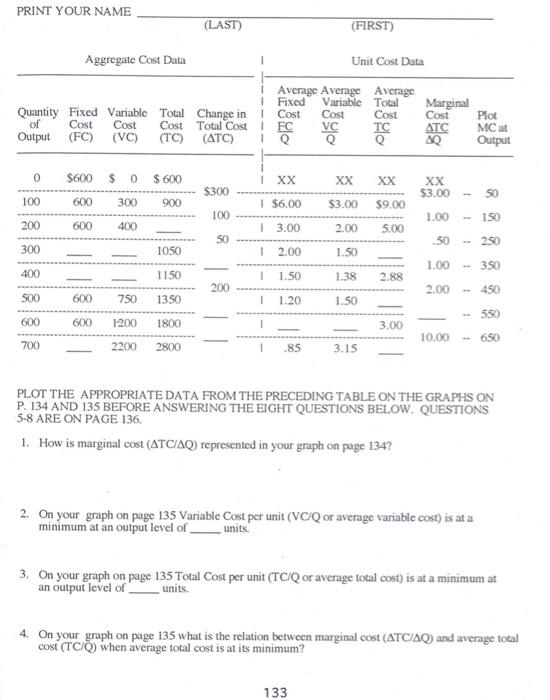
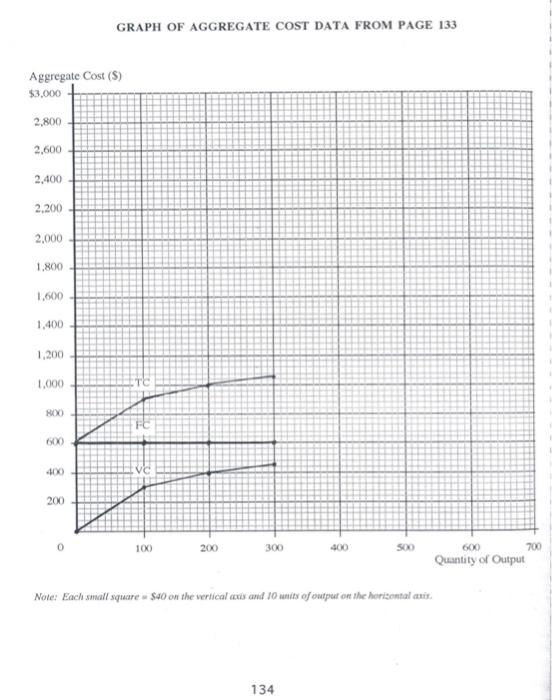
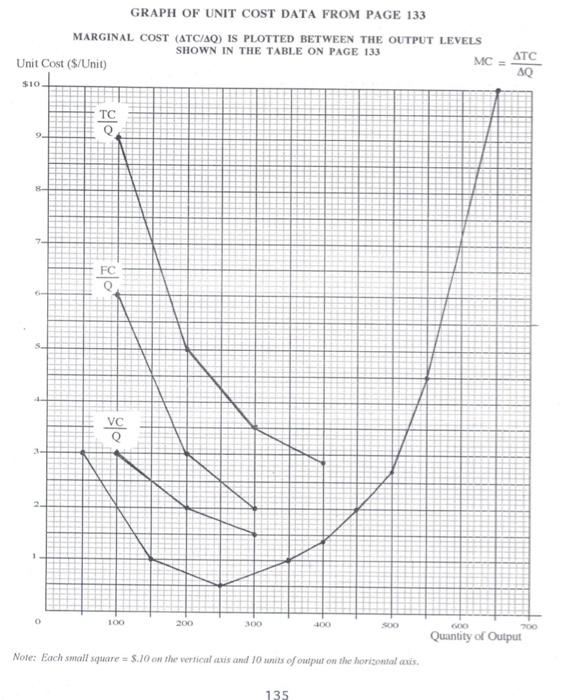
Homework Problem #19 Costs PRINT YOUR NAME (LAST) (FIRST) Try your best to answer each of the following questions. Your answers may be collected, checked for accuracy and returned to you later. 1. (Fill in the blanks.) M. I. Fortunate was employed as plant manager for a corporation at a salary of $50,000 a year and she had savings of $100,000 invested in securities which yielded an 8 percent annual income. She went into business for herself, investing all her savings in the enterprise. At the end of the first year, her accounts showed a net income of $55,000 after all expenses of operation. One accountant said this accounting profit represented a 55 percent return on her $100,000 investment Another accountant, who had taken introductory microcconomics, said, "No, you should pay yourself the $50,000 salary you would have cared anyway, and your accounting profit of $5,000 represents a return of 5 percent on your investment of $100,000. A serious student of introductory microeconomics, however, should say, "No, your true cconomic profit from going into business for yourself is $_ and this is a return of 9.* Was M. L. Fortunate, fortunate? (Yes/No Why? 11. (Fill in the blanks and then some.) The table on the next page shows a comprehensive set of cost data for a firm, with a given plant, at various levels of output. Study this table for awhile to understand how it is set up Marginal cost is the additional cost of producing an additional unit of output (ACIAD). In producing an additional 100 units of output adds $300 to total cost the marginal cost per unit is $300/100 = $30.00, etc., etc. Note that in the table the marginal changes are located between output levels. After you have filled in the blanks in the table on page 133, finish plotting the aggregate cost data for fixed cost, variable cost, and total cost (not change in total cost) on the axes provided on page 134. Also, finish plotting the unit cost data for FC/Q, VCQ, TCIQ and ATC/AQ on the set of axes provided on page 135. Note that marginal cost (ATCAQ) is plotted mid-way between the levels of output given in the first column of the tablc on page 133 After you have finished plotting, answer the eight questions beginning under the table on page 133 and continuing on page 136. 