How much (in aggregate) did PPR pay to acquire control of Puma? Do you believe that PPR was right to offer 330 Euros per Puma share? Use the 

 information provided in Appendix 5-7 to come up with DCF and relative valuation of Puma.
information provided in Appendix 5-7 to come up with DCF and relative valuation of Puma.
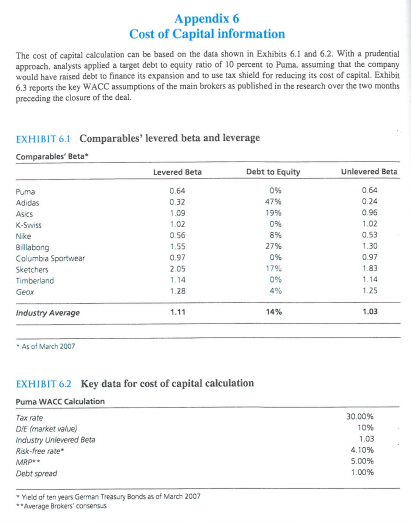
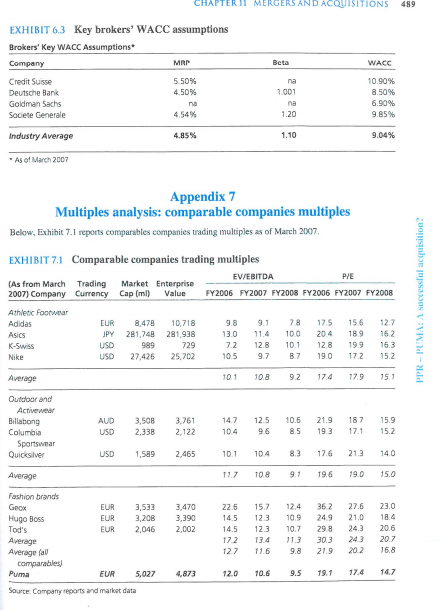
Appendix 5 Puma projected figures (2007-2016) To complete the valuation considerations, the analysts performed a DCF analysis (see Exhibit 5.1). The DCF projections were based on the following assumptions: . For the period running from 2007 to 2009, Puma's income statement projections were based on brokers' consensus. For the following years, estimates have been based on authors' assumptions. Top line growth is expected to level down to terminal growth rate of 2 percent in 2016E. Ebitda Margin is expected to gradually decrease to a constant 17.5 percent after the peak of 18.2 percent forecasted in 2009 on the basis of analysts' consensus. Capex are expected to level down to 120 percent of depreciation in 2016. The depreciation is assumed constant at 10 percent of the previous year operating fixed assets. . Working Capital is expected to be driven by top line growth and to keep constant at 16 percent of sales. A 30 percent stable tax rate is assumed for the entire period running from 2008 to 2016. In 2007, the expected tax rate is equal to 32 percent. EXHIBIT 5.1 Puma cash flow projections Unlevered Free Cash Flow Calculation Actual Brokers' consensus Authors' estimates ( in millions) 2006A 2007E 200BE 2009E 2010E 2011E 2012E 2013E 2014E CAGR 06-16 2015E 2016E TV Sales 4,304 4,433 3,941 80% 671 17.0% 27 4.139 5.0% 697 4,522 2.0% 761 746 2,556 7.9% 435 17.0% 22 0.9% 28 2,369.2 33.3% 366 15.5% 38 1.6% 405 17.1% (139) 38 0% (193) EBIT % margin + Depreciation % sales EBITDA margin 1. Cash Taxes % effective tax rates 1. 2,876 3,244.0 12.5% 12.8% 492 566 17.1% 17.5% 23 24 0.8% 0.7% 515 590 17.9% 18.2% (170) 30.0% 30.0% (49) 3,650 12.5% 633 17.3% 24 0.7% 657 18.0% (190) 30.0% (36) 30 0.7% 458 4,705 2.0% 791 16.8% 32 0.7% 823 17.5% (237) 30.0% (39) 724 16.8% 29 0.7% 753 17.5% (217) 30.0% (39) 698 17.7% (201) 300% (38) 17.9% 4.612.3 6.9% 2.0% 776 7.8% 168% 32 1.9% 0.7% 807 7.2% 17.5% (233) 5.3% 30.0% (38) 15.0% -1.5% 724 17.5% (209) 30.0% 139) 31 0.7% 791 17.5% (228) 30.0% 138) (139) 32.0% 151) 17.5% (224) 100% (39) 81% 503% (148) % sales % depreciation 1. Change in working Capital % sales growth 2.0% 230% (86) 1.9% -1.6% -1.5% -220% -184% -164% -173% (65) -1.5% 175% 1.5% 175% (26) 1.5% - 175% $211 -1.5% - 173% -1.5% -174% -15 (14) 25.0% FCFO 181 273 335 366 411 445 470 493 511 522 533 Source: Authors' cakulation based on it any contenu Appendix 6 Cost of Capital information The cost of capital calculation can be based on the data shown in Exhibits 6.1 and 6.2. With a prudential approach, analysts applied a target debt to equity ratio of 10 percent to Puma, assuming that the company