


Help here tutors
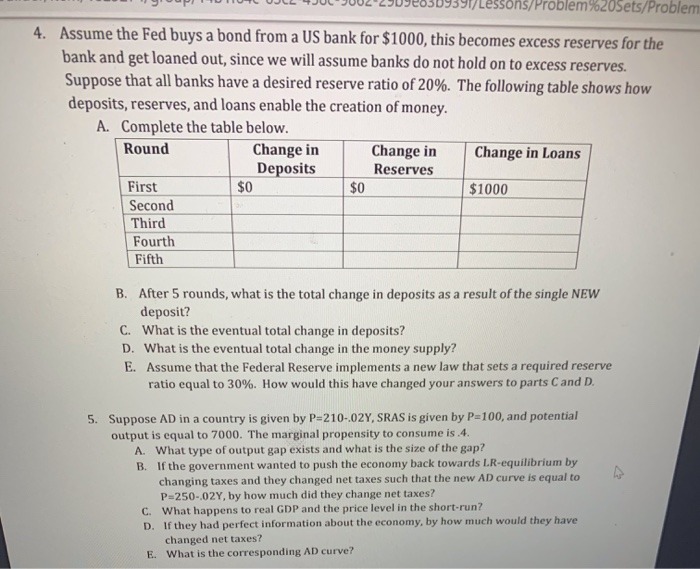
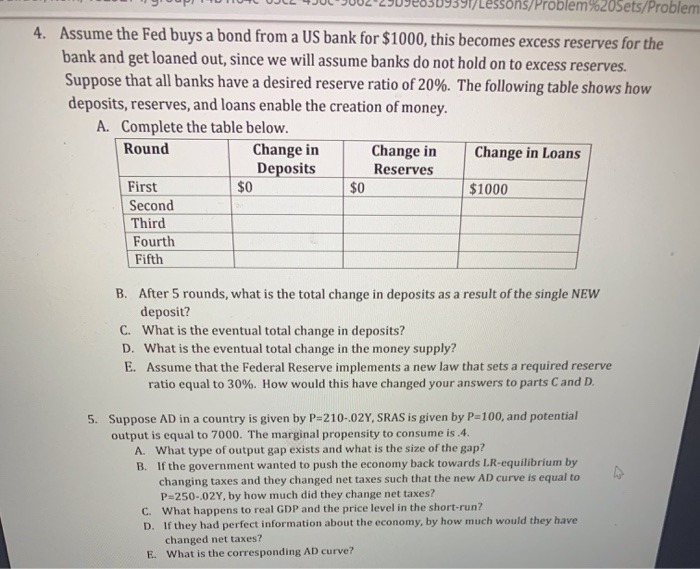
7531/Lessons/Problem 9%20sets/Problem 4. Assume the Fed buys a bond from a US bank for $1000, this becomes excess reserves for the bank and get loaned out, since we will assume banks do not hold on to excess reserves. Suppose that all banks have a desired reserve ratio of 20%. The following table shows how deposits, reserves, and loans enable the creation of money. A. Complete the table below. Round Change in Change in Change in Loans Deposits Reserves First $0 $1000 Second Third Fourth Fifth B. After 5 rounds, what is the total change in deposits as a result of the single NEW deposit? C. What is the eventual total change in deposits? D. What is the eventual total change in the money supply? E. Assume that the Federal Reserve implements a new law that sets a required reserve ratio equal to 30%. How would this have changed your answers to parts Cand D. 5. Suppose AD in a country is given by P=210-.02Y, SRAS is given by P=100, and potential output is equal to 7000. The marginal propensity to consume is .4. A. What type of output gap exists and what is the size of the gap? B. If the government wanted to push the economy back towards LR-equilibrium by changing taxes and they changed net taxes such that the new AD curve is equal to P=250-,02Y, by how much did they change net taxes? C. What happens to real GDP and the price level in the short-run? D. If they had perfect information about the economy, by how much would they have changed net taxes? E. What is the corresponding AD curve?2) Consumer research for Kraft foods has discovered the following relationships between sales of TANG (Yes, the orange drink used by astronauts!) and advertising expenditures for two districts. Sales (S) and advertising (A) are in millions. S, = 10+5A, -1.5A $2 = 12+4A, -.5A; Solve Kraft's maximization problem; maximize total sales across the two districts subject to a total advertising budget of $5M. How would a $1M increase in Kraft's advertising budget influence sales? 3) Stafford rug company produces wool rugs and cotton rugs. Total cost (in dollars) is given by C=7X, +9X; -1.5X,X2 Where X1 represents the number of wool rugs per day and X2 represents the number of cotton rugs per day. Stafford has commitments to deliver 10 rugs per day, but can deliver any combination of wool or cotton. Calculate the cost minimizing combination of rugs. What would the impact be on Stafford's costs if their orders increased by 50%? 4) Consider a consumer choosing between three goods. P = (P1, P2, P3), X = (X1, X2, X3) (i.e. three prices, three products) Each of the following groups represents choices of X1, X2, and X3 for various prices of X1, X2, and X3. Determine which group is inconsistent with rational choice. For example, in Group #1, when the prices of the three goods were $1, $2, and $3 respectively, this consumer chose 3 units of the first good, 2 units of the second good and 1 unit of the third good. Group #1: P = (1, 2, 3), X = (3, 2, 1) P = (2, 1, 2), X = (2, 2, 1) P = (3, 5, 1), X = (1, 2, 1) Group #2: P = (3, 4, 1), X = (5, 1, 3) P = (2, 3, 2), X = (3, 3, 3) P = (5, 3, 1), X = (4, 2, 2) Group #3: P = (4, 3, 2), X = (2, 2, 2) P = (5, 3, 3), X = (1, 3, 3) P = (5, 2, 3), X = (1, 3, 2) 5) Suppose that the price of good X is $4 and the price of good Y is $6. You have $100 to spend and your preferences over X and Y are defined as U(x, y) = x3 V3 Solve for your optimal choice of X and Y.1) Suppose that you are a firm that produces xylophones. You have a production technology to produce xylophones that can be written as: y = k212 Where k represents the units of capital employed at your production facility, I is the number of labor hours employed and y is your total production of xylophones. Assume that labor costs $10 per hour and that capital costs $250 per unit. a) Suppose that you are currently employing 100 units of capital. If you have expected sales equal to 1,000, calculate your optimal choice of labor. b) Given your answer to part (a), calculate your marginal cost of production. c) Given your answer to (a), calculate your average cost of production. d) Now, assume that you can adjust your capital as well as labor. Calculate your optimal capital/labor choice. e) Calculate your long run average cost and marginal cost. f) Show that in the long run, your expenditures will be 50% capital costs and 50% labor costs. 2) Suppose that you have two industries, each of witch has its own production function Industry A: YA = KAI- Industry B: VB = KB IB a) Describe what each industries marginal costs should look like in the short run (i.e. when capital is fixed) - specifically, which industry's marginal costs are increasing at a faster rate? b) If both of these industries are perfectly competitive, which industry should have a lower elasticity of supply (price elasticity) c) What should these two industry's cost functions look like in the long run (i.e. when capital adjustments can be made)? d) Which of the two industries would you expect to be monopolized by one or a few firms? Why? 3) Suppose that you are operating a firm with constant marginal costs of production equal to $5 and no fixed costs. You are facing a demand with a constant price elasticity of -3. a) Calculate your optimal (i.e profit maximizing) price. b) What would your firm's Lerner index be? c) Due to easy entry to the market, you would expect your industry to become more competitive over time. What should happen to your profit maximizing price in the long run? 4) Suppose that you have an industry with 5 firms. Below are the market shares of each firm: Firm Market Share 1 35 2 25 3 15 4 15 10 a) Calculate the concentration ratios for this industry. b) Calculate the Herfindahl-Hirschman index for this industry.1) Suppose that the demand curve for video rentals has been estimated to be Q = 2500 - 250P Further, your average costs of supplying videos is equal to AC =8-.0060 +.00000202 Calculate your optimal price, quantity and profits. 2) Suppose that you are a monopoly faced with a demand curve given by 0 =100 -2P You have a constant marginal cost equal to $10. Calculate your optimal price and quantity. Show that your price adheres to the optimal markup rule based on demand elasticity. 3) Suppose that the demand for loans depends on the annual interest rate charged ( r,), the annual fees charged (F), and the unemployment rate. Each loan is a $100,000, 30 year fixed APR mortgage. Assume that the unemployment rate is 5% (.05). Q =125 -624r, -.026F -90.4UR The bank has a monthly fixed cost of $10,000 plus an annual variable cost (interest paid on deposits plus various administrative expenses equal to 5% of the loans created) a) Suppose that the bank charges nothing in fees. Solve for the profit maximizing interest rate. What are the banks monthly profits? b) Calculate the interest elasticity of loan demand at the profit maximizing point. c) Now, suppose that the bank decides to charge $1200 per year in Fees. Calculate the bank's profit maximizing interest rate and monthly profits. d) How would (c) change if the Fee were a one time (i.e. closing costs)? 4) Suppose the demand for Bananas is given by 0 =50-5P The marginal cost of producing bananas is equal to $2. a) Calculate the price and quantity that would occur if this was a perfectly competitive market. b) Calculate the price and quantity a monopoly would produce c) Calculate the difference in consumer surplus between a perfectly competitive outcome and a monopolistic outcome 5) What characteristics are important when determining whether a market will be competitive or monopolistic