Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
Helping!!! data structure problems. Just need to finish the DP.java and pass the test. finishing the three part bupartition buminidistance bulcs using buttom-up likebucoinChange
Helping!!! data structure problems. Just need to finish the DP.java and pass the test. finishing the three part "bupartition" "buminidistance" "bulcs" using buttom-up like"bucoinChange" thank u
and create more test case of them Thank you very much
other files are in the picture
DP.java
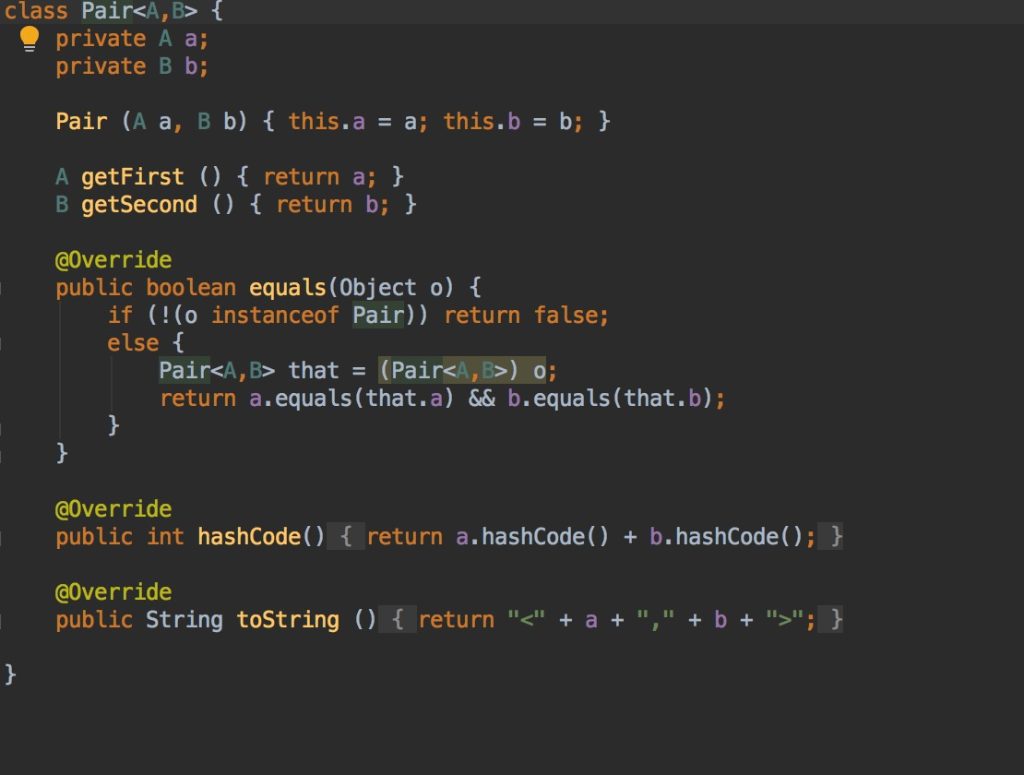
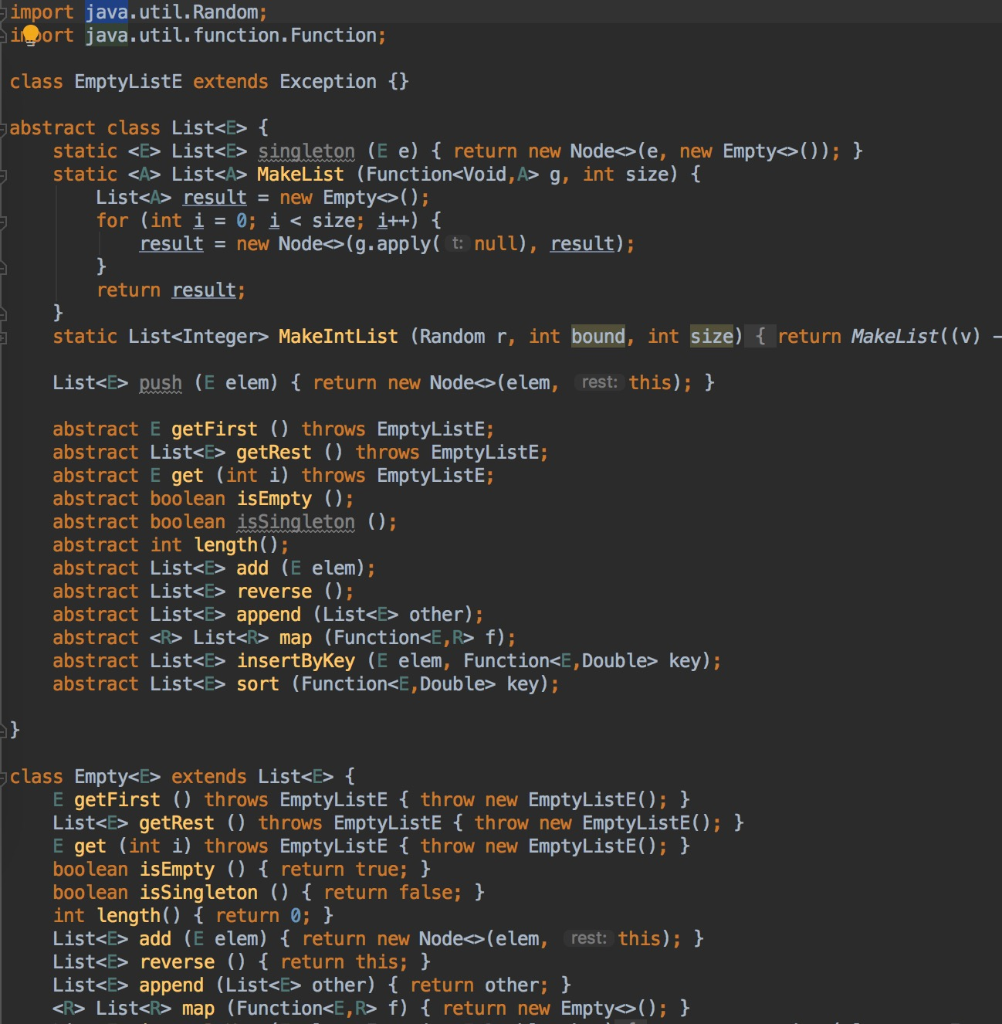
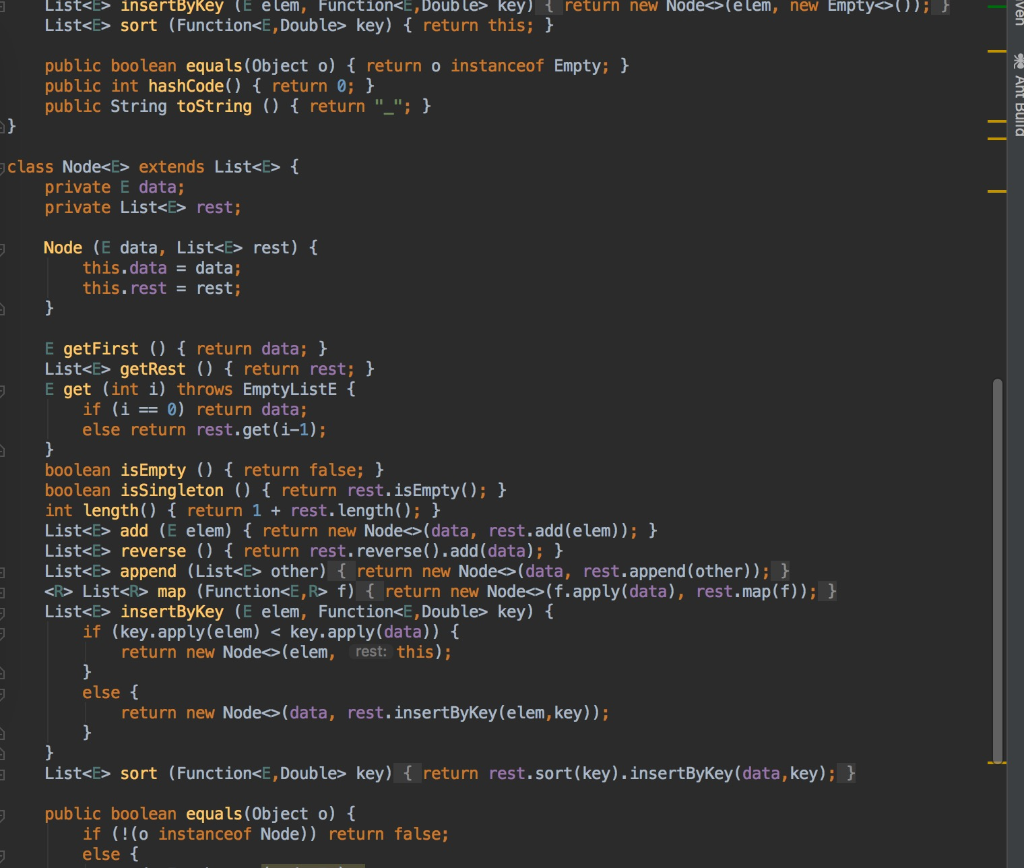
import java.util.Arrays; import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.Map; import java.util.WeakHashMap; import java.util.function.BiFunction; import java.util.function.Function; /* * Top down solutions */ class DP { * Given a list of possible coins that must include a penny, * and a number of pennies 'n', in how many ways can we use the * coins to make change for 'n'. */ static int coinChange (List coins, int n) { try { if (n coinChange(coins.getRest(), n) + coinChange(coins,n - coins.getFirst().getValue()); } catch (EmptyListE e) { return 0; // no way to make change } } /** * We create a hash table making sure it is called coinChangeMemo. * Each subproblem is determined by the list of coins and by the desired sum. * That combination should be the key. */ static Map,Integer>,Integer> coinChangeMemo = new WeakHashMap(); /** * We use computeIfAbsent. When we communicate with the