Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
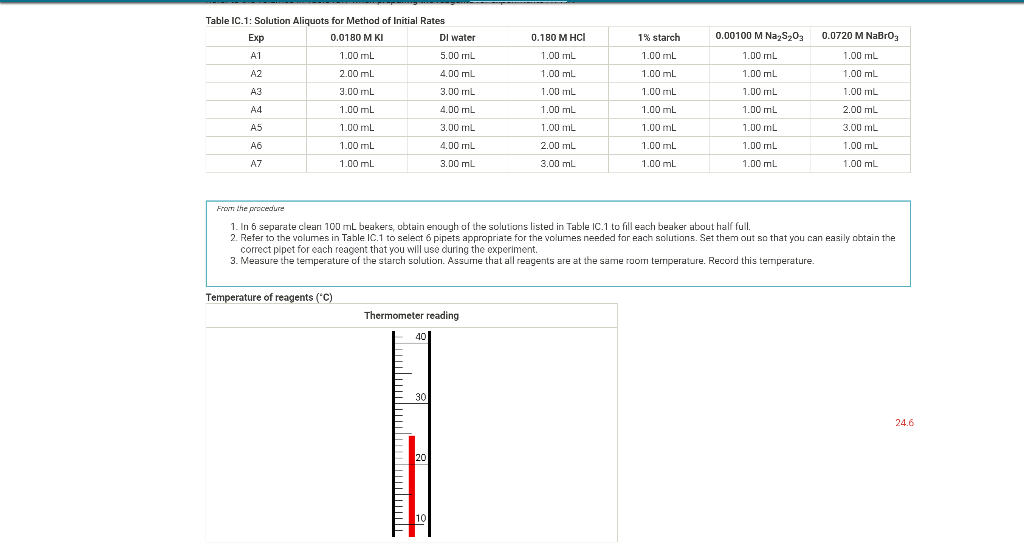
Help with tables please 0.180 M HCI 1% starch 0.00100 M Na2S203 1.00 mL 1.00 mL Table IC.1: Solution Aliquots for Method of Initial Rates

Help with tables please
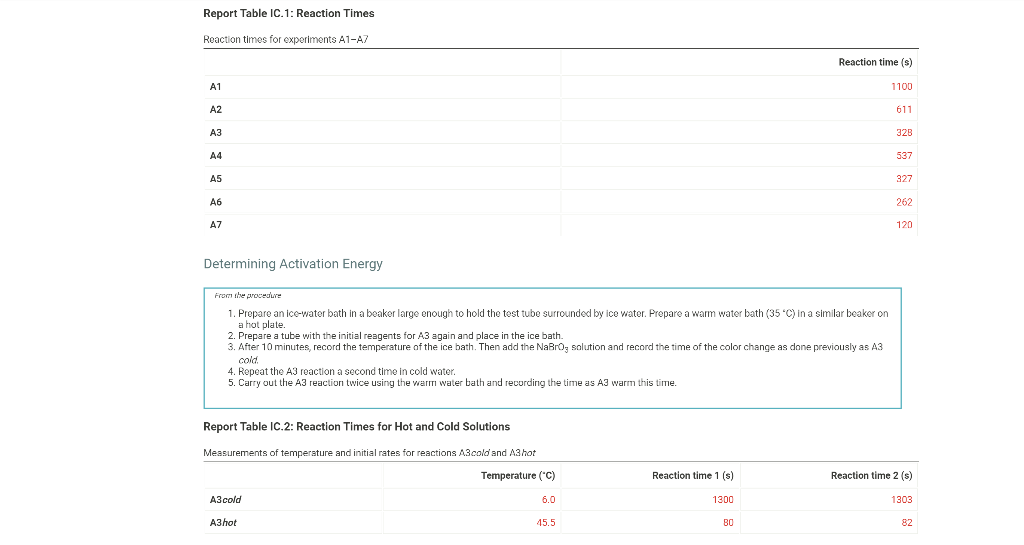
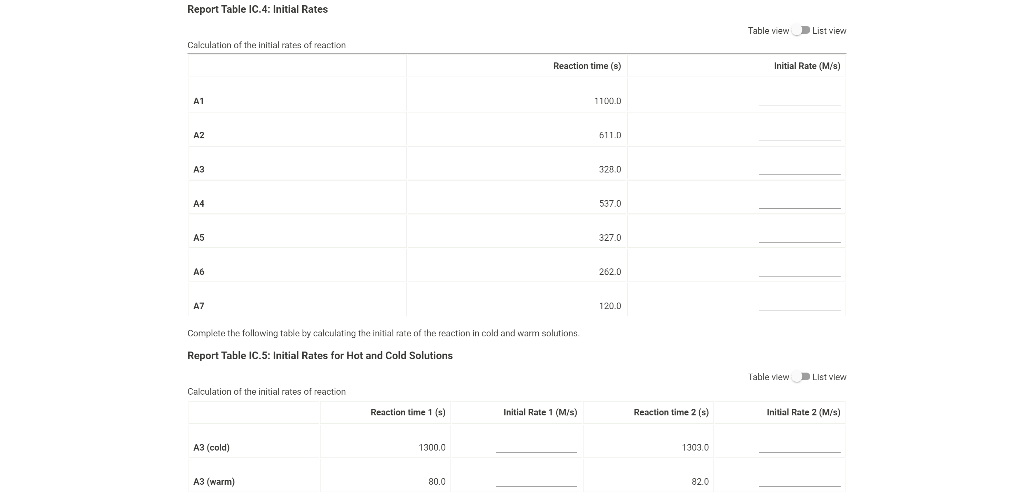
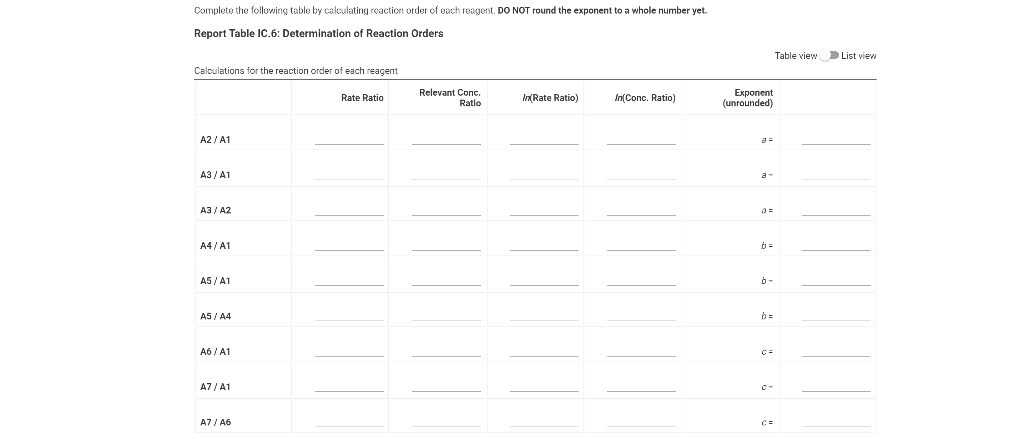
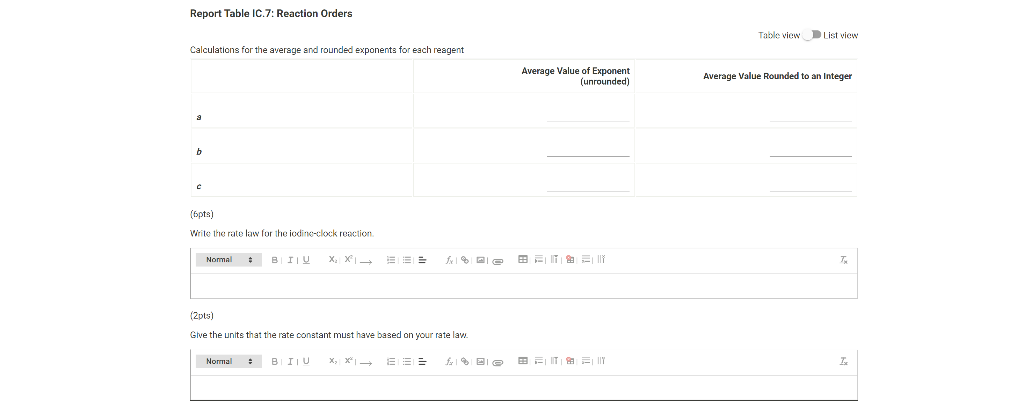
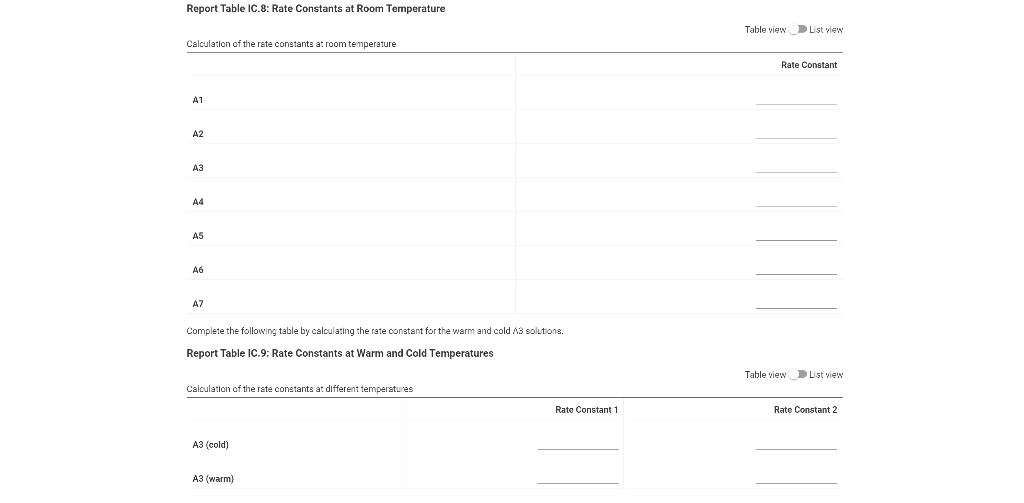
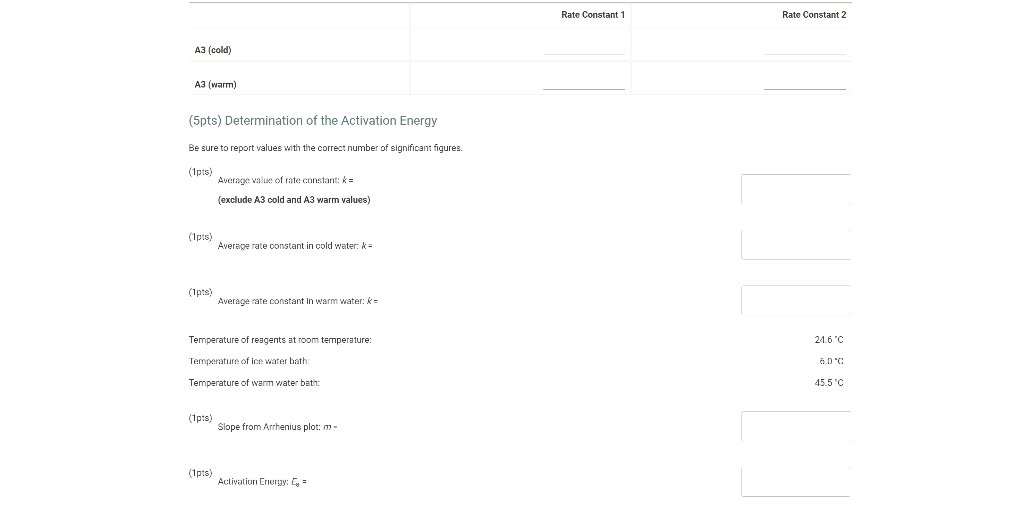
0.180 M HCI 1% starch 0.00100 M Na2S203 1.00 mL 1.00 mL Table IC.1: Solution Aliquots for Method of Initial Rates Exp 0.0180 M KI DI water A1 1.00 mL 5.00 ml A2 2.00 mL 4.00 mL A3 3.00 mL 3.00 mL A4 1.00 mL 4.00 mL A5 1.00 mL 3.00 mL 1.00 mL 1.00 mL 0.0720 M NaBro 1.00 ml 1.00 ml 1.00 mL 1.00 mL 1.00 mL 1.00 mL 1.00 mL 1.00 mL 1.00 mL 1.00 mL 2.00 mL 1.00 mL 1.00 mL 1.00 mL 1.00 mL 3.00 mL A6 4.00 mL 1.00 mL 1.00 mL 1.00 mL 1.00 mL 2.00 ml 3.00 mL 1.00 ml 1.00 mL AZ 3.00 mL 1.00 ml 1.00 mL From the procedure 1. In 6 separate clear 100 ml beakers, obtain enough of the solutions listed in Table IC.1 to fill each beaker about half full. 2. Refer to the volumes in Table IC.1 to select 6 pipets appropriate for the volumes needed for each solutions. Set them out so that you can easily obtain the correct pipet for each reagent that you will use during the experiment. 