Question: Hey i need these questions done please D2L Assignment - Mor X P30Module5Assig X P30Module8Assic x P30Module7Assic x Course Hero X *Course Hero * *Course
Hey i need these questions done please
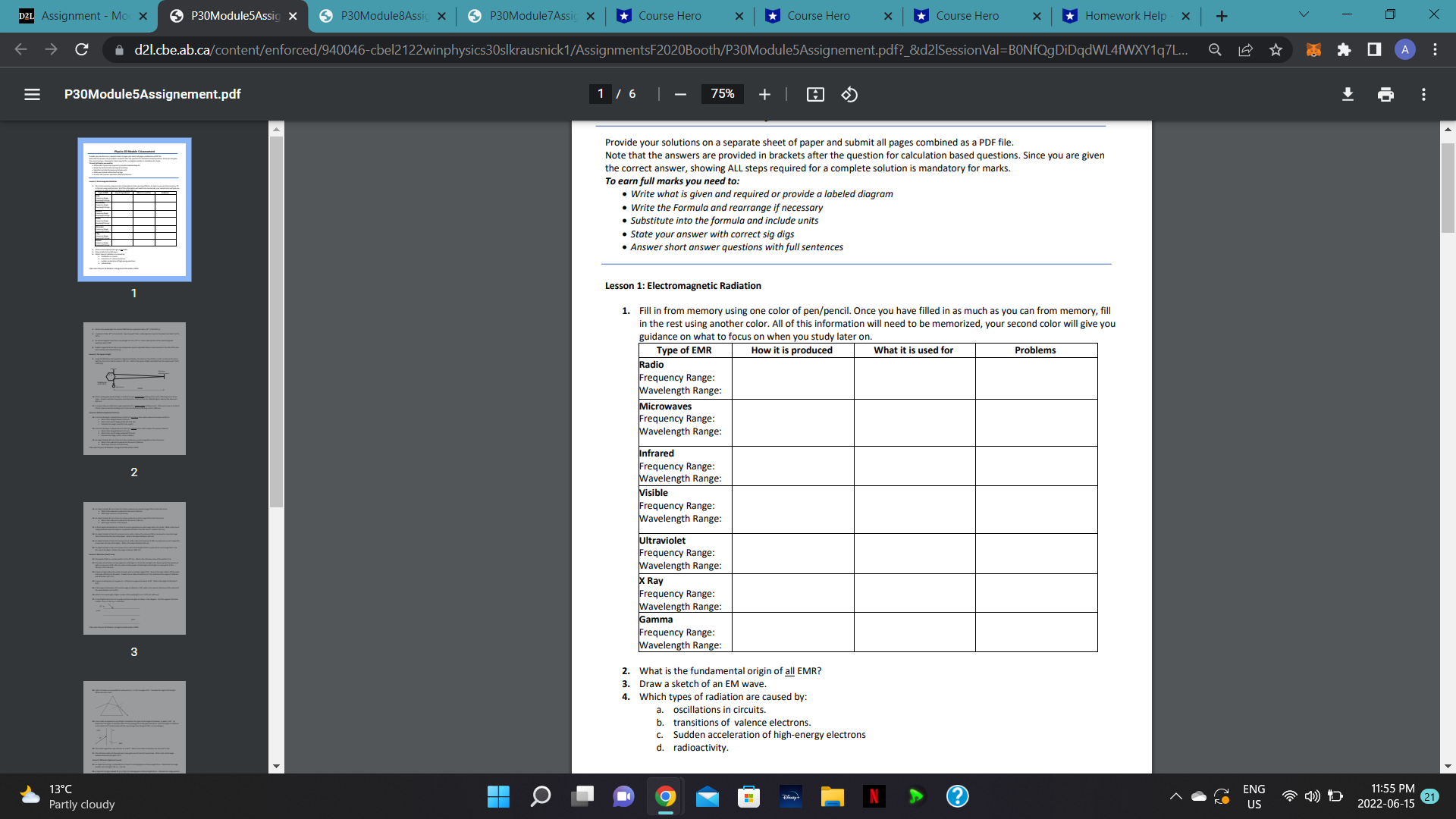
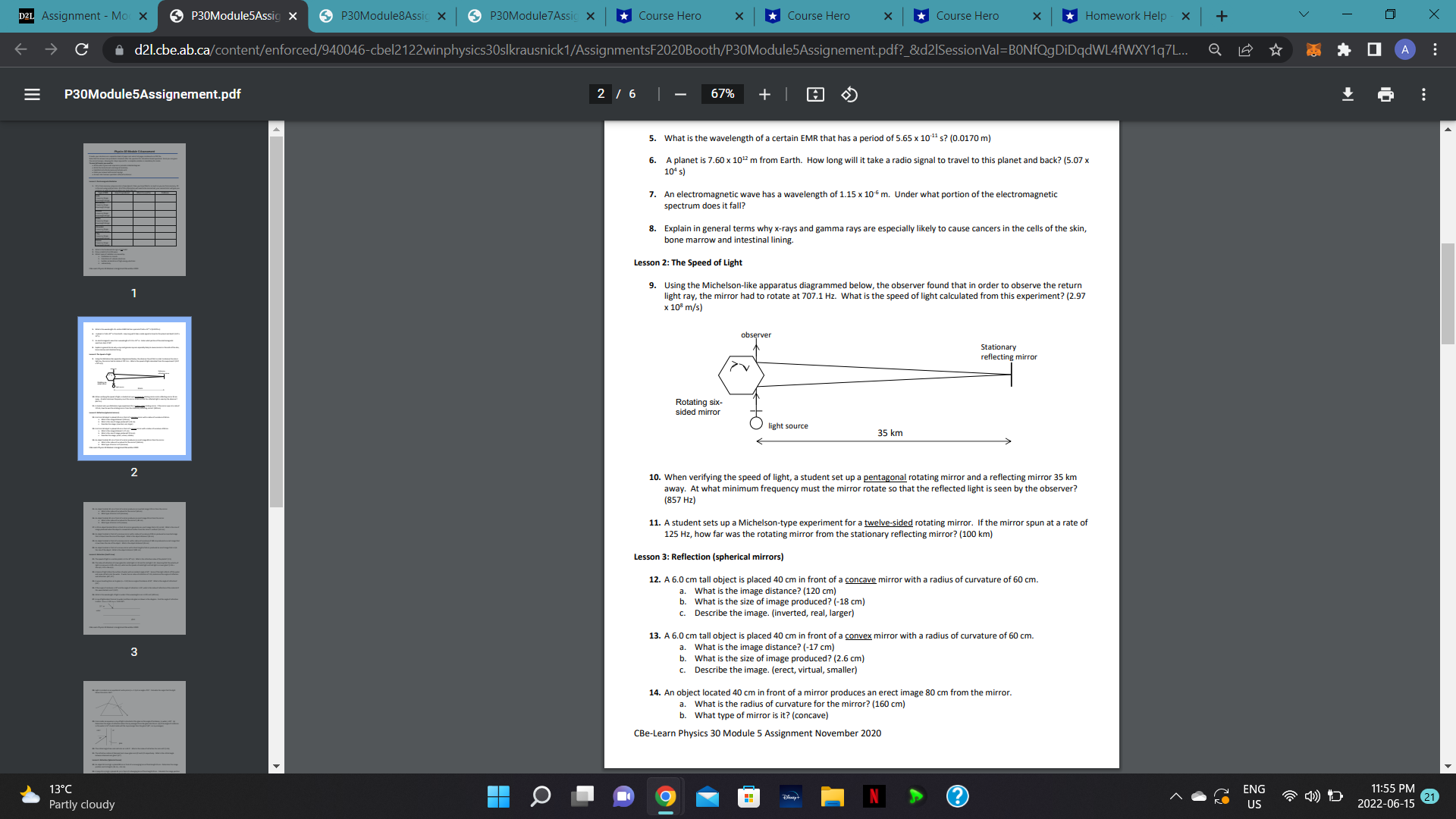
D2L Assignment - Mor X P30Module5Assig X P30Module8Assic x P30Module7Assic x Course Hero X *Course Hero * *Course Hero * *Homework Help X + V X C A d21.cbe.ab.ca/content/enforced/940046-cbel2122winphysics30slkrausnick 1/AssignmentsF2020Booth/P30Module5Assignement.pdf?_&d21SessionVal=BONfQgDiDqdWL4fWXY1q7L... 0 A E P30Module5Assignement.pdf 1 /6 | - 75% + Provide your solutions on a separate sheet of paper and submit all pages combined as a PDF file. Note that the answers are provided in brackets after the question for calculation based questions. Since you are given the correct answer, showing ALL steps required for a complete solution is mandatory for marks. To earn full marks you need to: . Write what is given and required or provide a labeled diagram . Write the Formula and rearrange if necessary Substitute into the formula and include units State your answer with correct sig digs Answer short answer questions with full sentences Lesson 1: Electromagnetic Radiation 1. Fill in from memory using one color of pen/pencil. Once you have filled in as much as you can from memory, fill in the rest using another color. All of this information will need to be memorized, your second color will give you guidance on what to focus on when you study later on. Type of EMR How it is produced What