hash table, we combine * all the information into a key and take back apart. */ static int mcoinChange (List coins1, int n1) { return coinChangeMemo.computeIfAbsent(new Pair(coins1,n1), p -> { List coins = p.getFirst(); int n = p.getSecond(); try { if (n mcoinChange(coins.getRest(), n) + mcoinChange(coins, n - coins.getFirst().getValue()); } catch (EmptyListE e) { return 0; // no way to make change } }); } /** * We now manage the memoization table manually. We can choose * to represent our memoization table as a WeakHashMap or we can * represent it as an array or whatever data structure gives efficient * access to the elements. In class we used a WeakHashMap. Here * we show how to use an array. */ static int bucoinChange (List coins, int n) throws EmptyListE { /* The possible lists of coins we will encounter are coins, coins.getRest(), * coins.getRest().getRest(), etc. We will refer to these using * array indices 0, 1, 2, ... * The possible sums we will encounter will be a subset of n, n-1, n-2, ... * We will use these directly as indices into the array */ int len = coins.length()+1; int[][] table = new int[len][n+1]; /* * The entries corresponding to the empty list are initialized with 0 (no solutions) * The entries corresponding to sum=0 are initialized with 1 (one solution) * These two initializations must be done in the given order */ for (int i=0; i=0; c--) { int v = coins.get(c).getValue(); for (int i = 1; i/** * Partition: take a list, a desired sum 's', and return * T/F depending on whether it is possible to find