Help me please, Kindly answer this with complete solution and clear explanation. Thank you.
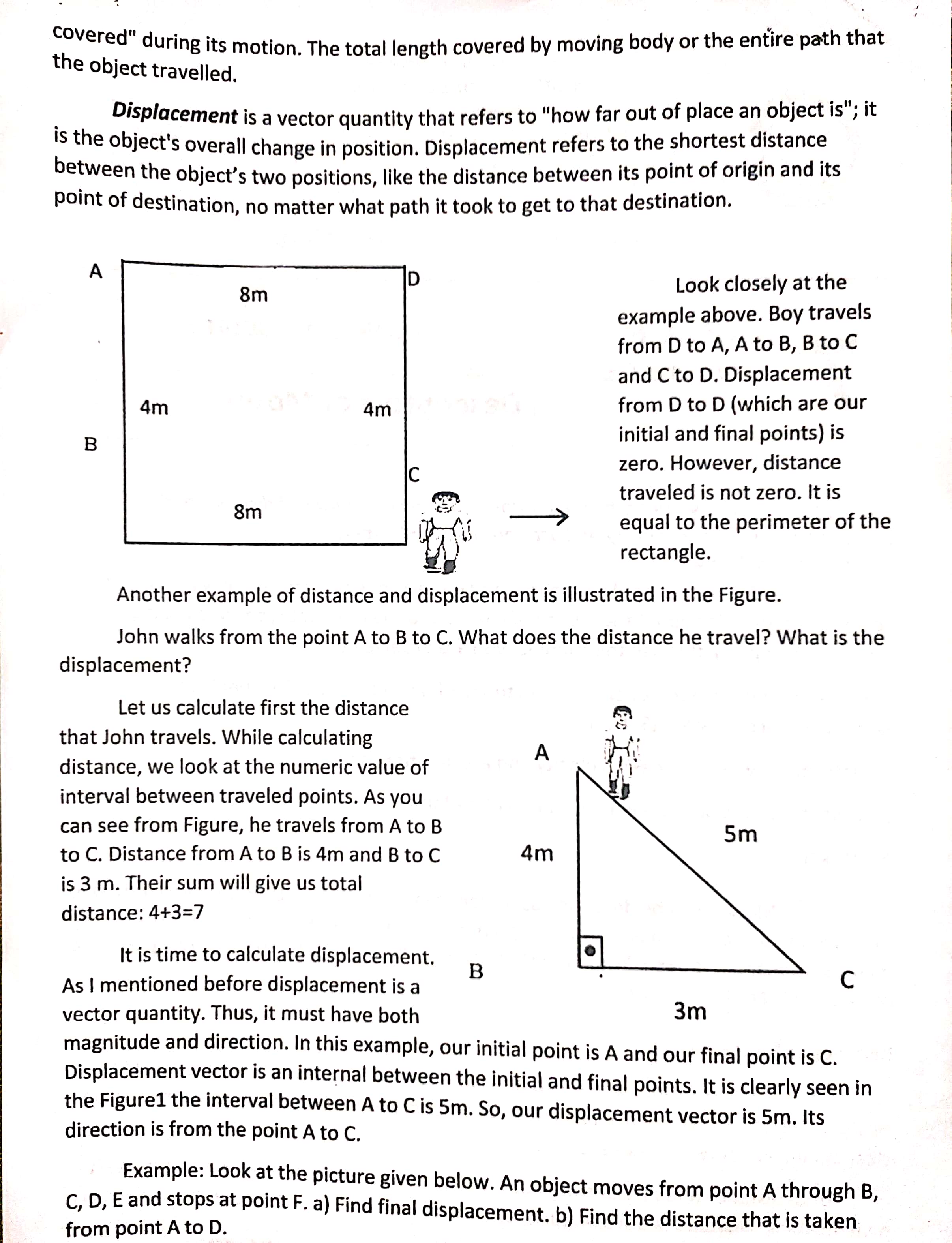
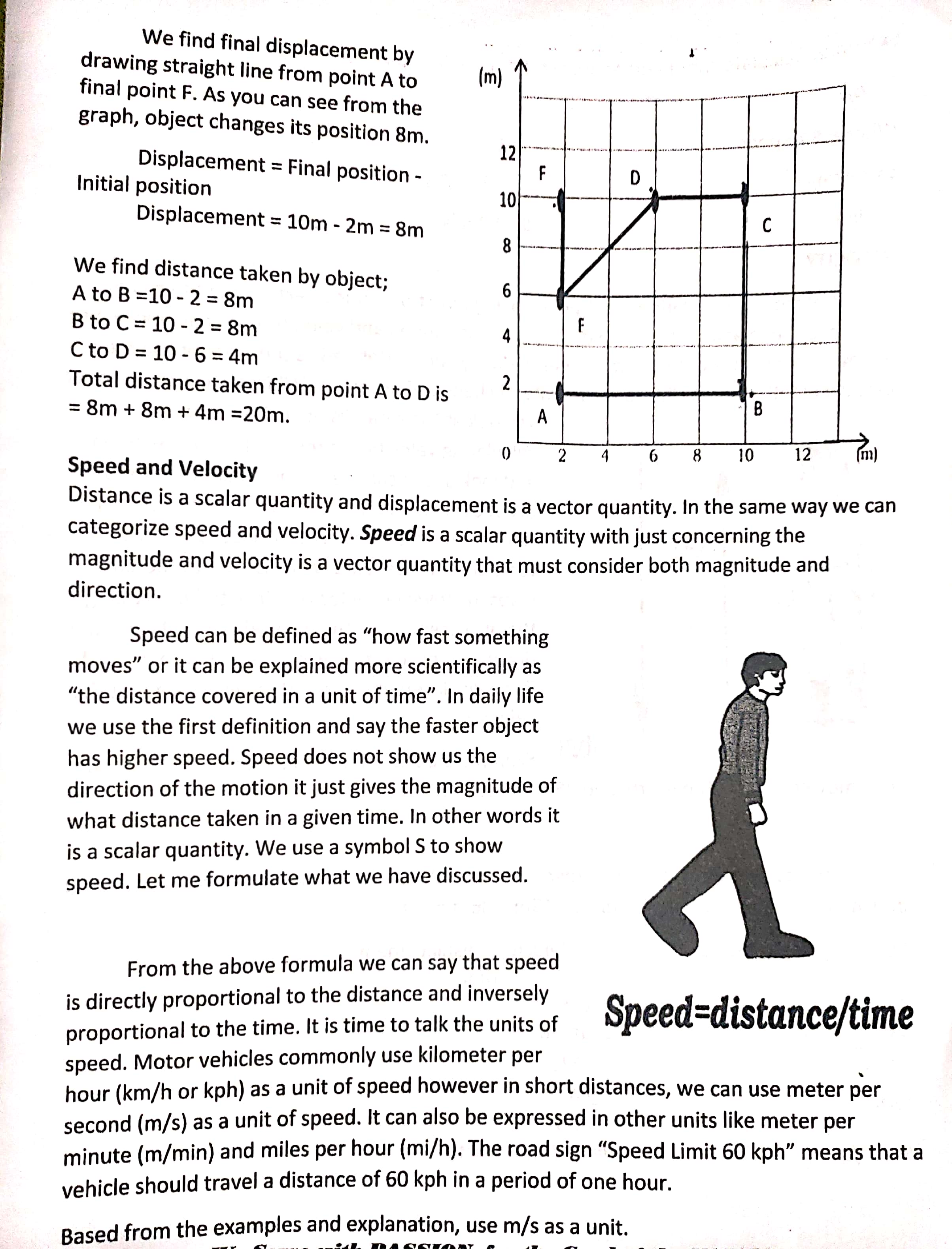
. Motion can be described as a change in position. However, to say that there is a change in posrtlon we must consrder a point of reference. A reference point is something that is stationary. It is fixed. You can determine whether a ' - n ObJECt moves b com ' ' posrtion to that of a fixed point. V Daring Its Distance vs Displacement There are expressions and terms in science that seem to have the same meaning. However, as you know, science aims to be exact and precise. Thus, it is necessary to have a clear distinction between these terms. Both distance and displacement are terms used in the study of motion. Each has its own meaning. Distance is a scalar quantity that refers to "how much ground an object has covered" during its motion. The total length covered by moving body or the entire path that the object travelled. Displacement is a vector quantity that refers to "how far out of place an object is"; it is the object's overall change in position. Displacement refers to the shortest distance between the object's two positions, like the distance between its point of origin and its point of destination, no matter what path it took to get to that destination. A 8m Look closely at the example above. Boy travels from D to A, A to B, B to C and C to D. Displacement 4m 4m from D to D (which are our B initial and final points) is C zero. However, distance traveled is not zero. It is 8m equal to the perimeter of the rectangle. Another example of distance and displacement is illustrated in the Figure. John walks from the point A to B to C. What does the distance he travel? What is the displacement? Let us calculate first the distance that John travels. While calculating A distance, we look at the numeric value of interval between traveled points. As you can see from Figure, he travels from A to B 5m to C. Distance from A to B is 4m and B to C 4m is 3 m. Their sum will give us total distance: 4+3=7 It is time to calculate displacement. As I mentioned before displacement is a B C vector quantity. Thus, it must have both 3m magnitude and direction. In this example, our initial point is A and our final point is C. Displacement vector is an internal between the initial and final points. It is clearly seen in the Figure1 the interval between A to C is 5m. So, our displacement vector is 5m. Its direction is from the point A to C. Example: Look at the picture given below. An object moves from point A through B, C, D, E and stops at point F. a) Find final displacement. b) Find the distance that is taken from point A to D.We find final displacement by drawing straight line from point A to (m) final point F. As you can see from the graph, object changes its position 8m. 12 Displacement = Final position - F Initial position 