help please with explanation
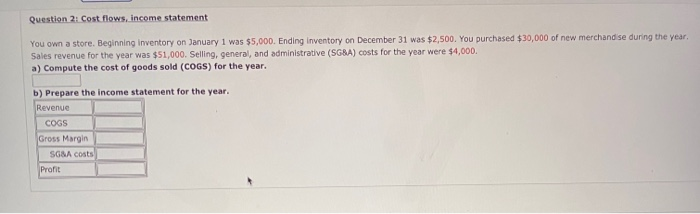

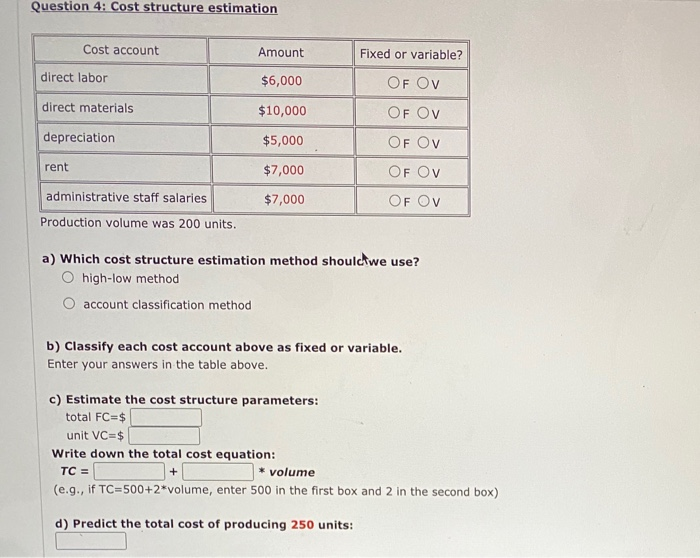
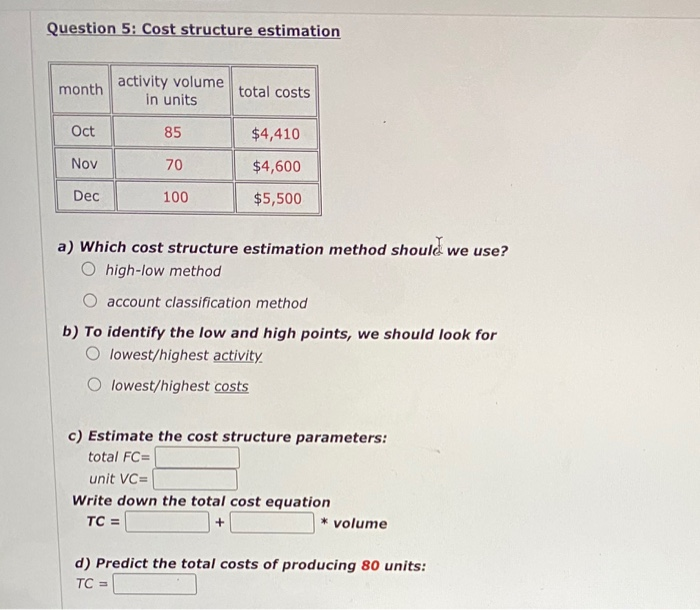

Question 2: Cost flows, income statement You own a store. Beginning inventory on January 1 was $5,000. Ending inventory on December 31 was $2,500. You purchased $30,000 of new merchandise during the year, Sales revenue for the year was $51,000. Selling, general, and administrative (SGBA) costs for the year were $4,000. a) Compute the cost of goods sold (COGS) for the year. b) Prepare the income statement for the year. Revenue COGS Gross Margin SG&A costs Profit Question 3: Cost terminology in manufacturing firms a) Direct materials include O only major materials and components O only raw materials such as steel and glass O all materials and components Direct labor includes O only hourly production workers (aka assembly workers) O all production labor including supervisors and maintenance staff O only managers who directly supervise the production process Manufacturing overhead includes O only big items that cannot be traced (e.g., factory rent) O only non-manufacturing costs both big items that cannot be traced (0.9., factory rent) and small items that are not worth tracing (0.9., glue, grease) O only small items that are not worth tracing (e....glue, grease) b) Classify the following items as direct materials (DM), direct labor (DL), or manufacturing overhead (OH) for a car assembly plant: Rent for the factory building ODL ODM OOH Cost of engines used in production ODLODM OOH Depreciation on production equipment ODL ODM OOM Cost of lubricant used in production ODL ODM OOH Production supervisor's salary ODL ODM OOH Assembly workers' wages ODL ODM OOH Question 4: Cost structure estimation Cost account Amount Fixed or variable? direct labor $6,000 OF OV direct materials $10,000 OF OV depreciation $5,000 OF Ov rent $7,000 OF Ov administrative staff salaries $7,000 OF OV Production volume was 200 units. a) Which cost structure estimation method should we use? high-low method account classification method b) Classify each cost account above as fixed or variable. Enter your answers in the table above. c) Estimate the cost structure parameters: total FC=$ unit VC=$ Write down the total cost equation: TC = * volume (e.g., if TC=500+2*volume, enter 500 in the first box and 2 in the second box) + d) Predict the total cost of producing 250 units: Question 5: Cost structure estimation month activity volume in units total costs Oct 85 $4,410 Nov 70 $4,600 Dec 100 $5,500 a) Which cost structure estimation method should we use? O high-low method account classification method b) To identify the low and high points, we should look for O lowest/highest activity lowest/highest costs c) Estimate the cost structure parameters: total FC= unit VC= Write down the total cost equation TC = + * volume d) Predict the total costs of producing 80 units: TC = TC = + * volume d) Predict the total costs of producing 80 units: TC = e) Can we use the estimates from (c) to predict costs at volume of 5,000 units? O YES: Just plug in volume =5,000 in the total cost equation. O NO: 5,000 units is outside the relevant range (the normal range of activity is around 70-100 units)