132 PRINT YOUR NAME (LAST) (FIRST) Aggregate Cost Data Unit Cost Data Average Average Average 1 Fixed Variable Total Quantity Fixed Variable Total Change in Cost Cost Cost of Cost Cost Cost Total Cost 1 FC VC TC Output (FC) (VC) (TC) (ATC) 1 Q Q Marginal Cost ATC AQ Plot MC at Output 0 $600 $0 $ 600 IXX XX XX xx $3.00 $300 50 100 600 300 900 I $6.00 $3.00 $9.00 100 1.00 150 200 600 400 13.00 2.00 5.00 SO .50 - 250 300 1050 12.00 1.50 350 400 1150 11.50 1.38 2.88 1.00 2.00 200 450 500 600 750 1350 11.20 1.50 -- 550 600 600 1200 1800 3.00 700 2200 10.00 - 650 2800 1.85 3.15 PLOT THE APPROPRIATE DATA FROM THE PRECEDING TABLE ON THE GRAPHS ON P. 134 AND 135 BEFORE ANSWERING THE EIGHT QUESTIONS BELOW. QUESTIONS 5-8 ARE ON PAGE 136. 1. How is marginal cost (ATC/AQ) represented in your graph on page 134? 2. On your graph on page 135 Variable Cost per unit (VCIQ or average variable cost) is at a minimum at an output level of units. 3. On your graph on page 135 Total Cost per unit (TCIQ or average total cost) is at a minimum at an output level of units. 4. On your graph on page 135 what is the relation between marginal cost (ATC/AQ) and average total cost (TCO) when average total cost is at its minimum? 133 GRAPH OF AGGREGATE COST DATA FROM PAGE 133 Aggregate Cost (5) $3.000 2.800 2,600 2,400 2.200 2,000 1.800 1.600 1.400 1,200 1.000 NEXO 600 400 VC 200 100 200 300 400 SCO 600 700 Quantity of Output Nole: Each small square - $40 on the vertical axis and 10 units of output on the horizontal arit 134 GRAPH OF UNIT COST DATA FROM PAGE 133 MARGINAL COST (ATC/AO) IS PLOTTED BETWEEN THE OUTPUT LEVELS SHOWN IN THE TABLE ON PAGE 133 Unit Cost ($/Unit) MC ATC 40 $10 TC Q 9 7 FC VC 1 100 200 300 100 SO 00 200 Quantity of Output Note: Each small square 5.10 on the vertical axis and 10 units of output on the horizontal axis. 135 5. On your graph on page 135 what is the relation between marginal cost (ATC/AQ) and average vanable cost (VC/) when average variable cost is at its minimum? 6. Explain why marginal cost on a unit cost graph always intersects average total cost and average variable cost at their minimum points 7. On your graph on page 135, what does the vertical distance between the TCIQ curve and VC/Q curve represent? 8. Explain why lixed cost has no influence on marginal cost 136