would have raised debt to finance its expansion and to use tax shield for reducing its cost of capital. Exhibit 6.3 reports the key WACC assumptions of the main brokers as poblished in the research over the two months preceding the closure of the deal. Unlevered Beta EXHIBIT 6.1 Comparables' levered beta and leverage Comparables' Beta Levered Beta Debt to Equity Puma 0.64 09 Adidas 0.32 47% Asics 1.09 19% K-Swiss 1.02 094 Nike 0.56 89 Billabong 1.55 27% Columbia Sportwear 0.92 09 Sketchers 2.05 179 Timberland 1.14 09 Geox 1.28 0.24 0.96 1.02 0.53 1.30 0.97 1.83 1.14 125 1.11 Industry Average 14% 1.03 * As of March 2007 EXHIBIT 6.2 Key data for cost of capital calculation Puma WACC Calculation Tax rate D/E market value) Industry Unlevered Beta Risk-free rate MRP Debt spred 30.00% 10% 1.03 4.10% 5.00% 1.00% *Yield of ten years German Treasury Bonds as of March 2007 **Average Brokers' consensus CHAPTER 11 MERGERS AND ACQUISITIONS 489 Beta WACC EXHIBIT 6.3 Key brokers' WACC assumptions Brokers' Key WACC Assumptions Company MRT Credit Suisse 5 50% Deutsche Bank 4.50% Goldman Sachs ma Societe Generale 4.54% na 1001 na 1.20 10.90% 8.50% 6.90% 9.85% Industry Average 4.85% 1.10 9.04% As of March 2007 Appendix 7 Multiples analysis: comparable companies multiples Below, Exhibit 7.1 reports comparables companies trading multiples as of March 2007 EXHIBIT 7.1 Comparable companies trading multiples EV/EBITDA PIE (As from March Trading Market Enterprise 2007) Company Currency Cap (ml) Value FY2006 FY2007 FY2008 FY2006 FY2007 FY2008 Athletic Footwear Adidas EUR 8,478 10,718 9.1 78 175 12.7 JPY 281,748 281,938 100 204 189 162 K-Swiss USD 989 729 7.2 12.8 101 12.8 199 163 Nike USD 27,426 25,702 10.5 9.7 87 19.0 172 15.2 PPR - PUMA: A successful acquisition? 156 98 13.0 Asics Average 10.1 10.8 92 17.4 779 15.1 12.5 Outdoor and Activewear Billabong Columbia Sportswear Quicksilver AUD USD 3,508 2.338 3,761 2,122 147 104 10.6 8.5 21.9 193 187 17.1 15.9 15.2 USD 1.589 2,465 10.1 10.4 8.3 12.6 21.3 14.0 Average 11.7 10.8 19.6 190 15.0 Fashion brands Geox EUR EUR EUR 3,533 3,208 2.046 3,470 3,390 2,002 Hugo Boss Tod's Average Average fall comparables Puma 22.6 14.5 14.5 172 12.7 15.7 123 12.3 13.4 11.6 12.4 10.9 10.7 11.3 9.8 362 249 298 30.3 21.9 27.6 21.0 243 243 202 23.0 18.4 20.6 20.7 16.8 EUR 5,027 4,873 12.0 10.6 9.5 19.1 14.7 Source: Company reports and market data Appendix 5 Puma projected figures (2007-2016) To complete the valuation considerations, the analysts performed a DCF analysis (see Exhibit 5.1). The DCF projections were based on the following assumptions: . For the period running from 2007 to 2009, Puma's income statement projections were based on brokers' consensus. For the following years, estimates have been based on authors' assumptions. Top line growth is expected to level down to terminal growth rate of 2 percent in 2016E. Ebitda Margin is expected to gradually decrease to a constant 17.5 percent after the peak of 18.2 percent forecasted in 2009 on the basis of