@ hi tutor please assist
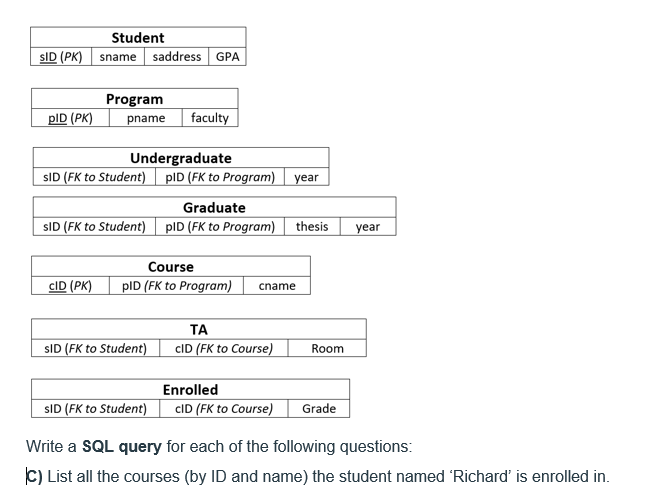
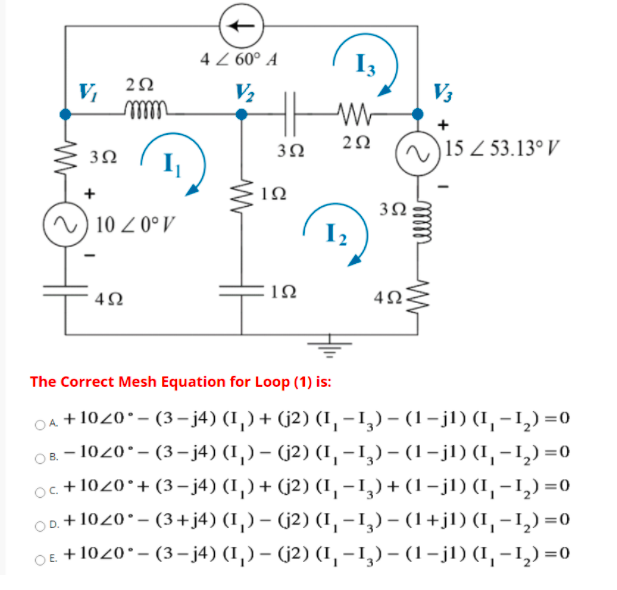
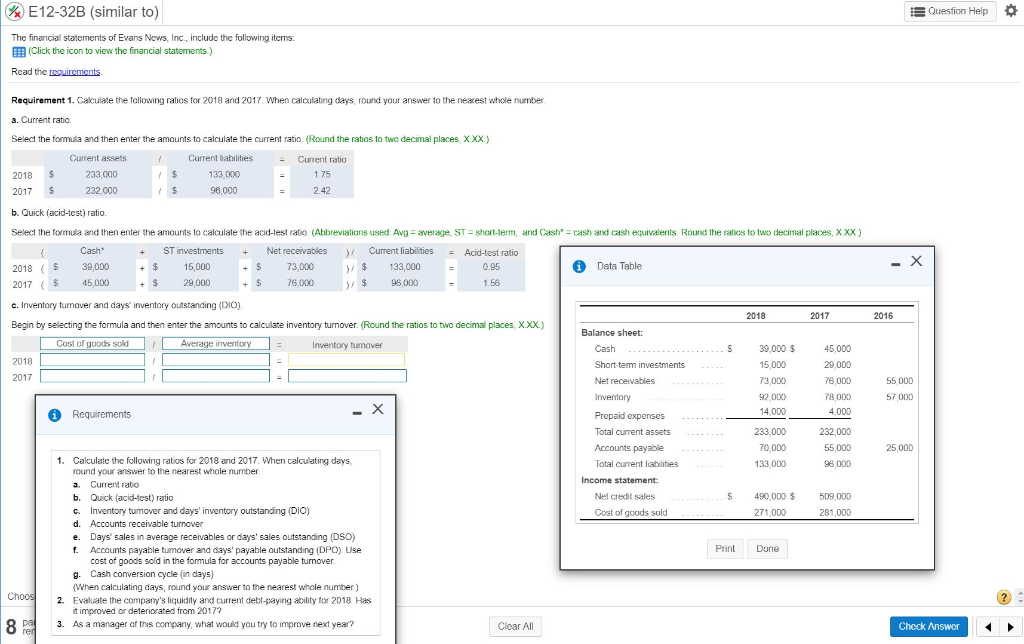
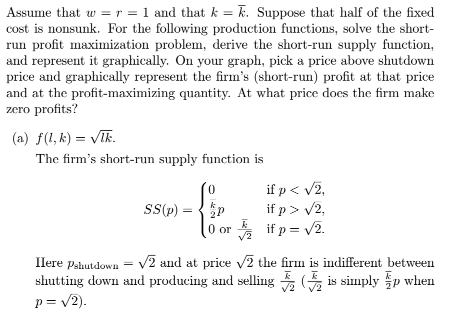
This is Actuarial Science 9. Sam purchased a stock that pays dividends. of 2Dl] at the end of the first year and increases by 5D each yearthereafter. At an annual effective interest rate of i, the price of this stock: is 46,3513. Calculate i. T. Consider a share of stock that pays annual dividends as follows: 200, 2il.09]l, EDil'E'}, 2UD.C|9}"2, , 2D{1.l]9]"12 at times CI, 1, 2, , 12 and level payments of 2DI]{1.D'9]"12 afterward at times 13, 14, Find the purchase price of this share of stock at an annual effective rate of interest i = 4%. 5. A stock pays a dividend of S at the end of the i'th year {at time 1"], 1with each subsequent annual dividend being k': greater than the preceding one. Find it ifthe price of this stock is 32,221.52 at an annual effective yield rate of 3%. Hint: The dividend discount model gives the price of the stoclc one year before the first dividend. Student SID (PK] sname saddress GPA Program PID (PK) pname faculty Undergraduate SID (FK to Student) PID (FK to Program) year Graduate SID (FK to Student) pID (FK to Program) thesis year Course CID (PK) PID (FK to Program) cname TA SID (FK to Student) CID (FK to Course) Room Enrolled SID (FK to Student) CID (FK to Course) Grade Write a SQL query for each of the following questions: [C) List all the courses (by ID and name) the student named 'Richard' is enrolled in.4 2 60 A 13 V 20 V2 V3 mm + 30 20 30 N 15 2 53.13. V + 2 10 30 10 ZOV 1 2 40 10 The Correct Mesh Equation for Loop (1) is: OA + 1020 - (3-j4) (1 ) + (2) (1 -12) - (1-j1) (1-12)=0 OB. - 1020 - (3-14) (1,) - (2) (1, -12) - (1-j1) (1,-1,)=0 Oc. + 1020.+ (3-j4) (1 )+ (12) (1, - 1,)+ (1-j1) (1-1,)=0 OD. + 1020 - (3+j4) (1 ) - (2) (1, -1,) - (1+j1) (1-1,)=0 OE + 1020 - (3-j4) (1 ) - (2) (1, -1,)- (1-j1) (1, -1,)=0E12-32B (similar to) Question Help The financial statements of Evans News, Inc., include the following items: (Click the icon to view the financial statements.) Read the requirements. Requirement 1. Calculate the following ratios for 2018 and 2017. When calculating days, round your answer to the nearest whole number. a. Current ratio. Select the formula and then enter the amounts to calculate the current ratio. (Round the ratios to two decimal places, X xx ) Current assets Current habilities Current ratio 2018 233,000 133 000 1.75 2017 $ 232,000 96,000 2.42 b. Quick (acid-test) ratio. Select the formula and then enter the amounts to calculate the acid-test