Question
Help on these quiz. Question: CASE STUDY Based on a case study of Lyft - Patrick Zhuwao - 10th May 2021 Introduction Lyft, with a
Help on these quiz.
Question:
CASE STUDY
Based on a case study of Lyft - Patrick Zhuwao - 10th May 2021
Introduction
Lyft, with a 30% market share, is the second-largest ride sharing company in the United States after Uber. Lyft develops, markets, and operates a mobile app offering vehicles for hire, motorized scooters, a bicycle-sharing system, and a food delivery service amongst other services.
The company is based in San Francisco, California and operates in 644 cities in the United States
and 12 cities in Canada. In March 2019, Lyft became the first ride-sharing company to hold an initial public offering raising $2.34 billion. The company set aside some shares to be given to long-time drivers. In April 2021, Lyft sold the self-driving technology it had been developing to Toyota for US$550 million
Lyft services and operations
Depending on the location, Lyft offers various service levels including shared rides with other passengers traveling in the same general direction (suspended during the Covid-19 Pandemic), private rides, or larger or luxury vehicles.
Lyft service is generally accessed via mobile app. Riders must download the Lyft mobile app to their smartphone, sign up, enter a valid phone number, and enter a valid form of payment (either a credit card, Lyft Gift card, or link to an Apple Pay, Google Wallet, or PayPal account).
Users set up a personal profile with a name, phone number, other information, and payment preference, which could be a credit card, e-commerce payment system or, in some cases, cash. Once the trip is completed, funds are debited from the funding source.
Drivers provide a vehicle, which could be owned, rented, or leased. Drivers must meet
requirements for age, health, car age and type, have a driver's licence and a smartphone or tablet, and may be required to pass a background check. In many cities, vehicles must pass annual safety inspections and/or must have an emblem posted in the passenger window. Some cities also require drivers to have a business license. After each transaction, drivers and customers may rate each other and users with low ratings may be deactivated.
Origins and early history of Lyft as Zimride
Lyft was launched in the summer of 2012 by computer programmers Logan Green and John Zimmer as a service of Zimride, a long-distance intercity carpooling company they founded in 2007. The name Zimride came from the country Zimbabwe, where, during a trip in 2005, Green observed locals sharing minivan taxis. Zimride launched at Cornell University, where, after six months, the service had signed up 20% of the campus. Zimride was focused on college campuses.
When Facebook opened its API to third-party developers in 2008, Green said he thought "Here's the missing ingredient." Zimride linked drivers and passengers through the Facebook Connect application. By using Facebook profile information, student drivers and passengers could learn about each other.
Recent history and developments at Lyft
In May 2013, the company officially changed its name from Zimride to Lyft. Lyft launched as a ridesharing company for shorter trips within cities. The change from Zimride to Lyft was the result of a hackathon that sought a means of daily engagement with its users, instead of once or twice a year. In July 2013, Lyft sold Zimride to Enterprise Holdings, the parent company of Enterprise Rent-A-Car, to enable the company to focus exclusively on the growth of Lyft.
Regulatory issues
In April 2014, Lyft hired two lobbying firms, TwinLogic Strategies, and Jochum Shore & Trossevin, to address the regulatory barriers and opposition it had received since its launch. Due to regulatory hurdles in New York City, the company altered its business model when establishing Lyft on the East Coast of the United States. Lyft's launch in New York City occurred on the evening of July 25, 2014, and, in accordance with the Taxi and Limousine Commission (TLC) and
the approval of the Manhattan Supreme Court, only drivers registered with the TLC were
permitted to drive Lyft-branded vehicles in New York City. Lyft and other ride sharing companies have, in some cases, been accused of unfair practices when dynamic pricing has resulted in extreme surcharges during emergencies such as Hurricane Sandy, the 2014 Sydney hostage crisis, and the 2017 London Bridge attack. Due to dynamic
pricing models, prices for the same route may vary based on the supply and demand for rides at the time the ride is requested. When rides are in high demand in a certain area and there are not enough drivers in such area, fares increase to get more drivers to that area. In the United States, drivers do not have any control over the fares they charge; lawsuits allege that this is an illegal restraint on trade in violation of the Sherman Antitrust Act of 1890.
Growth
In August 2014, the company introduced a shared ride concept, which provides cheaper fares. In December 2015, Lyft became the first ridesharing company allowed to pick up passengers at Los Angeles International Airport. In December 2017, Lyft expanded into Canada, with operations in the Greater Toronto Area, Hamilton, Ontario and Ottawa.
In March 2018, Lyft partnered with Allscripts to create a platform allowing healthcare providers to arrange rides for patients who lack transportation to appointments. The service would be available to 2,500 hospitals, 180,000 physicians, and approximately 7 million patients. In
November 2018, Lyft acquired Motivate, a bicycle-sharing system and the operator of Capital Bikeshare and Citi Bike. The company also announced plans to add 28,000 Citi Bikes and expand its service. In August 2020 Lyft began its partnership with rental car company Sixt in order to let users access rental cars through the "Rentals" tab in their app. Most of the rental cars are owned and operated by Sixt, a predominantly European company (German-owned) with 85 locations in the US. For each car rental made through the app, Lyft will receive a commission. The program began as Lyft Rentals in 2019 with Lyft owning and operating its own rental fleet in Los Angeles and San Francisco
Developing autonomous vehicles
In January 2016, Lyft announced an autonomous car partnership with General Motors. On May 5, 2016, Lyft and General Motors announced, as part of their partnership, that it planned to begin testing self-driving cars within the next year. On June 6, 2017, Lyft announced a new partnership with Boston-based autonomous self-driving car start-up NuTonomy to eventually put autonomous, on-demand vehicles on the road. In September 2017, Lyft partnered with Ford Motor Company to develop and test autonomous vehicles.
