Ho to do the Question 7-10, need question 7-10, please. below include question 7-10 and answer 1-6.
7. Prepare a combined cash budget, using the following format
8. Budgeted manufacturing cost per unit
9. budgeted income statement for the ending march 31
10.partial budgeted balance sheet for march 31


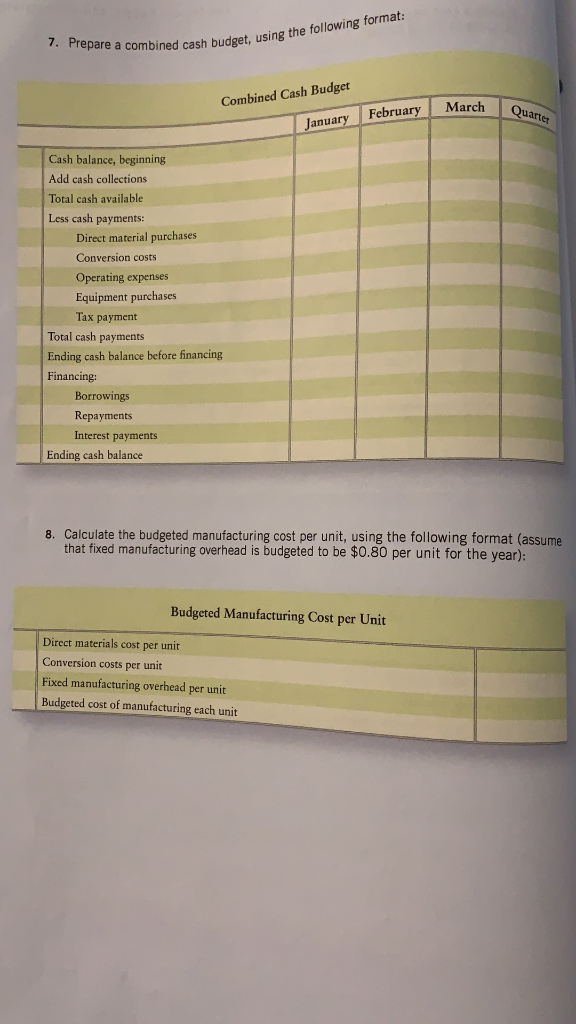

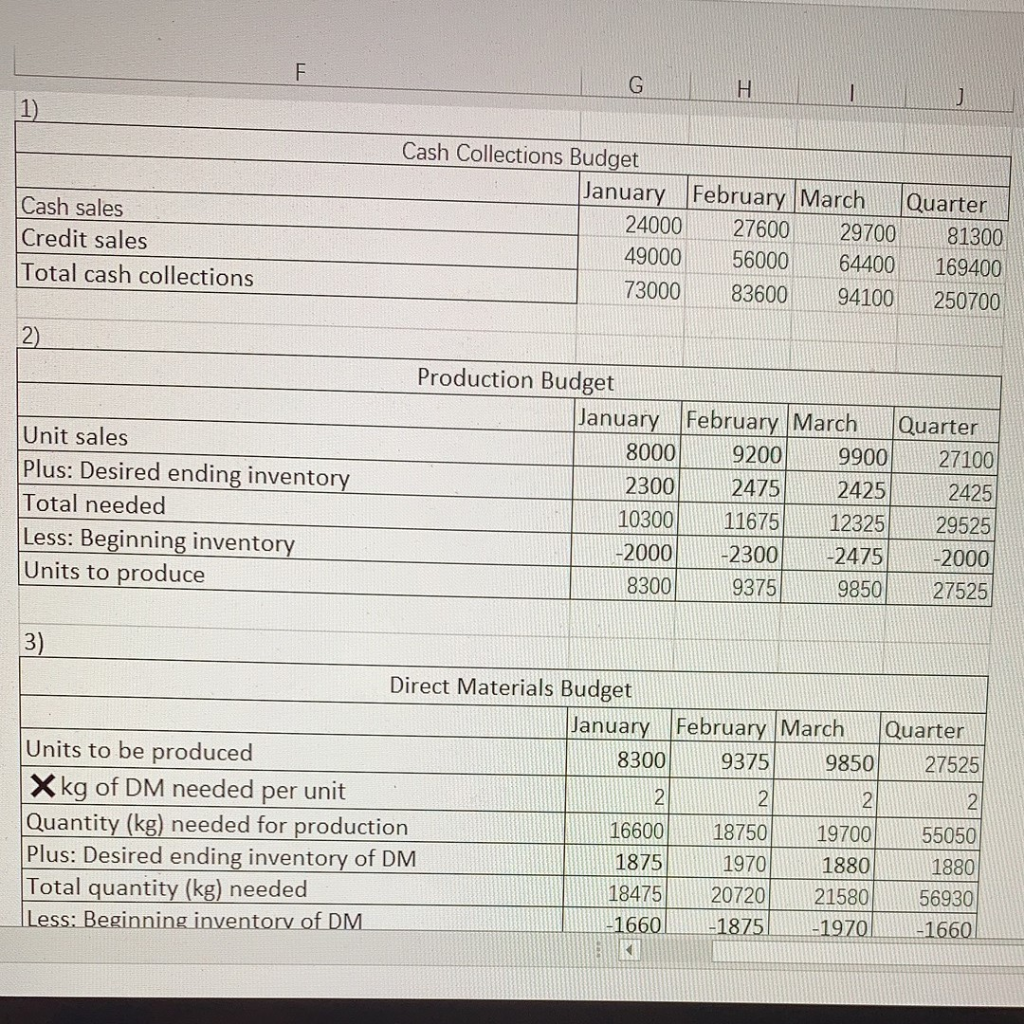
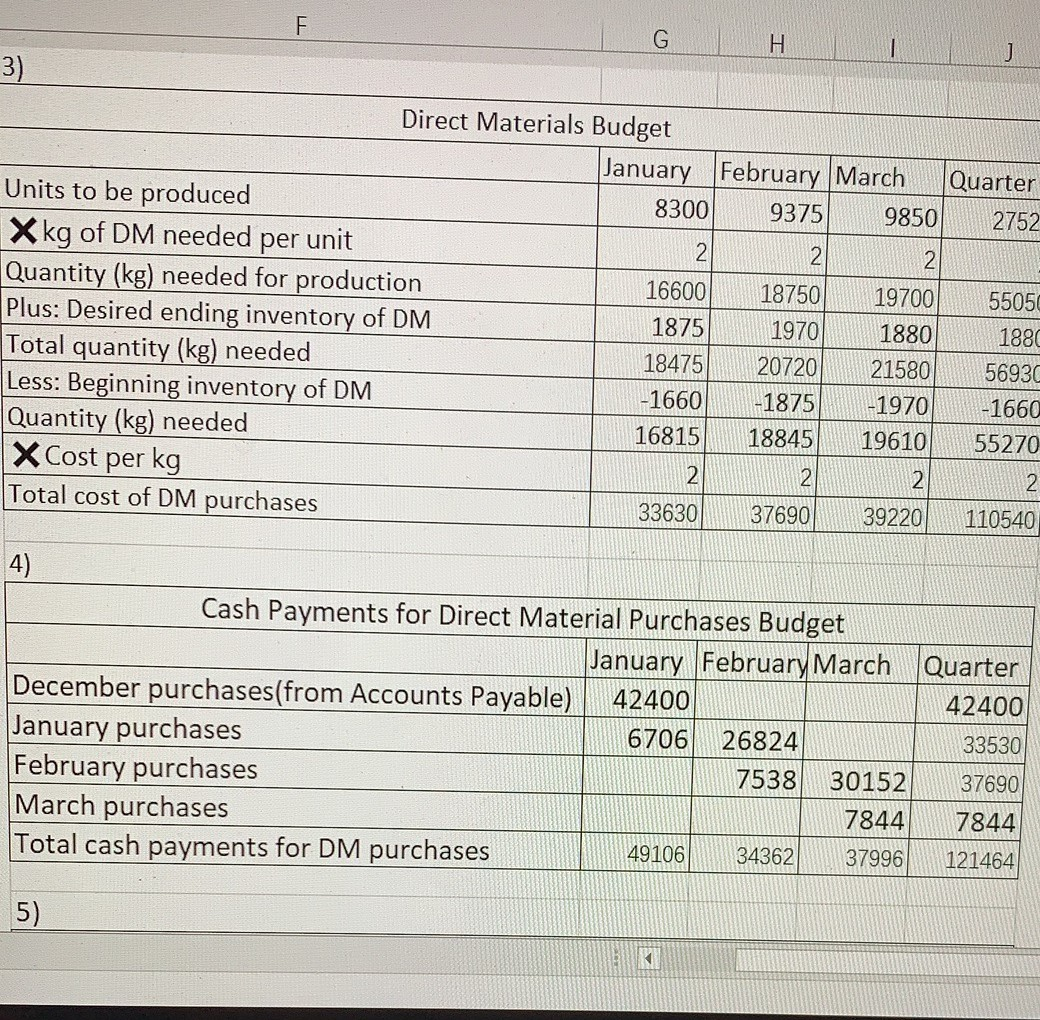
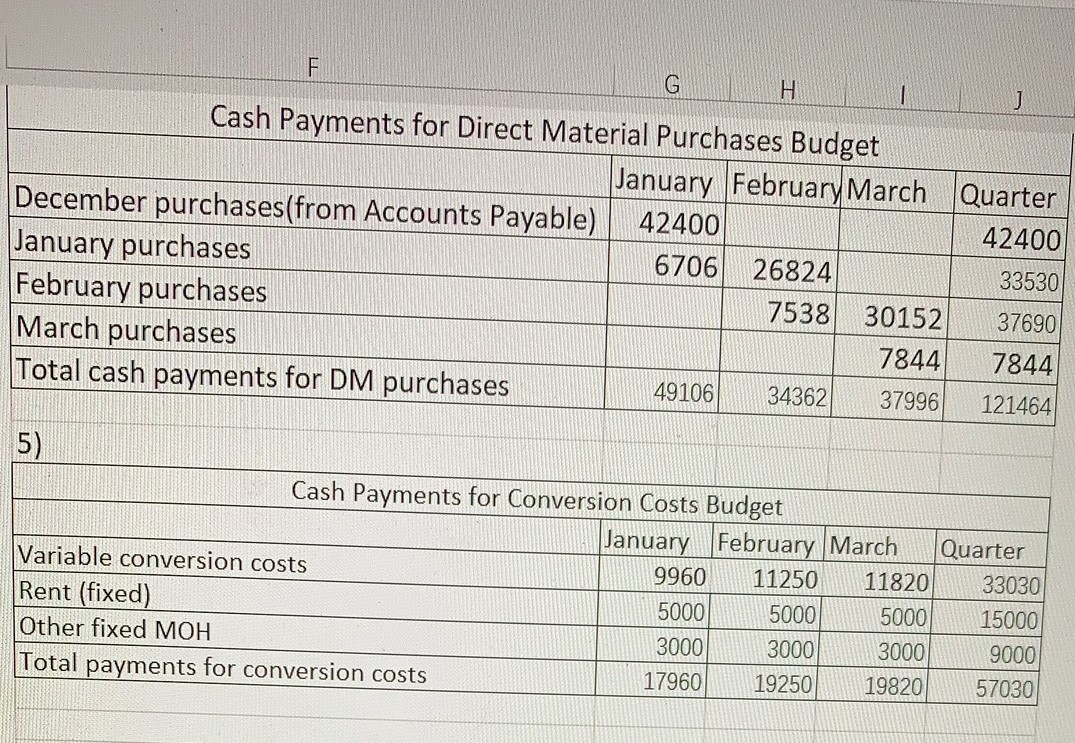
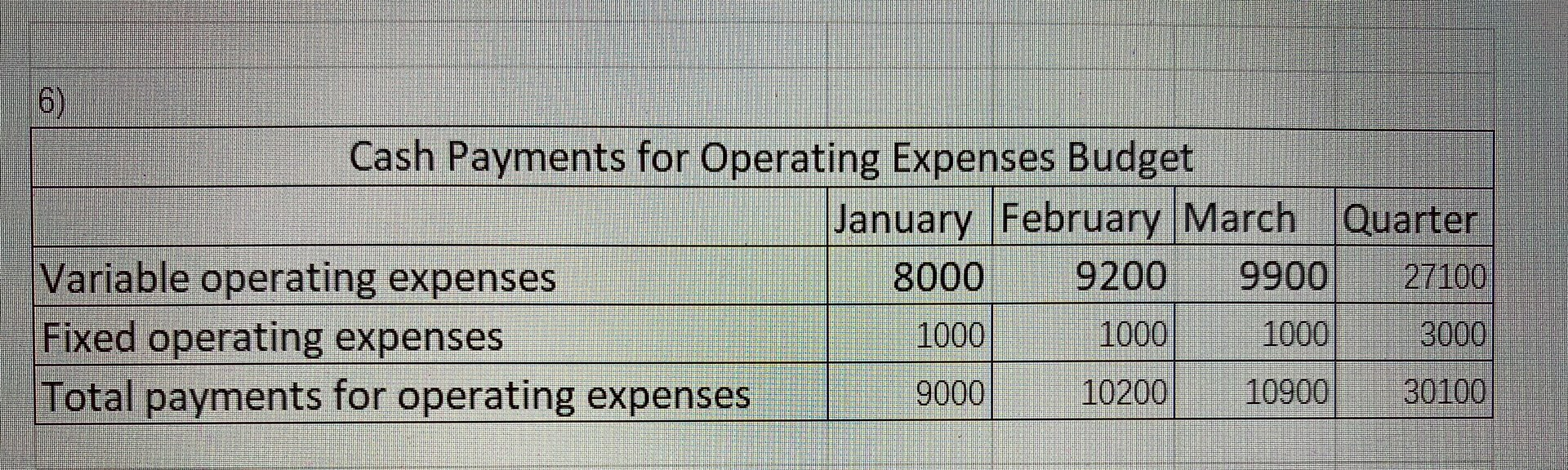
PRUDLEMS Group A P9-61A Solve a comprehensive budgeting problem (Learning Objectives 2 & 3) Cicek Manufacturing is preparing its master budget for the first quarter of the upcoming year. The following data pertain to Cicek Manufacturing's operations: Current Assets as of December 31 (prior year): Cash. Accounts receivable, net. Inventory Property, plant, and equipment, net .. Accounts payable Capital stock..... Retained earnings.... $ 4,500 $ 49,000 $ 15,320 $121,500 $ 42,400 $125,000 $ 22,920 a. Actual sales in December were $70.000, Selling price per unit is projected to remain stable at $10 per unit throughout the budget period, Sales for the first five months of the upcoming year are budgeted to be as follows: January... February March.. April...... $80,000 $92,000 $99,000 $97.000 $85,000 May............ ............................................. b. Sales are 30% cash and 70% credit. All credit sales are collected in the month following the sale. C. Cicek Manufacturing has a policy that states that each month's ending inventory of finished goods should be 25% of the following month's sales (in units). d. Of each month's direct material purchases, 20% are paid for in the month of purchase, while the remainder is paid for in the month following purchase. Two kilograms of direct material is needed per unit at $2/kg. Ending inventory of direct materials should be 10% of next month's production needs. e. Monthly manufacturing conversion costs are $5,000 for factory rent, $3,000 for other fixed manufacturing expenses, and $1.20 per unit for variable manufacturing overhead. No depreciation is included in these figures. All expenses are paid in the month in which they are incurred. f. Computer equipment for the administrative offices will be purchased in the upcoming quarter. In January, Cicek Manufacturing will purchase equipment for $5,000 (cash), while February's cash expenditure will be $12,000 and March's cash expenditure will be $16,000. g. Operating expenses are budgeted to be $1 per unit sold plus fixed operating expenses of $1,000 per month. All operating expenses are paid in the month in which they are incurred. h. Depreciation on the building and equipment for the general and administrative offices is budgeted to be $6,000 for the entire quarter, which includes depreciation on new acquisitions. i. Cicek Manufacturing has a policy that the ending cash balance in each month must be at least $4,000. It has a line of credit with a local