it is used for Problems Radio Frequency Range: Wavelength Range: Microwaves Frequency Range: Wavelength Range: Infrared 2 Frequency Range: Wavelength Range: Visible Frequency Range Wavelength Range: Ultraviolet Frequency Range: Wavelength Range: X Ray Frequency Range: Wavelength Range: Gamma Frequency Range: 13 Wavelength Range: 2. What is the fundamental origin of all EMR? 3. Draw a sketch of an EM wave. 4. Which types of radiation are caused by: a. oscillations in circuits. b. transitions of valence electrons. c. Sudden acceleration of high-energy electrons d. radioactivity. 13.C 11:55 PM Partly cloudy N ?) ENG US ( D 2022-06-15 21D2L Assignment - Mo X P30Module5Assig X P30Module8Assic x P30Module7Assic x Course Hero X *Course Hero * *Course Hero * *Homework Help X + V X C d21.cbe.ab.ca/content/enforced/940046-cbel2122winphysics30slkrausnick 1/AssignmentsF2020Booth/P30Module5Assignement.pdf?_&d21SessionVal=BONfQgDiDqdWL4fWXY1q7L.. 0 A E P30Module5Assignement.pdf 2 /6 | - 67% + 5. What is the wavelength of a certain EMR that has a period of 5.65 x 10# s? (0.0170 m) 6. A planet is 7.60 x 1012 m from Earth. How long will it take a radio signal to travel to this planet and back? (5.07 x 104 5) 7. An electromagnetic wave has a wavelength of 1.15 x 105 m. Under what portion of the electromagnetic spectrum does it fall? 8. Explain in general terms why x-rays and gamma rays are especially likely to cause cancers in the cells of the skin, bone marrow and intestinal lining. Lesson 2: The Speed of Light 9. Using the Michelson-like apparatus diagrammed below, the observer