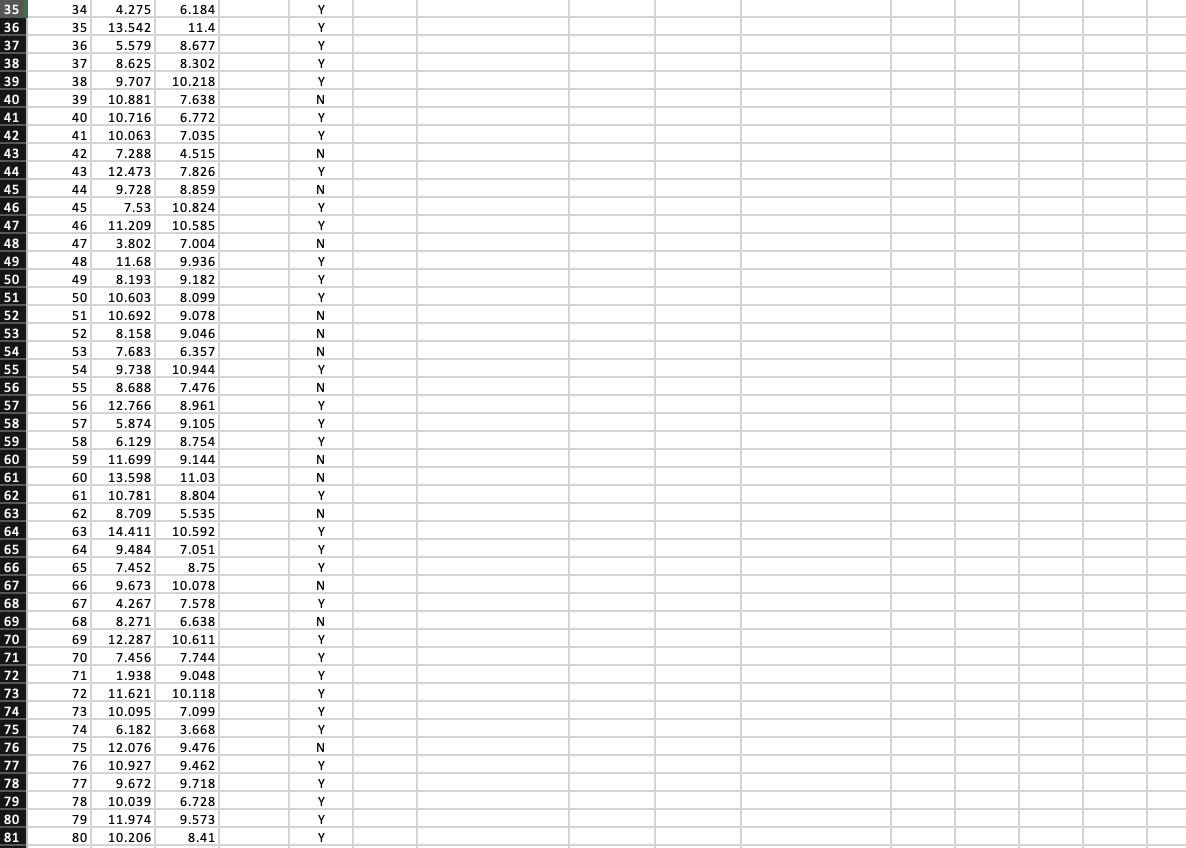
| Subject | Visual | Auditory | Differences | Job | ||||||
| 1 | 9.432 | 8.436 | Y | Hypothesis Test 1 | Hypothesis Test 2 | |||||
| 2 | 8.369 | 6.291 | Y | sample size, n | number of "Y"s | |||||
| 3 | 7.484 | 6.846 | N | point estimate, d-bar | point estimate, p-hat | |||||
| 4 | 8.455 | 7.795 | Y | standard deviation, s(d) | ||||||
| 5 | 9.563 | 9.396 | Y | |||||||
| 6 | 9.691 | 7.688 | N | standard error, s(d-bar) | standard error,s(p-hat) | |||||
| 7 | 14.481 | 12.13 | N | |||||||
| 8 | 6.7 | 11.335 | N | test statistic | test statistic | |||||
| 9 | 5.971 | 4.69 | Y | |||||||
| 10 | 8.276 | 9.111 | Y | |||||||
| 11 | 3.548 | 3.82 | Y | |||||||
| 12 | 7.402 | 8.238 | Y | |||||||
| 13 | 9.66 | 8.13 | Y | |||||||
| 14 | 7.698 | 8.144 | Y | |||||||
| 15 | 7.231 | 5.682 | Y | |||||||
| 16 | 5.904 | 8.034 | N | |||||||
| 17 | 8.769 | 6.989 | N | |||||||
| 18 | 5.02 | 8.91 | Y | |||||||
| 19 | 7.857 | 9.623 | N | |||||||
| 20 | 12.151 | 9.242 | Y | |||||||
| 21 | 10.006 | 8.616 | Y | |||||||
| 22 | 6.133 | 7.99 | N | |||||||
| 23 | 6.783 | 8.205 | Y | |||||||
| 24 | 5.496 | 8.232 | N | |||||||
| 25 | 5.651 | 9.047 | Y | |||||||
| 26 | 5.336 | 7.723 | Y | |||||||
| 27 | 12.041 | 9.802 | Y | |||||||
| 28 | 10.477 | 7.894 | Y | |||||||
| 29 | 10.673 | 7.538 | Y | |||||||
| 30 | 6.632 | 7.213 | Y | |||||||
| 31 | 8.341 | 8.141 | Y | |||||||
| 32 | 13.563 | 9.91 | N | |||||||
| 33 | 10.77 | 7.629 | N | |||||||
| 34 | 4.275 | 6.184 | Y | |||||||
| 35 | 13.542 | 11.4 | Y | |||||||
| 36 | 5.579 | 8.677 | Y | |||||||
| 37 | 8.625 | 8.302 | Y | |||||||