a * subsequence of the list whose sum is exactly 's' */ static boolean partition (List s, int sum) { try { return partition(s.getRest(), sum - s.getFirst()) || partition(s.getRest(), sum); } catch (EmptyListE e) { return sum == 0; } } static Map,Integer>,Boolean> partitionMemo = new WeakHashMap(); static boolean mpartition (List s1, int sum1) { return partitionMemo.computeIfAbsent(new Pair(s1, sum1), p -> { List s = p.getFirst(); int sum = p.getSecond(); try { return mpartition(s.getRest(), sum - s.getFirst()) || mpartition(s.getRest(), sum); } catch (EmptyListE e) { return sum == 0; } }); } static boolean bupartition (List s, int sum) { return false; } final static int GAP = 2; final static int MATCH = 0; final static int MISMATCH = 1; enum BASE { A, T, G, C } static int min (int d1, int d2) { return d1 dna1, List,List lcs (List cs1, List cs2) { try { if (cs1.getFirst().equals(cs2.getFirst())) { return new Node(cs1.getFirst(), lcs(cs1.getRest(),cs2.getRest())); } else { List r1 = lcs(cs1,cs2.getRest()); List r2 = lcs(cs1.getRest(),cs2); if (r1.length() > r2.length()) return r1; else return r2; } } catch (EmptyListE e) { return new Empty(); } } static Map,List>,List> lcsMemo = new WeakHashMap(); static List mlcs (List cs11, List cs21) { return lcsMemo.computeIfAbsent(new Pair(cs11,cs21), p -> { List cs1 = p.getFirst(); List cs2 = p.getSecond(); try { if (cs1.getFirst().equals(cs2.getFirst())) { return new Node(cs1.getFirst(), mlcs(cs1.getRest(), cs2.getRest())); } else { List r1 = mlcs(cs1, cs2.getRest()); List r2 = mlcs(cs1.getRest(), cs2); if (r1.length() > r2.length()) return r1; else return r2; } } catch (EmptyListE e) { return new Empty(); } }); } static List bulcs (List cs1, List cs2) { int len1 = cs1.length()+1; } } <><> Dptest.java