found that in order to observe the return light ray, the mirror had to rotate at 707.1 Hz. What is the speed of light calculated from this experiment? (2.97 x 10# m/s) observer Stationary reflecting mirror Rotating six- sided mirror light source 35 km 2 10. When verifying the speed of light, a student set up a pentagonal rotating mirror and a reflecting mirror 35 km away. At what minimum frequency must the mirror rotate so that the reflected light is seen by the observer? (857 Hz) 11. A student sets up a Michelson-type experiment for a twelve-sided rotating mirror. If the mirror spun at a rate of 125 Hz, how far was the rotating mirror from the stationary reflecting mirror? (100 km) Lesson 3: Reflection (spherical mirrors 12. A 6.0 cm tall object is placed 40 cm in front of a concave mirror with a radius of curvature of 60 cm. a. What is the image distance? (120 cm) b. What is the size of image produced? (-18 cm c. Describe the image. (inverted, real, larger) 13. A 6.0 cm tall object is placed 40 cm in front of a convex mirror with a radius of curvature of 60 cm. 13 a. What is the image distance? (-17 cm) b. What is the size of image produced? (2.6 cm) c. Describe the image. (erect, virtual, smaller) 14. An object located 40 cm in front of a mirror produces an erect image 80 cm from the mirror. a. What is the radius of curvature for the mirror? (160 cm) b. What type of mirror is it? (concave) CBe-Learn Physics 30 Module 5 Assignment November 2020 13.C O 11:55 PM Partly cloudy N ? ENG US ( D 2022-06-15 21
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