ratio (Abbreviations used: Avg = average, ST = short-term, and Cash* = cash and cash equivalents. Round the ratios to two decimal places, XXX ) Cash ST investments Net receivables )/ Current liabilities Acid-test ratio 2018 ( $ 38,000 15,000 73,000 )/ $ 133,000 = 0.25 Data Table - X 2017 $ 45,0DO 29,000 76,000 )/ $ 96,DOD 1 56 c. Inventory turnover and days' inventory outstanding (DIO), 2018 2017 2016 Begin by selecting the formula and then enter the amounts to calculate inventory turnover. (Round the ratios to two decimal places, X.XX.) Balance sheet: Cost of goods sold Average inventory Inventory tumover Cash - . . . . . 5 30,000 $ 45,000 2018 Short-term investments 15,000 29,000 2017 Net receivables 73,000 76,000 55,000 Inventory 78,000 57,000 1 Requirements - X Prepaid expenses 14.000 4,000 Total current assets 233,000 232,000 Accounts payable 70,0DO 55,000 25,000 Calculate the following ratios for 2018 and 2017. When calculating days, Total current liabilities 133,000 96,000 round your answer to the nearest whole number a. Current ratio Income statement b. Quick (acid-test) ratio Net credit sales 490,000 $ 509,000 C. Inventory turnover and days' inventory outstanding (DIO) Cost of goods sold 271.000 281,000 d. Accounts receivable turnover e . Days' sales in average receivables or days' sales outstanding (DSO) f. Accounts payable tumover and days' payable outstanding (DPO) Use Print Done cost of goods sold in the formula for accounts payable turnover. g. Cash conversion cycle (in days) (When calculating days, round your answer to the nearest whole number. ) Choos Evaluate the company's liquidity and current debt-paying ability for 2018 Has ? it improved or deteriorated from 2017? 8 pa ren 3. As a manager of this company, what would you try to improve next year? Clear All Check Answer5.3 (0) Ambrose, the nut and berry consumer, has a utility function U(21, 12) = 4vm1 + 12, where m1 is his consumption of nuts and 72 is his consumption of berries. (b) Suppose that the price of a unit of nuts is 1, the price of a unit of berries is 2. and Ambrose's income is 24. How many units of nuts does he choose to buy? 16 (c) How many units of berries? 4 units. (d) Find some points on the indifference curve that gives him a utility of 25 (e) Now suppose that the prices are as before. but Ambrose's income is 34. How many units of nuts will he choose? 16 units. How many units of berries? 