| 38 | 9.707 | 10.218 | Y | |||||||
| 39 | 10.881 | 7.638 | N | |||||||
| 40 | 10.716 | 6.772 | Y | |||||||
| 41 | 10.063 | 7.035 | Y | |||||||
| 42 | 7.288 | 4.515 | N | |||||||
| 43 | 12.473 | 7.826 | Y | |||||||
| 44 | 9.728 | 8.859 | N | |||||||
| 45 | 7.53 | 10.824 | Y | |||||||
| 46 | 11.209 | 10.585 | Y | |||||||
| 47 | 3.802 | 7.004 | N | |||||||
| 48 | 11.68 | 9.936 | Y | |||||||
| 49 | 8.193 | 9.182 | Y | |||||||
| 50 | 10.603 | 8.099 | Y | |||||||
| 51 | 10.692 | 9.078 | N | |||||||
| 52 | 8.158 | 9.046 | N | |||||||
| 53 | 7.683 | 6.357 | N | |||||||
| 54 | 9.738 | 10.944 | Y | |||||||
| 55 | 8.688 | 7.476 | N | |||||||
| 56 | 12.766 | 8.961 | Y | |||||||
| 57 | 5.874 | 9.105 | Y | |||||||
| 58 | 6.129 | 8.754 | Y | |||||||
| 59 | 11.699 | 9.144 | N | |||||||
| 60 | 13.598 | 11.03 | N | |||||||
| 61 | 10.781 | 8.804 | Y | |||||||
| 62 | 8.709 | 5.535 | N | |||||||
| 63 | 14.411 | 10.592 | Y | |||||||
| 64 | 9.484 | 7.051 | Y | |||||||
| 65 | 7.452 | 8.75 | Y | |||||||
| 66 | 9.673 | 10.078 | N | |||||||
| 67 | 4.267 | 7.578 | Y | |||||||
| 68 | 8.271 | 6.638 | N | |||||||
| 69 | 12.287 | 10.611 | Y | |||||||
| 70 | 7.456 | 7.744 | Y | |||||||
| 71 | 1.938 | 9.048 | Y | |||||||
| 72 | 11.621 | 10.118 | Y | |||||||
| 73 | 10.095 | 7.099 | Y | |||||||
| 74 | 6.182 | 3.668 | Y | |||||||
| 75 | 12.076 | 9.476 | N | |||||||
| 76 | 10.927 | 9.462 | Y | |||||||
| 77 | 9.672 | 9.718 | Y | |||||||
| 78 | 10.039 | 6.728 | Y | |||||||
| 79 | 11.974 | 9.573 | Y | |||||||
| 80 | 10.206 | 8.41 | Y |
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