import org.junit.Test; import java.util.Random; import java.util.function.BiFunction; import java.util.function.Function; import static org.junit.Assert.*; public class DPTest { // Timers static long time1(Function f, A a) { long start = System.nanoTime(); f.apply(a); long end = System.nanoTime(); return (end - start) / 1000000; } static long time2(BiFunction f, A a, B b) { long start = System.nanoTime(); f.apply(a, b); long end = System.nanoTime(); return (end - start) / 1000000; } // Testing coinChange correctness and timing @Test public void coinsC() throws EmptyListE { Coin quarter = new Coin(25); Coin dime = new Coin(10); Coin nickel = new Coin(5); Coin penny = new Coin(1); List coins = new Node(quarter, new Node(dime, new Node(nickel, new Node(penny, new Empty())))); assertEquals(1, DP.coinChange(coins, 3)); assertEquals(2, DP.coinChange(coins, 6)); assertEquals(242, DP.coinChange(coins, 100)); assertEquals(1, DP.bucoinChange(coins, 3)); assertEquals(2, DP.bucoinChange(coins, 6)); assertEquals(242, DP.bucoinChange(coins, 100)); } @Test(timeout = 500) public void coinsT1() { List coins = new Node(new Coin(3), new Node(new Coin(2), new Node(new Coin(1), new Empty()))); DP.coinChangeMemo.clear(); DP.mcoinChange(coins, 1000); } // Testing partition correctness and timing @Test public void