In March 2018, Lyft partnered with GoMentum Station to test its self-driving technology. On March 14, 2018, Lyft partnered with Magna International to co-fund, develop, and manufacture autonomous vehicle systems to produce self driving technology that will be available to all car manufacturers. In October 2018, Lyft acquired Blue Vision Labs, a London-based augmented
reality startup, for $72 million. This expertise is expected to help autonomous cars to extract useful information from street-level images.
In December 2020, Lyft announced that it will launch a multi-city U.S. robotaxi service in 2023 with Motional.
Lyft sells its self-driving technology to Toyota for US$550 million
In April 2021, Lyft sold its self-driving technology to Toyota for US$550 million in a deal that
allowed Lyft to offload a cash burning burden and risk of developing a costly technology that has
yet to enter the mainstream. Lyft will now focus on what it can do best with autonomous
vehicles by offering services such as routing, consumer interface and managing, and maintaining and cleaning partners' autonomous vehicle fleets, which could mean added revenue.Lyft intends to focus on reviving their core division following a bruising pandemic year. Lyft also believes human ride-hail drivers will remain important for the foreseeable future to serve customers during peak demand periods, bad weather, or in areas that self-driving cars are unable to navigate.
Lyft already allows consumers to book rides in self-driving vehicles in select cities in partnerships with Alphabet Inc's Waymo and Motional, the joint venture between Hyundai Motor Co and Aptiv. It will continue to collect real-world driving data through some 10,000 vehicles it rents out to consumers and ride-hail drivers. The data is valuable for the development of self-driving vehicles that Toyota's Woven Planet will have access to under the deal.
QUESTIONS
Ansoff Matrix
Can you apply the Ansoff Matrix to describe the growth of Lyft and its product portfolio from its origins at Cornell University when it was launched as Zimride in 2007 to its plans for launching a robo-taxi service in the US in 2023?
(8 marks)
1.2
Horizons of Growth
Can you describe the importance of the three horizons of growth and apply them to the
development Lyft and its product portfolio?
(8 marks)
.3
Technological Disruption 5 marks
Can you identify and explain how Lyft has used at least 3 of the root causes of technological disruption and how may these affect the company's profits?
(5 marks)
1.4
Abundance and Scarcity 3 marks
Can you identify and explain one instance of how abundance has assisted in the development of Lyft and its product portfolio?
(3 marks)
Explain abundance (1 mark), identify an instance of abundance (1 mark) and apply to Lyft (1 mark).
1.5
Platform Power 6 marks
How have the components of platform power assisted the growth of Lyft within the US and hindered the development of a similar enterprise within Zimbabwe from where the original idea was conceived?
(6 marks)
1.6
Critical Mass
Which tactics has Lyft used to attempt to get to critical mass since it was established as Zimride in 2007? (6 marks)
1.7
Massive Transformative Purpose 4 marks
Based on the development of Lyft since its launch as Zimride in 2007, can you suggest a Massive Transformative Purpose for the company and motivate how that MTP can deliver value to the company?
(4 marks)
1.8
SCALE 4 marks
Which would you consider to be the two most important features of external SCALE components for Lyft as a potential exponential organisation and why those two?
(4 marks)

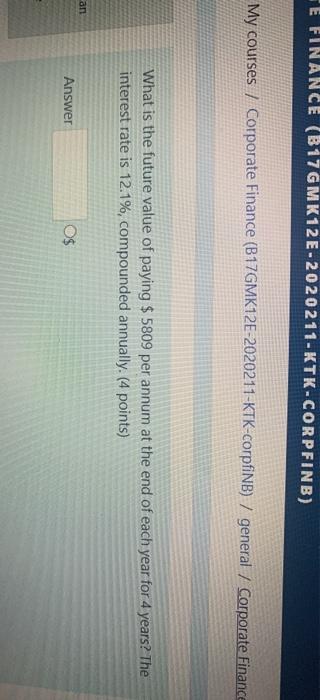

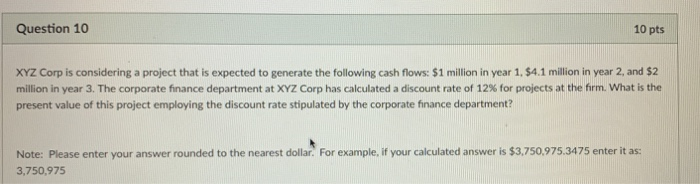
Please answer ASAP Tilburg University offers its BSE program students the following three elective courses: Corporate Finance, Principles of Marketing and Introduction to Programming. In total, there are 80 BSE students. There are 19 BSE students in Corporate Finance, 28 students in Principles of Marketing, and 21 students in Introduction to Programming. There are 5 students who are in both Corporate Finance and Principles of Marketing, 4 students who are both in Corporate Finance and Introduction to Programming, and 8 students who are both in Principals of Marketing and Introduction to Programming. There are 3 students who take all three electives. 1) If a BSE student is chosen randomly, what is the probability that he or she is taking at least one elective class? 2) If 10 students are chosen randomly, what is the probability that at least one is taking no elective classes? Please write all probabilities and give broad explanation
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