bank. The company can borrow in increments of $1,000 at the beginning of each month, up to a total outstanding loan balance of $100,000. The interest rate on these loans is 1% per month simple intere (not compounded). Cicek Manufacturing pays down on the line of credit balance if it excess funds at the end of the quarter. The company also pays the accumulated intere at the end of the quarter on the funds borrowed during the quarter. expense. The Coincome tax rate is projected to the end of February in estimated tarteres e company's income tax rate is proiected to be 30% of operating income less interes ise. The company pays $10.000 cash at the end of February in estimated taxes 7. Prepare a combined cash budget, cash budget, using the following format: Combined Cash Budget March Quarter January February Cash balance, beginning Add cash collections Total cash available Less cash payments: Direct material purchases Conversion costs Operating expenses Equipment purchases Tax payment Total cash payments Ending cash balance before financing Financing: Borrowings Repayments Interest payments Ending cash balance 8. Calculate the budgeted manufacturing cost per unit, using the following format (assume that fixed manufacturing overhead is budgeted to be $0.80 per unit for the year): Budgeted Manufacturing Cost per Unit Direct materials cost per unit Conversion costs per unit Fixed manufacturing overhead per unit Budgeted cost of manufacturing each unit 9. Prepare a budgeted income statement for the quarter ending March 31, using the following format: Budgeted Income Statement For the Quarter Ending March 31 Pront .............. Sales ..... Cost of goods sold*.... Gross profit. Operating expenses ................ Depreciation....... Operating income.. Less interest expense .............. Less provision for income taxes... Net income..... * Cost of goods sold = Budgeted cost of manufacturing each unit x Number of units sold 10. Prepare a partial budgeted balance sheet for March 31. Follow the same format as t original balance sheet provided for December 31, adding Loans Payable and Income Tax Payable. H Cash sales Credit sales Total cash collections Cash Collections Budget January February March Quarter 24000 27600 29700 81300 49000 56000 64400 169400 73000 83600 94100 250700 Unit sales Plus: Desired ending inventory Total needed Less: Beginning inventory Units to produce Production Budget January February March Quarter 8000 9200 990027100 2300 2475 2425 2425 10300 11675 12325 2 9525 -2000 -2300 -2475 -2000 8300 9375 9 850 27525 3) Direct Materials Budget January February March Quarter Units to be produced 8300 9375 9850 27525 X kg of DM needed per unit . 222 Quantity (kg) needed for production 16600 18750 19700 55050 Plus: Desired ending inventory of DM 1875 1970 1 880 1880 Total quantity (kg) needed 18475 20720 2158056930 Less: Beginning inventory of DM 1660 -1875 -1970) MINI-1660 Direct Materials Budget January February March Quarter Units to be produced 