how do i do periodic inventory systems based off problem 6-4b?

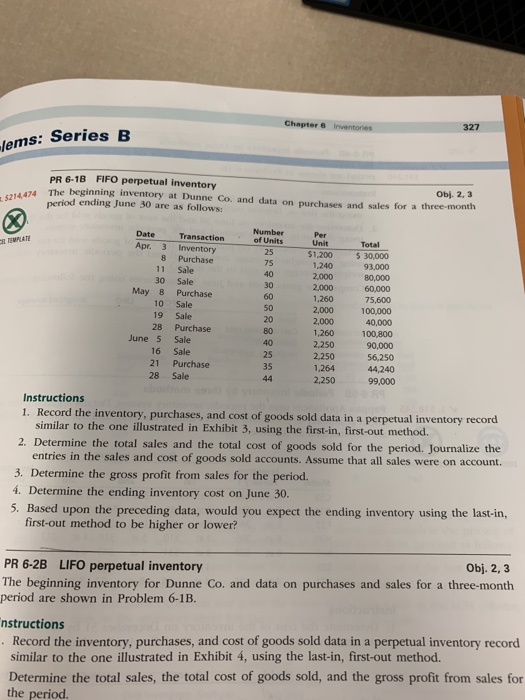
Chapter 6 Inventories Obj. 2, 3 PR 6-4B Periodic inventory by three methods ventory e-month The beginning inventory for Dunne Co and data on purchases and sales for a three-mon $31,240 period are shown in Problem 6-1B. Instructions 1. Determine the inventory on June 30 and the cost of goods sold for the three-month period using the first-in, first-out method and the periodic inventory system. 2. Determine the inventory on June 30 and the cost of goods sold for the three-month period using the last in, first-out method and the periodic inventory system. 3. Determine the inventory on June 30 and the cost of goods sold for the three-month period using the weighted average cost method and the periodic inventory system. (Round the weighted average unit cost to the dollar.) Compare the gross profit and June 30 inventories using the following column headings: FIFO LIFO Weighted Average Sales Cost of goods sold Gross profit Inventory, June 30 PR 6-5B Periodic inventory by three methods Pappa's Appliances uses the periodic inventory system. Details regarding the inventory of appli- ances at January 1, purchases invoices during the year, and the inventory count at December 31 are summarized as follows: Obj. 2,4 Purchases Invoices Model 1st C55 Inventory Count, December 31 011 F32 Inventory, January 1 3 at $1,040 3 9 at 6397 5 at 240 6 at 305 6 at 520 - 4 at 35 H29 K47 533 2nd 3rd at $1,054 3 at $1,060 3 at $1,070 at 645 6 at 666 6 at 675 3 at 260 1 at 260 1 at 280 3 at 310 3 at 316 4 at 317 8 at 5314 at 549 6 at 542 4 at 2224 at 232 - 6 at 36 8 at 37 7 at 39 X74 ructions Determine the Chapters Jems: Series B PR 6-13 FIFO perpetual inventory Obj. 2,3 The beginning inventory at Dunne Co. and data on purchases and sales for a three-month period ending June 30 are as follows: The he 5214.474 Number of Units 30 Date Apr. 3 8 11 30 May 8 10 19 28 June 5 16 21 28 Transaction inventory Purchase Sale Sale Purchase Sale Sale Purchase Sale Sale Purchase Sale Per Unit $1.200 1.200 2.000 2.000 1.260 2,000 2.000 1,260 2.250 2,250 1,264 2.250 Total $ 30.000 93.000 80,000 60.000 75.600 100,000 40,000 100.800 90,000 56,250 44.240 99,000 Instructions 1. Record the inventory, purchases, and cost of goods sold data in a perpetual inventory record similar to the one illustrated in Exhibit 3, using the first-in, first-out method. 2. Determine the total sales and the total cost of goods sold for the period. Journalize the entries in the sales and cost of goods sold accounts. Assume that all sales were on account. 3. Determine the gross profit from sales for the period. 4. Determine the ending inventory cost on June 30. 5. Based upon the preceding data, would you expect the ending inventory using the last-in, first-out method to be higher or lower? PR 6-2B LIFO perpetual inventory Obj. 2, 3 The beginning inventory for Dunne Co, and data on purchases and sales for a three-month period are shown in Problem 6-1B. nstructions Record the inventory, purchases, and cost of goods sold data in a perpetual inventory record similar to the one illustrated in Exhibit 4, using the last-in, first-out method. Determine the total sales, the total cost of goods sold, and the gross profit from sales for the period