Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
help with 2 please. explaing each step and code using just matlab. skelton script attached in pic 2. Construct your own FBP algorithm using the
help with 2 please. explaing each step and code using just matlab. skelton script attached in pic 
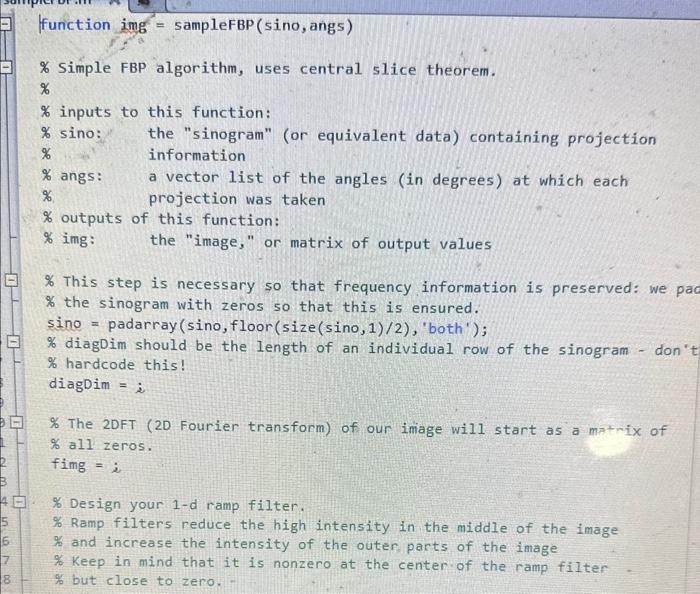
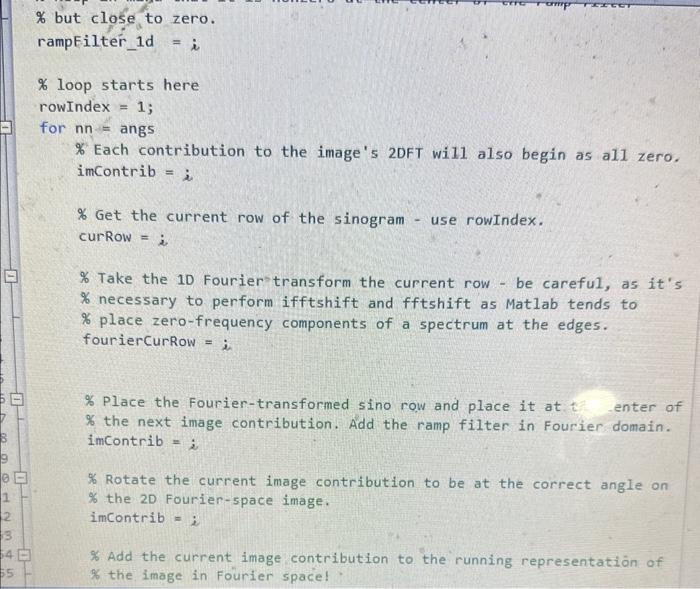
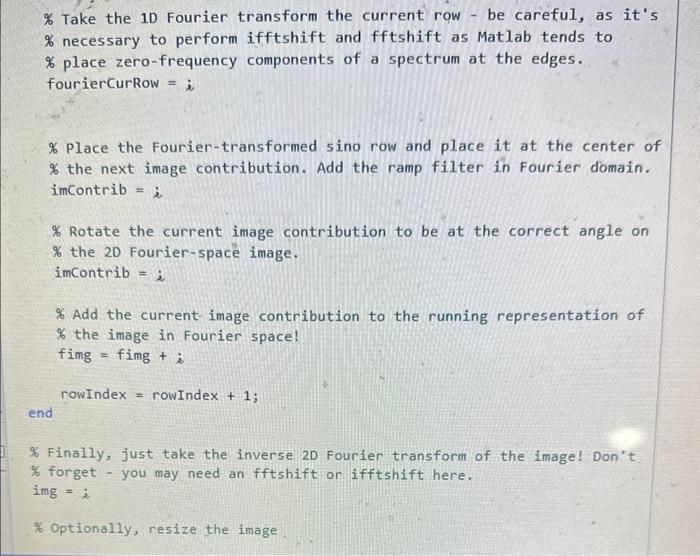
2. Construct your own FBP algorithm using the central slice theorem a. You will be given a skeleton script to help you with this problem. You are not required to use the skeleton script. b. You will be provided a sinogram to use for your image data. Assume the sinogram was acquired with parallel beam data and was sampled every 1 from 0 to 179. c. Plot the first projection of the sinogram d. Your 1-D ramp filter e. The 2DFT of the image before the ramp filter f. The 2DFT of the image after applying the ramp filter g. The reconstructed image after not having the ramp filter applied in the frequency domain. h. The reconstructed image after having the ramp filter applied in the frequency domain. i. Use the iradon transform to reconstruct your image. How does this compare with your reconstruction? j. Write your image to a dicom file using the dicomwrite function. Attach this file to your report. You can use dicomread to verify that your image has been written to the dicom file correctly. k. Respond to these questions in your report: i. Why do you need to apply a ramp filter to the image? ii. What differences do you see between the image that is and isn't ramp filtered? iii. What would the image look like if it were sampled every 5? for 3 bonus points, show this image. function img = sampleFBP (sino, angs) \% Simple FBP algorithm, uses central slice theorem. % \% inputs to this function: \% sino: the "sinogram" (or equivalent data) containing projection \% information % angs: a vector list of the angles (in degrees) at which each \% projection was taken % outputs of this function: \% img: the "image," or matrix of output values \% This step is necessary so that frequency information is preserved: we pac \% the sinogram with zeros so that this is ensured. sino = padarray ( sino, floor (size(sino,1)/2), 'both' ); % diagDim should be the length of an individual row of the sinogram - don't % hardcode this! diagDim =i \% The 2DFT (2D Fourier transform) of our image will start as a matrix of % all zeros. fimg = i \% Design your 1-d ramp filter. \% Ramp filters reduce the high intensity in the middle of the image % and increase the intensity of the outer parts of the image % Keep in mind that it is nonzero at the center of the ramp filter \% but close to zero. ampEilter_1d =i 6 loop starts here rowIndex = 1 for nn= angs \% Each contribution to the image's 2DFT will also begin as all zero. imContrib =i \% Get the current row of the sinogram - use rowIndex. curRow =i \% Take the 10 Fourier'transform the current row - be careful, as it's \% necessary to perform ifftshift and fftshift as Matlab tends to \% place zero-frequency components of a spectrum at the edges. fouriercurRow = i \% Place the Fourier-transformed sino row and place it at t. enter of \% the next image contribution. Add the ramp filter in Fourier domain. imContrib =i \% Rotate the current image contribution to be at the correct angle on % the 2D Fourier-space image. imContrib =i \% Add the current image contribution to the running representation of \% Take the 1D Fourier transform the current row - be careful, as it's % necessary to perform ifftshift and fftshift as Matlab tends to \% place zero-frequency components of a spectrum at the edges. fourierCurRow =i \% Place the Fourier-transformed sino row and place it at the center of \% the next image contribution. Add the ramp filter in Fourier domain. imcontrib =i \% Rotate the current image contribution to be at the correct angle on % the 2D Fourier-space image. imcontrib =i \% Add the current image contribution to the running representation of \% the image in Fourier space! fimg =fimg+i rowIndex = rowIndex +1; \% Finally, just take the inverse 2D Fourier transform of the image! Don " t \% forget - you may need an fftshift or ifftshift here. img = i \% Optionally, resize the image 



Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