10 Displacement = 10m - 2m = 8m C We find distance taken by object; A to B =10 - 2 = 8m B to C = 10 - 2 = 8m C to D = 10 - 6 = 4m Total distance taken from point A to D is 2 = 8m + 8m + 4m =20m. B A 8 10 12 (m) Speed and Velocity Distance is a scalar quantity and displacement is a vector quantity. In the same way we can categorize speed and velocity. Speed is a scalar quantity with just concerning the magnitude and velocity is a vector quantity that must consider both magnitude and direction. Speed can be defined as "how fast something moves" or it can be explained more scientifically as "the distance covered in a unit of time". In daily life we use the first definition and say the faster object has higher speed. Speed does not show us the direction of the motion it just gives the magnitude of what distance taken in a given time. In other words it is a scalar quantity. We use a symbol S to show speed. Let me formulate what we have discussed. From the above formula we can say that speed is directly proportional to the distance and inversely proportional to the time. It is time to talk the units of Speed=distance/time speed. Motor vehicles commonly use kilometer per hour (km/h or kph) as a unit of speed however in short distances, we can use meter per second (m/s) as a unit of speed. It can also be expressed in other units like meter per minute (m/min) and miles per hour (mi/h). The road sign "Speed Limit 60 kph" means that a vehicle should travel a distance of 60 kph in a period of one hour. Based from the examples and explanation, use m/s as a unit.Example: Calculate the speed of the car that travels 450m in 9 seconds. S = d/t Where: S = speed S = d/t d= distance S = 450m/9s t= time S = 50m/s VELOCITY Velocity can be defined as "speed having direction". It is a vector quantity having both magnitude and direction. In daily life, we use speed and velocity interchangeably, but in physics they have different meanings. Velocity can be defined as the "rate of change of displacement" whereas "the speed is rate of change of distance". While we calculate speed, we look at the total distance, however, in calculating velocity, we must consider the direction and look at the change in position not the whole distance traveled. If a man walks 5m to east and 5m 45m to west speed of that man calculated by dividing total distance traveled which is 10m to the time elapsed, however, velocity calculated by dividing the displacement to the elapsed time, which is Om divided elapsed time gives us zero. In other words, if the displacement is zero then, we talk about the velocity. 