9 units. (f) Now let us explore a case where there is a "boundary solution." Sup- pose that the price of nuts is still 1 and the price of berries is 2, but Ambrose's income is only 9. What is the slope of his indifference curve at the point (9,0)? - 2/3. (g) What is the slope of his budget line at this point? -1/2. (h) Which is steeper at this point, the budget line or the indifference curve? Indifference curve. (i) Can Ambrose afford any bundles that he likes better than the point (9, 0)? No.Assume that w = = 1 and that * = k. Suppose that half of the fixed cost is nonsunk. For the following production functions, solve the short- run profit maximization problem, derive the short-run supply function, and represent it graphically. On your graph, pick a price above shutdown price and graphically represent the firm's (short-run) profit at that price and at the profit-maximizing quantity. At what price does the firm make zero profits? (a) f(1, k) = VIK. The firm's short-run supply function is if p v2. 19 0 or V2 if p = v2. Here Pahutdown - V2 and at price v 2 the firm is indifferent between shutting down and producing and selling % (2 is simply up when p = v2).(b) f (1, k ) = 1aka. In this case we have SC(() = # + k, NSC(q) = + 4, ANSO(q) = & + 1, SAC(q) = 4 + 4, and SMO(q) = 2 (soc Figure 1). Recall that the firm shuts down if p > 0. The q that minimizes ANSO(q) is ka "T. It can be found by setting ANSC(q) = SMC(q) and solving for q. The minimum of ANSC(q) (i.e., Pshutdown) is 343 It can be found by plugging & into either 13 SMC(q) or ANSC(q). Given p > Pshutdown, there is only one q such that p = SMO(): 4 = V 3. ke . Therefore, if pe 3ka 43 SS(p) = kp if p > wa 43 0 or if p = 3k$ (see Figure 1)- Consider price p* in Figure 1. At p* and at the corresponding profit- maximizing quantity, call it q', the firm makes negative (short-run) profits. Profits at (p*, q') are p*q* - SC(q*) = q"(p* - SAC(q*)), so (short-run) profits at (p*, q' ) are equal to negative the blue area of the rectangle in Figure 1. The price at which (short-run) profits are zero is the minimum of SAC(q).Part 2: Questions from the Instructor. 1. The following equations describe the macro-economy: Consumption function: C = 50 + 0.5(Y - T) Taxes: T = 0.2Y Government spending: G = 100 Investment: 200 - 10000i Real Money supply: M/P = 100 Real Money demand: Md /P = 2Y - 20000i Notice that taxes are no longer fixed: they are proportional to the amount of income. a) Derive the IS and LM curves. b) Calculate the equilibrium output and interest rate. c) At the equilibrium, is the government having a budget surplus, budget deficit, or balanced budget? d) Suppose the government wants to adjust the tax rate from 0.2 to another level in order to change output to 260. What should that new tax rate be? Show your steps clearly