8300 9375 9850 2752 X kg of DM needed per unit 22 Quantity (kg) needed for production 16600 18750 19700 5505 Plus: Desired ending inventory of DM 1875 1970 1880 1881 Total quantity (kg) needed 18475 20720 21580 56931 Less: Beginning inventory of DM -1660 -1875 -1970 -1660 Quantity (kg) needed 1681518845/ 19610 55270 X Cost per kg 2 Total cost of DM purchases 33630/ 37690/ 39220 110540 Cash Payments for Direct Material Purchases Budget January February March Quarter December purchases(from Accounts Payable) 42400 42400 January purchases 6706 26824 33530 February purchases 7538 30152 37690 March purchases 7844 7844 Total cash payments for DM purchases 49106 34362 37996 121464 G H I J Cash Payments for Direct Material Purchases Budget January February March Quarter December purchases(from Accounts Payable) 42400 42400 January purchases 6706 26824 33530 February purchases 7538 30152 37690 March purchases 7844 7844 Total cash payments for DM purchases 49106 34362 37996 121464 Cash Payments for Conversion Costs Budget MUA January February March Quarter Variable conversion costs | 9960 11250 1182033030 Rent (fixed) 5000 5000 5000 15000 Other fixed MOH 3000 3000 3000 9000 Total payments for conversion costs 17960 19250 19820 57030 Cash Payments for Operating Expenses Budget January February March Quarter Variable operating expenses 8000 9200 990027100 Fixed operating expenses 1000 1000 1000 3000 Total payments for operating expenses 9000 10200 10900 30100 100 1000 100














