Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
Here is the main.cpp For this assignment complete the following requirements in order: 1. (5 pts) You must take a screen shot or picture of



Here is the main.cpp

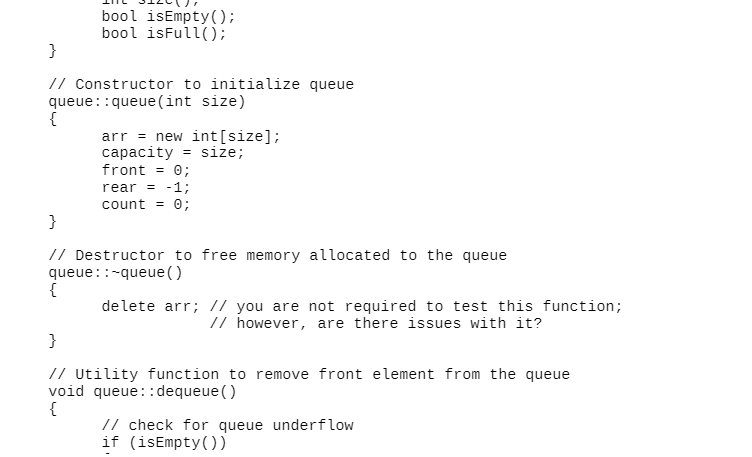
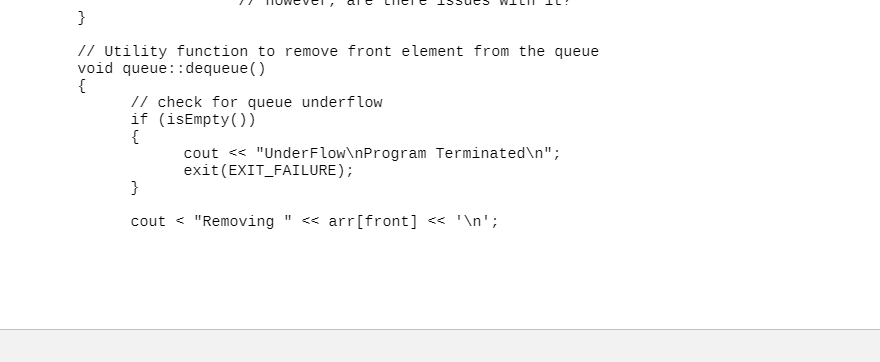



For this assignment complete the following requirements in order: 1. (5 pts) You must take a screen shot or picture of the syntax errors listed in the initial code after you build the code with cmake in the Linux terminal. This should demonstrate that you are using a Linux environment. The picture should end up in a .pdf file in your MA1 folder. Make sure your CMakeLists.txt contains the following set commands: set(CMAKE_CXX_STANDARD 11) set(CMAKE_CXX_FLAGS "${CMAKE_CXX_FLAGS} -Wall") set(CMAKE_BUILD_TYPE Debug) 2. (15 pts) You are required to fix all syntax and build errors. If the error is directly related to an environment specific condition (i.e. only works on Linux, but not Windows), then comment out the statement causing the problem. You do NOT need to find an equivalent fix for the other environment. 3. (45 pts - 5 pts/test case) Once you have fixed all syntax and build errors, you are required to write unit tests for all functions or units, excluding main (), the constructor, and the destructor, in the project. Your objective is to achieve 100% branch coverage for each unit. For each unit test you are required to construct a comment block with the information described in the background section What is a test case?", and implement a test function for the corresponding test case. Each test function must have a function declaration that is placed in a file called testQueue.h or testQueue.hpp and all test function definitions and comment blocks must be placed in a file called testQueue.cpp. A test function should always be declared as void testFunctionName (void). This means we want these tests to be self-contained. They do not accept any arguments and do not return any results. All setup and evaluation for the test is done inside the function. Hint: you will need 1 test case for each of the following functions: queue::size() queue::isEmpty () Hint: you will need 1 test case for each of the following functions: queue::size() queue::isEmpty 0 queue::isFull (), you will need 2 test cases for the following: queue::dequeue queue::enqueue () queue::peek () Call your test functions from main (). At this point do NOT fix the bugs discovered! This will be done as part of the next step! Place the results of each test case, i.e. pass or fail in the same comment block as the test case comment block. 4. (20 pts) Fix all bugs revealed by your test cases. Show a screen shot or picture of one break point that you have added to a unit to debug, where the bug was identified by one of your test cases. The debugger used must be a Linux tool (gbd, CLion, or VS Code)! The picture should end up in a .pdf file. 5. (15 pts - 3 pts/attribute) Using your understanding of design choices, software principles, and coding standards, which we will group under the general label "attributes" - list and describe 5 attributes demonstrated by the code that you would consider poor. These should NOT be related to the syntax errors. Examples of poor attributes could be related to comments, file structure, data structure selection, algorithm efficiency, etc. Place your list in a comment block at the top of the main.cpp file. #include
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