partitionCorrectness() { List ns = new Node(5, new Node(3, new Node(7, new Node(1, new Empty())))); assertFalse(DP.partition(ns, 2)); assertTrue(DP.partition(ns, 8)); assertTrue(DP.partition(ns, 6)); } @Test public void partitionTiming() { Random r = new Random(1); List s = List.MakeIntList(r, 100, 1000); DP.partitionMemo.clear(); long t = time2(DP::mpartition, s, 50000); assertTrue(t dna1 = new Node(DP.BASE.A, new Node(DP.BASE.C, new Empty())); List dna2 = new Node(DP.BASE.A, new Node(DP.BASE.G, new Empty())); assertEquals(1, DP.minDistance(dna1, dna2)); } @Test public void minDistance2() { Random r = new Random(1); Function g = v -> DP.BASE.class.getEnumConstants()[r.nextInt(4)]; List dna1 = List.MakeList(g, 521); List dna2 = List.MakeList(g, 450); assertEquals(337, DP.mminDistance(dna1, dna2)); } // longest common subsequence @Test public void lcs() { List cs1 = new Node('A', new Node('B', new Node('C', new Node('B', new Node('D', new Node('A', new Node('B', new Empty()))))))); List cs2 = new Node('B', new Node('D', new Node('C', new Node('A', new Node('B', new Node('A', new Empty())))))); List c = new Node('B', new Node('D', new Node('A', new Node('B', new Empty())))); assertEquals(c, DP.lcs(cs1, cs2)); } @Test public void lcs2() { Random r = new Random(1); Function g = v -> Character.forDigit(r.nextInt(256), 10); List cs1 = List.MakeList(g, 310); List cs2 = List.MakeList(g, 250); assertEquals(240, DP.mlcs(cs1, cs2).length()); } } 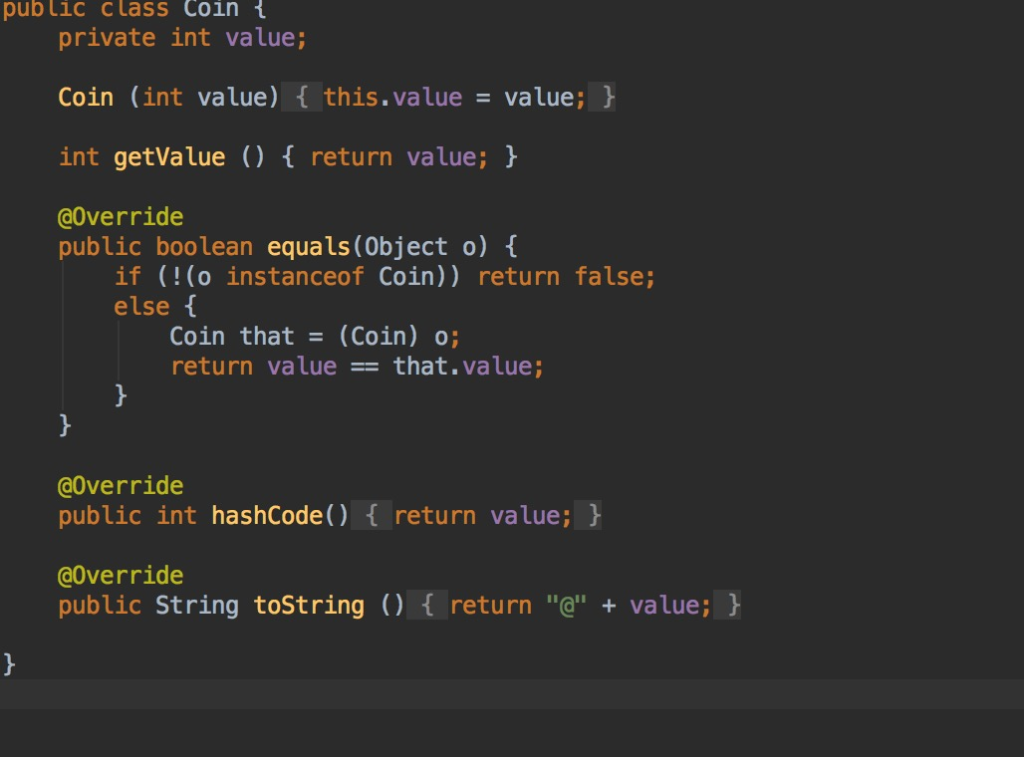
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