3. Measure the temperature of the starch solution. Assume that all reagents are at the same room temperature. Record this temperature. Temperature of reagents (C) Thermometer reading 40 30 24.6 20 J. 10 Report Table IC.1: Reaction Times Reaction times for experiments A1-A7 Reaction time (s) A1 1100 A2 611 A3 328 A4 537 A5 327 A6 262 AZ 120 Determining Activation Energy from the procedure 1. Prepare an ice-water bath in a beaker large enough to hold the test tube surrounded by ice water. Prepare a warm water bath (35 C) in a similar beaker on a hot plate 2. Prepare a tube with the initial reagents for A3 again and place in the ice bath. 3. After 10 minutes, record the temperature of the ice bath. Then add the NaBro, solution and record the time of the color change as done previously as A3 cold. 4. Repeat the A3 reaction a second time in cold water. 5. Carry out the A3 reaction twice using the wariri water bath and recording the time as A3 warm this time Report Table IC.2: Reaction Times for Hot and Cold Solutions Measurements of temperature and initial rates for reactions A3 cold and A3 hot Temperature ("C) Reaction time 1 (s) Reaction time 2 (s) A3 cold 6.0 1300 1303 A3 hot 45.5 82 (39pts) Initial Rates Complete the following table calculating the initial concentration of reagents. Be sure to report values with the correct number of significant figures. Report Table IC.3: Initial Concentrations Table view List view Concentrations of reagents IS202-1. (M) [1] (M) [Bros lo (M) [H*lo (M) A1 A2 A3 A4 A5 A6 A7 Report Table IC.4: Initial Rates Table view List View Calculation of the initial rates of reaction Reaction time (8) Initial Rate (M/s) A1 1100.0 AZ 611D A3 3280 A4 537.0 A5 327.0 A6 262.0 AZ 120.0 Complete the following table by calculating the initial rate of the reaction in cold and warm solutions Report Table IC.5: Initial Rates for Hot and Cold Solutions Table view List View Calculation of the initial rates of reaction Reaction time 1 (s) Initial Rate 1 (M/s) Reaction time 2 (s) Initial Rate 2 (M/s) A3 (cold) 1300.0 13030 A3 (warm) 80.0 82.0 Complete the following table by calculating reaction order of each reagent DO NOT round the exponent to a whole number yet. Report Table IC.6: Determination of Reaction Orders Table view List view Calculations for the reaction order of each reagent Rate Ratio Relevant Conc. Ratlo In Rate Ratio) In(Conc. Ratio) Exponent (unrounded) A2/A1 a A3/A1 A3 / A2 A4/A1 = A5 / A1 A5 / A4 ha A6 / A1 A7/A1 A7 / A6 Report Table IC.7: Reaction Orders Table view List view Calculations for the average and rounded exponents for each reagent Average Value of Exponent (unrounded) Average Value Rounded to an Integer (bpta) Write the rate law for the iodine-clock reaction Normal BIU XX fx % 12pts) Give the units that the rate constant must have based on your rate law Normal X, ESE BITIY Report Table IC.8: Rate Constants at Room Temperature Table view List view Calculation of the rate constants at room temperature Rate Constant A1 A2 A3 A4 AS A6 A7 Complete the following table by calculating the rate constant for the warm and cold A3 solutions. Report Table IC.9: Rate Constants at Warm and Cold Temperatures Table view List View Calculation of the rate constants at different temperatures Rate Constant 1 Rate Constant 2 A3 (cold) A3 (warm) Rate Constant 1 Rate Constant 2 A3 (cold) A3 (warm) (5pts) Determination of the Activation Energy Be sure to report values with the correct number of significant figures. (Ipts) Average value of rate constant k = (exclude A3 cold and A3 warm values) (Ipts) Average rate constant in cold water: k = (1pts) Average rate constant in warm water: k = Temperature of reagents at room temperature: 24.6 'C Temperature of ice water bath: 60C Temperature of warm water bath: 45.5 C (1pts) Slope from Arrhenius plot: m- (1pts) Activation Energy Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


