Help out with the following questions please
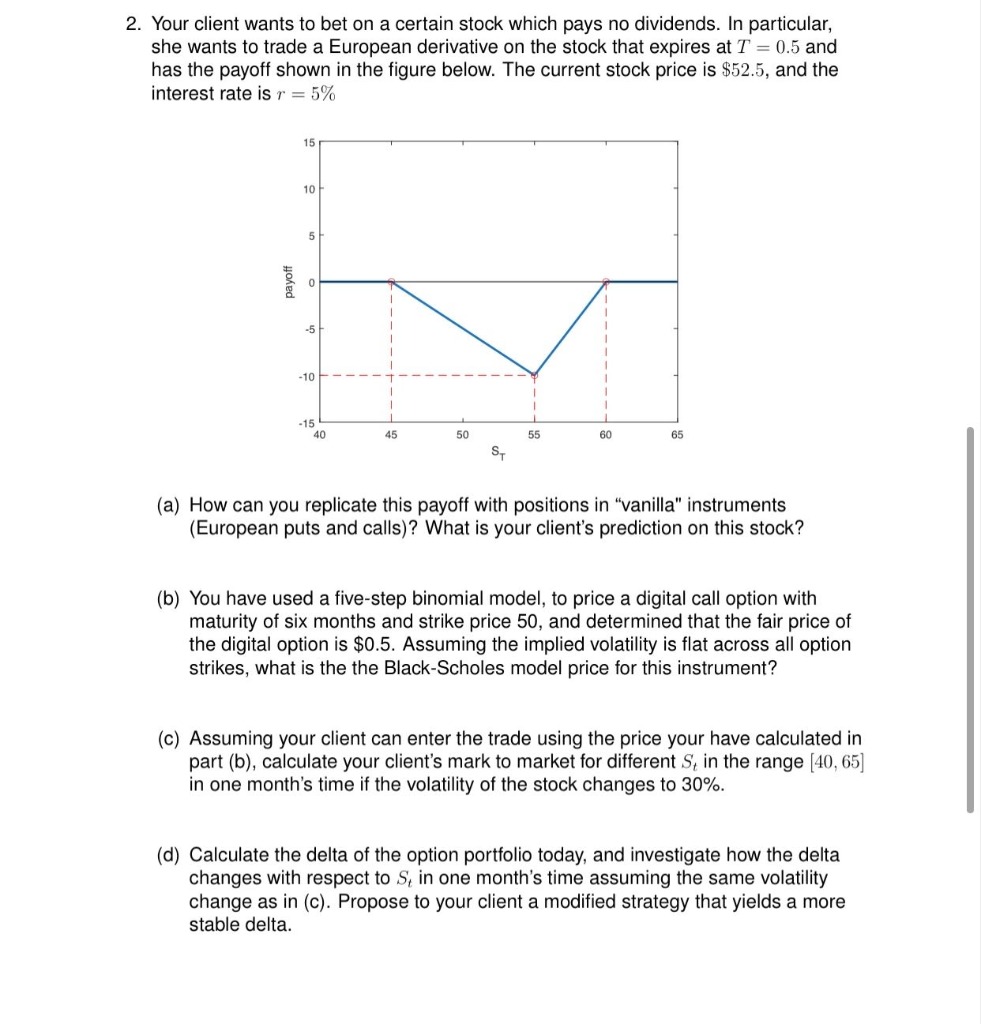
2. Your client wants to bet on a certain stock which pays no dividends. In particular, she wants to trade a European derivative on the stock that expires at T = 0.5 and has the payoff shown in the figure below. The current stock price is $52.5, and the interest rate is r = 5% (a) How can you replicate this payoff with positions in \"vanilla" instruments (European puts and calls)? la'llhat is your client's prediction on this stock? (b) You have used a five-step binomial model. to price a digital call option with maturity of six months and strike price 50, and determined that the fair price of the digital option is $0.5. Assuming the implied volatility is flat across all option strikes, what is the the BIack-Scholes model price for this instrument? to) Assuming your client can enter the trade using the price your have calculated in part (b). calculate your client's mark to market for different 3; in the range [40, 65} in one month's time if the volatility of the stock changes to 30%. (d) Calculate the delta of the option portfolio today, and investigate how the delta changes with respect to S,_ in one month's time assuming the same volatility change as in (c). Propose to your client a modified strategy that yields a more stable delta. 1. Consider the market for a good where the demand curve is given by P = 100 - 0.1Q and the supply curve is given by P = 20 + 0.06Q. a. Find the equilibrium price and quantity. b. Find a numerical value for consumer surplus and producer surplus. c. Suppose the government institutes a price ceiling of $35 per unit. Find the quantity supplied, quantity demanded, consumer surplus, producer surplus, and deadweight loss. d. Given the existence of deadweight loss, why would a country adopt a price ceiling? Please explain. 2. Consider the market for a good where the demand curve facing a firm who has considerable market power is given by P = 80 - 0.05Q, the marginal revenue curve is given by MR = 80- 0.1Q, and the firm's marginal cost curve is given by MC = 17 + 0.02Q. a. If the firm behaves like a competitive firm, find equilibrium price and quantity. Now find consumer and producer surplus. b. If the firm behaves like a monopolist, find equilibrium price and quantity. Now find consumer and producer surplus, and deadweight loss.Exercise 1 Three oligopolists operate in a market with inverse demand given by P(Q) = a - Q, where Q = qi +92 + 93 and q; is the quantity produced by firm i. Each firm has a constant marginal cost of production, c, and no fixed cost. The firms choose their quantities as follows: (1) firm 1 chooses q, 2 0; (2) firms 2 and 3 observe q and then simultaneously choose 92 and 93, respectively. What is the sub game-perfect outcome? Exercise 2 The simultaneous-move game (below) is played twice, with the outcome of the first stage observed before the second stage begins. There is no discounting. Can the payoff (4,4) be achieved in the first stage in a pure-strategy sub game-perfect Nash equilibrium? If so, give strategies that do so. If not, prove why not. Player 2 L C R T (3, 1) (0,0) (5.0) Player 1 M (2, 1) (1,2) (3,1) B (1,2) (0,1) (4,4) Exercise 3 What is a strategy in a repeated game? What is a subgame in a repeated game? What is a subgame-perfect Nash equilibrium?Consider a market where there are two firms. The inverse demand in this market is p = 33-Q, where as usual Q = q, + 4, denotes the total output produced by the two firms. Both firms have the same constant marginal cost of $15 per unit produced. Furthermore, if firm #2 chooses to produce a positive amount, it also incurs a fixed cost F = 10. Suppose that firm #1 is constraint to choose between one of three output levels: 41 =6, q1 =9, and 41 = 12. Similarly, firm $2 gets to choose one of three output levels: 42 =0, 42 = 4, and q2 =6 (note: you can interpret 42 = 0 as meaning that the firms does not enter this market). (a) Compute each firm's profit for all possible output combinations, and use them to complete the following payoff table: Firm # 2 42 =0 42 = 4 42 = 6 4 =6 41=9 Firm # 1 41 = 12 (b) Find the Nash equilibrium (NE) of the game under the assumption that the two firms choose their output simultaneously. What is the payoff to firm #1 in this NE? What is the payoff of firm #2 in this NE? (c) Now suppose that firm #1 gets to choose its output level first. Firm #2 sees what #1 has chosen before deciding on its own output level. Find the "subgame perfect" NE of this game. What is the payoff to firm #1 in this NE? What is the payoff of firm #2 in this NE? (d) Comment on the differences between the answers to parts (b) and (c)