Question: home / study / engineering / computer science / computer science questions and answers / python: windchill calculator gui using tkinter this assignment is cacluating
home / study / engineering / computer science / computer science questions and answers / python: windchill calculator gui using tkinter this assignment is cacluating the windchill ...
Question: Python: Windchill Calculator GUI using tkinter This assignment is cacluating the windchill except...
Python: Windchill Calculator GUI using tkinter
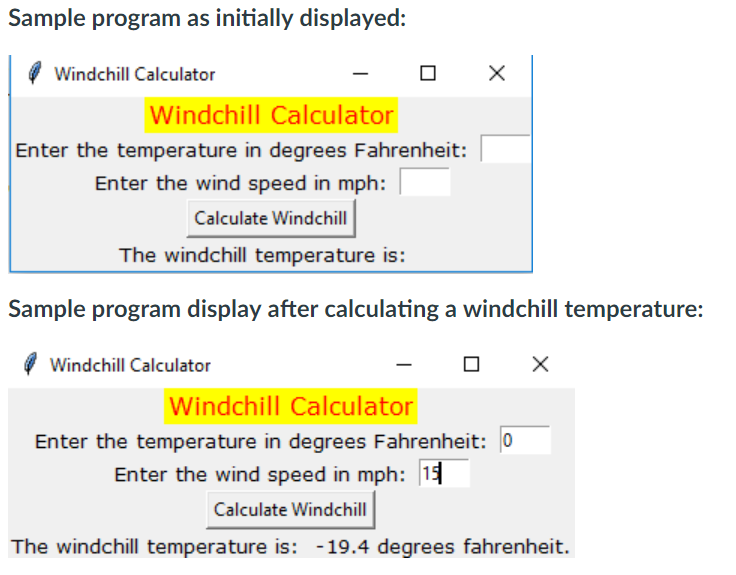
This assignment is cacluating the windchill except that this program will have a GUI interface to the user instead of a console interface. This program will demonstrate the difference in programming using event driven programming. The GUI will have the appearance of the example demonstrated below. You will use the calculateWindchill function that you wrote for Programming Assignment 11 to calculate the windchill in this program. You can assume that the wind speed and Fahrenheit temperature entered by the user is valid. You may do validation checking, if you desire. The GUI will contain two entry widgets for entering the temperature and wind speed and a label for displaying the windchill as shown in the example below. Just a reminder: there should be no loop in your program to keep the GUI running. A good start for this assignment would be to base it on the kilo_converter2 program in the 'tkinter python programs' folder.
Kilo_converter2 program:
import tkinter class KiloConverterGUI: def __init__(self): # Create the main window. self.main_window = tkinter.Tk() # Create three frames to group widgets. self.top_frame = tkinter.Frame() self.mid_frame = tkinter.Frame() self.bottom_frame = tkinter.Frame() # Create the widgets for the top frame. self.prompt_label = tkinter.Label(self.top_frame, \ text='Enter a distance in kilometers:') self.kilo_entry = tkinter.Entry(self.top_frame, \ width=10) # Pack the top frame's widgets. self.prompt_label.pack(side='left') self.kilo_entry.pack(side='left') # Create the widgets for the middle frame. self.descr_label = tkinter.Label(self.mid_frame, \ text='Converted to miles:') # We need a StringVar object to associate with # an output label. Use the object's set method # to store a string of blank characters. self.value = tkinter.StringVar() # Create a label and associate it with the # StringVar object. Any value stored in the # StringVar object will automatically be displayed # in the label. self.miles_label = tkinter.Label(self.mid_frame, \ textvariable=self.value) # Pack the middle frame's widgets. self.descr_label.pack(side='left') self.miles_label.pack(side='left') # Create the button widgets for the bottom frame. self.calc_button = tkinter.Button(self.bottom_frame, \ text='Convert', \ command=self.convert) self.quit_button = tkinter.Button(self.bottom_frame, \ text='Quit', \ command=self.main_window.destroy) # Pack the buttons. self.calc_button.pack(side='left') self.quit_button.pack(side='left') # Pack the frames. self.top_frame.pack() self.mid_frame.pack() self.bottom_frame.pack() # Enter the tkinter main loop. tkinter.mainloop() # The convert method is a callback function for # the Calculate button. def convert(self): # Get the value entered by the user into the # kilo_entry widget. kilo = float(self.kilo_entry.get()) # Convert kilometers to miles. miles = kilo * 0.6214 # Convert miles to a string and store it # in the StringVar object. This will automatically # update the miles_label widget. self.value.set(miles) # Create an instance of the KiloConverterGUI class. kilo_conv = KiloConverterGUI()
Assignment 11 program:
print ("This program calculates the windchill from the fahrenheit temperature and the wind speed.") # This creates a function which gets the user input and returns the temperature and wind speed. def read_input(): temperature = int(input("Enter the Fahrenheit temperature: ")) speed = int(input("Enter the wind speed: ")) return temperature, speed # This calculates the winchill from the inputed temperature and speed. def calculateWindchill(temperature, speed): return 35.74 + 0.6215 * temperature - 35.75 * speed**0.16 + 0.4275 * temperature * speed**0.16 temperature, speed = read_input() # This tells the user what the calculated windchill is. print("The windchill is: ", format(calculateWindchill(temperature, speed),'.1f')) # This allows the user to run through the program again or quit. decision = input("Would you like to calculate another windchill? Enter 'y' or 'n': ") # This creates a while loop to continuously ask the user for input till they no longer want a calculation. # When the user types in 'n', the program stops. while decision == 'n': break; # If the user did not type in 'n', the program continues. else: # This gets the input from the user. temperature = int(input("Enter the Fahrenheit temperature: ")) speed = int(input("Enter the wind speed: ")) # This recalls the function calculateWindchill and retures the calculates wind chill. print("The windchill is: ", format(calculateWindchill(temperature, speed), '.1f')) # This allows the user to decide whether or not they want to loop through the program again. decision = input("Would you like to calculate another windchill? Enter 'y' or 'n': ")Thanks!
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