36m Example:1 Calculate the speed and velocity of the man moving 45m to the north, and 36m to the south in 27 seconds. First, calculate the distance traveled and displacement of the man to calculate speed and velocity. Total distance covered = 45m + 36m = 81m Speed = total distance Velocity = displacement time of travel time S=d/t V=d/t =45m +36m = (45-36) m 27s 27s =81m =9m 27 s 27 s S=3m/s V=0.33m/s, Northmust be change in the velocity of the object. This change can be in the magnitude (speed) of the velocity or the direction of the velocity. In daily life, we use the term acceleration for the speeding up objects and decelerating for the slowing down objects. In physics, we use acceleration concept which is different from its daily life usage. If there is a change in the velocity, whether it is slowing down or speeding up, or changing its direction, we say that object is accelerating. Acceleration= Change in A motorcycle drives 100m/s - 50m/s Velocity at 50 m/s to 100 = 5 s Time m/s within 5 50m/s Interval seconds. Compute = the acceleration of 5 s the motorcycle. =10m/s2 Example: A boy having 3m/s2 acceleration starts to run. Calculate the boy's final velocity after 15 seconds ? Accelerate = Change in Velocity Time Interval Change in Velocity = Acceleration X Time a =3 m/s' t = 15 s Vf- Vi = 3 m/s X 15 s Vf-0 = 45 m/s2 Vf = 45 m/s2is sT he e'xam Example 2- A ca ple above shows that the speed and velocity are not the same thing. ' r travels 100 m In 4 seconds. What is the velocutv of the car? at Uniform velocity a distance of AVerage Speed and Instantaneous Speed A moving object does not have the same speed during its travel. Sometimes it Speeds up and sometimes slows down. At a given instant time, what we read from the SPeedometer is instantaneous speed. For example, a car moving with a constant speed travels to another city, it must stop at red lights in the traffic, or it should slow down when unwanted situations occur in the road. At the end of the trip, if we want to learn average Speed of the ca r, we divide total distance to total time the trip takes. Average Speed = Total distance traveled Time Interval Assume that car travels 500 km in a 5 hour. When we calculate the average speed, it is 100km/h. Of course the car does not travel with a 100 km/h constant speed. it has many instantaneous speeds and 100 km/ h is the average of those instantaneous speeds. Average Velocity and Instantaneous Velocity You may follow the same steps used in the definition of average and instantaneous speed while defining average and instantaneous velocity. instantaneous velocity is the velocity at a given instant of time, however, as in the case of speed, average velocity is calculated with displacement over time interval. Average Velocity = Displacement Time Interval Average Velocity =Dlsglacement Time Interval Example: A man is traveling with his car 150m to the east and 70m to the west. Calculate the average speed and velocity Displacement=150m~70m=80m of the car if the travel takeslo seconds. Average VE'OCitV = 931 105 ACCELERATION The definition of acceleration is different from speed and velocity. Average Velocity = 8m/s east Acceleration is defined as the "change in velocity\". Based from the definition, there '- 2;\" 1. It refers to the length of the entire path that the object travelled. A. displacement C. speed B. distance D. velocity 2. Acceleration is the change in velocity per unit of A. distance C. speed B. speed D. time 3. It refers to the shortest distance between the object's two positions, like the distance between its point of origin and its point of destination, no matter what path it took to get to that destination. A. displacement C. speed B. distance D. velocity 4. Which is a unit for speed? A. m C. kph B. km D. s/m 5. If car travel with a total distance of 800 m is covered in 40 seconds. What is the average speed of the car? A. 5 m/s C. 15 m/s B. 10 m/s D. 20 m/s s. Which is NOT a scalar quantity? A. acceleration C. speed B. distance D. time 7. It is the distance travelled over the time to cover such distance. A. average speed C. instantaneous speed B. constant speed D. instantaneous velocity 8. Lydia de Vega is a world known Filipino track and field athlete. She can run the 300 m dash in about 33.0seconds. What is her average speed? A. 9.09 m/s C. 11.09 m/s B. 10.09 m/s D. 12.09 m/s 9. Which of the following is TRUE about speed and velocity? A. Speed is a vector and velocity is scalar. B. Velocity is the speed in a particular direction. C. An object can accelerate even if the velocity is constant. D. A change in speed causes an acceleration. A change in velocity causes deceleration.10. A bus starts to move and reaches the velocity 150m/s in 10 seconds. Calculate the acceleration of the bus. A. 12 m/s? C. 14 m/s2 B. 13 m/s2 D. 15 m/s2 B. DRAW ME! Directions: Draw a happy face ( @) if the statement describes velocity or acceleration and then draw a sad face ( ;: ), if the statement does not describe velocity or acceleration. (10 points) _1. A car moves 80km/h east in 25s. 2. The wind moves at 160 km/h north of east. 3. Rowena walks 5m along the highway from their school. 4. A bus travels 75m/s. 5. A car travels a distance of 50 km from Manila to Bulacan in 30 min. 6. A boat moves at the rate of 4.5km/h in still water. 7. The light travels approximately at 300 000 000m/s. 8. The motorcycle has a constant velocity of 60km/h in 30s. 9. An airplane flies a distance of 180 km in an easterly direction. 10. Joseph runs 1800m/s south of west. ii. Performance Standard Assessment SPEED TEST: Directions: For each situation, identify and calculate the distance travelled, the time that passed, and the speed. 1. Cardo threw a volleyball that travelled 10 m in 3 sec. Calculate the speed of the ball? 2. A dog runs 6 m in 4 s. What is its speed? 3. How long does it take for Angel to reach her friend's house 50 m away if she has an average speed of 1.5 m/s? 4. How long does it take for a cyclist to travel 100 m if it goes a speed of 6 m/s? 5. How long will your trip take (in hours) if you travel 350 km at an average speed of 80 km/hr? NO DISTANCE (d) TIME (t) SPEED (v) 7 2 3 A