Question: Help on 3 & 4 please 1. Show how you calculated (pKa=7.20) the volumes of 0.200MNaH2PO4,0.200M Na2HPO4 and water required to prepare the pH6.00 buffer.
Help on 3 & 4 please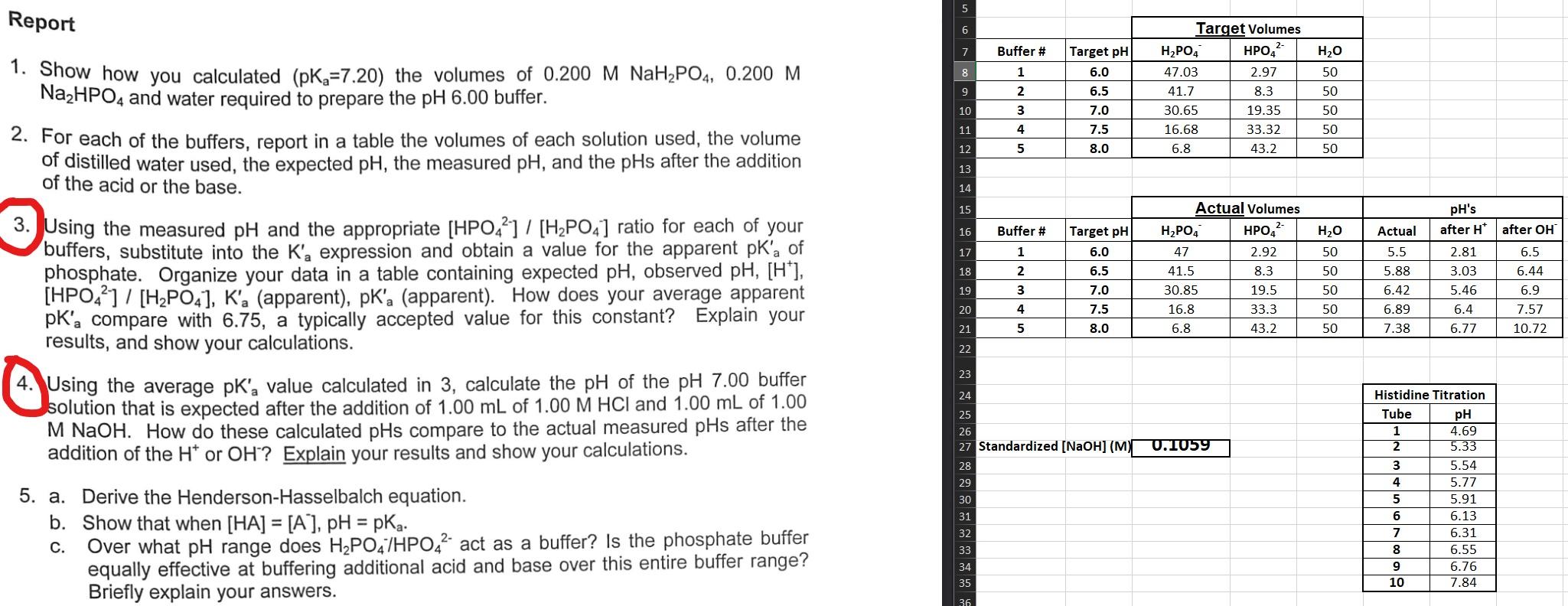
1. Show how you calculated (pKa=7.20) the volumes of 0.200MNaH2PO4,0.200M Na2HPO4 and water required to prepare the pH6.00 buffer. 2. For each of the buffers, report in a table the volumes of each solution used, the volume of distilled water used, the expected pH, the measured pH, and the pH after the addition of the acid or the base. 3. Using the measured pH and the appropriate [HPO42]/[H2PO4]ratio for each of your buffers, substitute into the Ka expression and obtain a value for the apparent pKa of phosphate. Organize your data in a table containing expected pH, observed pH,[H+], [HPO42]/[H2PO4],Ka (apparent), pKa (apparent). How does your average apparent pKa compare with 6.75, a typically accepted value for this constant? Explain your results, and show your calculations. 4. Using the average pKa value calculated in 3 , calculate the pH of the pH7.00 buffer solution that is expected after the addition of 1.00mL of 1.00MHCl and 1.00mL of 1.00 MNaOH. How do these calculated pHs compare to the actual measured pHs after the addition of the H+or OH? Explain your results and show your calculations. 5. a. Derive the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation. b. Show that when [HA]=[A],pH=pKa. c. Over what pH range does H2PO4/HPO42 act as a buffer? Is the phosphate buffer equally effective at buffering additional acid and base over this entire buffer range? Briefly explain your answers. 1. Show how you calculated (pKa=7.20) the volumes of 0.200MNaH2PO4,0.200M Na2HPO4 and water required to prepare the pH6.00 buffer. 2. For each of the buffers, report in a table the volumes of each solution used, the volume of distilled water used, the expected pH, the measured pH, and the pH after the addition of the acid or the base. 3. Using the measured pH and the appropriate [HPO42]/[H2PO4]ratio for each of your buffers, substitute into the Ka expression and obtain a value for the apparent pKa of phosphate. Organize your data in a table containing expected pH, observed pH,[H+], [HPO42]/[H2PO4],Ka (apparent), pKa (apparent). How does your average apparent pKa compare with 6.75, a typically accepted value for this constant? Explain your results, and show your calculations. 4. Using the average pKa value calculated in 3 , calculate the pH of the pH7.00 buffer solution that is expected after the addition of 1.00mL of 1.00MHCl and 1.00mL of 1.00 MNaOH. How do these calculated pHs compare to the actual measured pHs after the addition of the H+or OH? Explain your results and show your calculations. 5. a. Derive the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation. b. Show that when [HA]=[A],pH=pKa. c. Over what pH range does H2PO4/HPO42 act as a buffer? Is the phosphate buffer equally effective at buffering additional acid and base over this entire buffer range? Briefly explain your answers
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


