


Henri was employed as an executive chef at an exclusive restaurant for many years. He was internationally famous for many of his gourmet dishes, and was the author of several books on gourmet cooking.
A small chain of exclusive hotels wished to incorporate gourmet restaurant facilities in each hotel as an added incentive for executives and wealthy clientele to patronize its establishments. Henri was approached by the President of the hotel chain and offered the opportunity to manage the gourmet restaurant facilities throughout the chain, and to assume responsibility for all aspects of the operation. Henri accepted the position, and proceeded to set up the restaurants at each hotel, to hire and train the new staff, and to plan all menus and food management.
The restaurants proved to be a great success initially, and for several years proved to be a significant contributor to the profits of the hotel chain. A downturn of the economy, unfortunately, affected the hotel industry generally, and the small chain in particular. In an effort to economize, the President approached Henri with a request to reduce the costs of operation of the gourmet restaurants through staff reductions, and the use of lower cost food ingredients. Henri refused, and in the heated discussion that followed, Henri was terminated for insubordination. Henri then instituted legal proceedings against the hotel chain, claiming wrongful dismissal.
1. Outline the positions of each of the parties in this case.
2. How might the court consider these arguments? Render, with reasons, a decision.
3. Who is the plaintiff and defendant?
4. What charge of the case?
5. What are the argument for Henri and the President of the hotel?
6. What is the Final opinion?
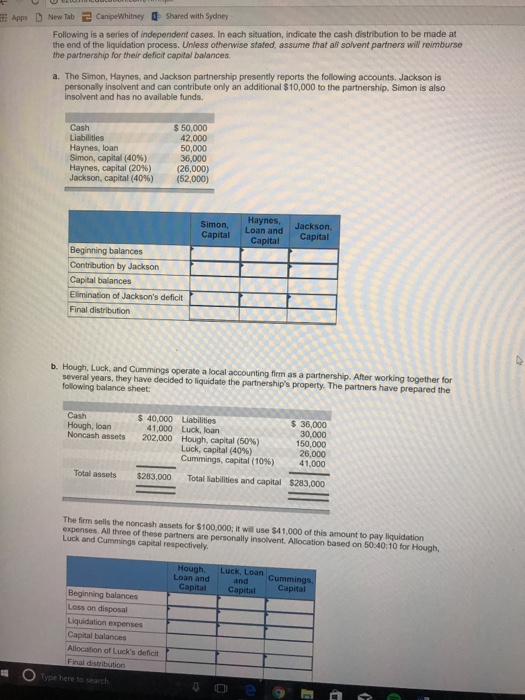
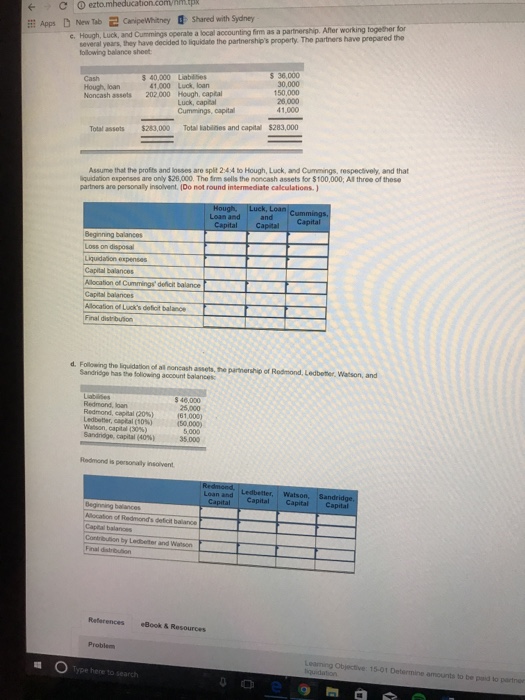
Apps ) New Tab CanipeWhitney 0 Shared with Sydney Following is a series of independent cases. In each situation, indicate the cash distribution to be made at the end of the liquidation process. Unless otherwise stated, assume that all solvent partners will reimburse the partnership for their deficit capital balances. a. The Simon, Haynes, and Jackson partnership presently reports the following accounts, Jackson is personaly insolvent and can contribute only an additional $10,000 to the partnership. Simon is also insolvent and has no available funds. $ 50,000 Liabilities 42,000 Haynes, loan 50,000 Simon, capital (40%) 36.000 Haynes, capital (2096) (26,000) Jackson, capital (40%) (52,000) Simon, Haynes, Capital Loan and Jackson. Capital Capital Beginning balances Contribution by Jackson Capital balances Elimination of Jackson's deficit Final distribution b. Hough, Luck, and Cummings operate a local accounting firm as a partnership. After working together for several years, they have decided to liquidate the partnership's property. The partners have prepared the following balance sheet: Cash $ 40,000 Liabilities $ 36,000 Hough, loan 41,000 Luck, loan 30.000 Noncash assets 202,000 Hough, capital (50%%) 150,000 Luck, capital (40%) 26,000 Cummings, capital (10%) 41.000 Total assets $283,000 Total Habilities and capital $283,000 The firm sells the noncash assets for $100,000; it will use $41,000 of this amount to pay liquidation expenses, All three of those partners are personally insolvent. Allocation based on 50:40:10 for Hough, Luck and Cummings capital respectively. Hough, Loan and Luck, Loan cummings, and Capital Capital Capital Beginning balances Loss on disposal Liquidation exporises Capital balances Allocation of Luck's deficit Final distribution O Type here to searchC O extomheducation.com/rimipx Apps [ New Tab CamipeWhitney 1 Shared with Sydney c. Hough, Luck, and Cummings operate a local accounting firm as a partnership. After working together for several yours, they have decided to liquidate the partnership's property. The partners have prepared the folowing balance sheet 540 000 Liabison $ 30,000 Cash 30,000 Hough, loan 41000 Luck, loan 150,000 Noncash ajob 202 000 Hough, capital Luck, capital 241000 Cummings, capital 41 040 Total mascots $20 007000 Toil Habilrios and capital $283,000 Assume that the profits and losses are split 2:4:4 to Hough, Luck, and Cummings, respectively, and that quidation expenses are only $26,000. The firm sells the noncash assets for $100,000; All three of thong partners are personally insolvent. (Do not round intermediate calculations. ] Hough, Luck, Loan Cummings, Loan and and Capital Capital Capital Beginning balancing Lose on disposal Liquidation expenses Capital balances Allocation of Cummings' deficit balance Capital balances Allocation of Luck's deficit balance Final distribution d, Following the liquidation of all poncash astols, The parmership of Redmond, Ledbetter. Watson, and Sandridge has the following account balances Redmond, loan Rodmond, capital post 181 000) Ledbatter, social CION] Hutton, capital (30) 5000 Sandridge, capital MOT 35090 Redmond is personally intoivent Redmond, Loan and Ledbetter, Watson, Sandridge, Capital Capital Capital Capital Mlocation of Redmond's deficit balance Capital balances Contribution by Ledbuffer and Watson Final distribution Plotarences .Book & Resources Problem liquidation Lolming Objective: 15-01 Determine amounts to be puld to partner Type here to search e 9Question 3 ccounting theorists? Some researchers who utilise Legitimacy Theory posit that organisations will attempt to operate within the terms of their 'social contract'. What is a social contract? Question 4 In 2006 the Australian Government established an inquiry into corporate social responsibilities with the aim of deciding whether the Corporations Act should be amended so as to specifically include particular social and environmental responsibilities within the Act. At the completion of the inquiry it was decided that no specific regulations would be added to the legislation, and that instead, 'market forces' would be relied upon to encourage companies to do the 'right thing' (that is, the view was expressed that if companies did not look after the environment, or did not act in a socially responsible manner, then people would not want to consume the organisations' products, and people would not want to invest in the organisation, work for them, and so forth. Because companies were aware of such market forces they would do the 'right thing' even in the absence of legislation). You are required to explain the decision of the government that no specific regulation be introduced from the perspective of: 1. Public Interest Theory 2. Capture Theory 3. Economic Interest Group Theory of regulation.ct Question 7 0 / 2 pts Use the following Total Tax / Annual Income relationship to determine which of the following would be used to calculated the Total Tax for an Annual Income of $58,900? Annual Income x $0. 10. 1f 50 5 Annual Income $ $9.525 $952. 50 + (Annual Income - 9,525) x 50.12, if $9,525
