analysts' consensus. Capex are expected to level down to 120 percent of depreciation in 2016. The depreciation is assumed constant at 10 percent of the previous year operating fixed assets. . Working Capital is expected to be driven by top line growth and to keep constant at 16 percent of sales. A 30 percent stable tax rate is assumed for the entire period running from 2008 to 2016. In 2007, the expected tax rate is equal to 32 percent. EXHIBIT 5.1 Puma cash flow projections Unlevered Free Cash Flow Calculation Actual Brokers' consensus Authors' estimates ( in millions) 2006A 2007E 200BE 2009E 2010E 2011E 2012E 2013E 2014E CAGR 06-16 2015E 2016E TV Sales 4,304 4,433 3,941 80% 671 17.0% 27 4.139 5.0% 697 4,522 2.0% 761 746 2,556 7.9% 435 17.0% 22 0.9% 28 2,369.2 33.3% 366 15.5% 38 1.6% 405 17.1% (139) 38 0% (193) EBIT % margin + Depreciation % sales EBITDA margin 1. Cash Taxes % effective tax rates 1. 2,876 3,244.0 12.5% 12.8% 492 566 17.1% 17.5% 23 24 0.8% 0.7% 515 590 17.9% 18.2% (170) 30.0% 30.0% (49) 3,650 12.5% 633 17.3% 24 0.7% 657 18.0% (190) 30.0% (36) 30 0.7% 458 4,705 2.0% 791 16.8% 32 0.7% 823 17.5% (237) 30.0% (39) 724 16.8% 29 0.7% 753 17.5% (217) 30.0% (39) 698 17.7% (201) 300% (38) 17.9% 4.612.3 6.9% 2.0% 776 7.8% 168% 32 1.9% 0.7% 807 7.2% 17.5% (233) 5.3% 30.0% (38) 15.0% -1.5% 724 17.5% (209) 30.0% 139) 31 0.7% 791 17.5% (228) 30.0% 138) (139) 32.0% 151) 17.5% (224) 100% (39) 81% 503% (148) % sales % depreciation 1. Change in working Capital % sales growth 2.0% 230% (86) 1.9% -1.6% -1.5% -220% -184% -164% -173% (65) -1.5% 175% 1.5% 175% (26) 1.5% - 175% $211 -1.5% - 173% -1.5% -174% -15 (14) 25.0% FCFO 181 273 335 366 411 445 470 493 511 522 533 Source: Authors' cakulation based on it any contenu Appendix 6 Cost of Capital information The cost of capital calculation can be based on the data shown in Exhibits 6.1 and 6.2. With a prudential approach, analysts applied a target debt to equity ratio of 10 percent to Puma, assuming that the company would have raised debt to finance its expansion and to use tax shield for reducing its cost of capital. Exhibit 6.3 reports the key WACC assumptions of the main brokers as poblished in the research over the two months preceding the closure of the deal. Unlevered Beta EXHIBIT 6.1 Comparables' levered beta and leverage Comparables' Beta Levered Beta Debt to Equity Puma 0.64 09 Adidas 0.32 47% Asics 1.09 19% K-Swiss 1.02 094 Nike 0.56 89 Billabong 1.55 27% Columbia Sportwear 0.92 09 Sketchers 2.05 179 Timberland 1.14 09 Geox 1.28 0.24 0.96 1.02 0.53 1.30 0.97 1.83 1.14 125 1.11 Industry Average 14% 1.03 * As of March 2007 EXHIBIT 6.2 Key data for cost of capital calculation Puma WACC Calculation Tax rate D/E market value) Industry Unlevered Beta Risk-free rate MRP Debt spred 30.00% 10% 1.03 4.10% 5.00% 1.00% *Yield of ten years German Treasury Bonds as of March 2007 **Average Brokers' consensus CHAPTER 11 MERGERS AND ACQUISITIONS 489 Beta WACC EXHIBIT 6.3 Key brokers' WACC assumptions Brokers' Key WACC Assumptions Company MRT Credit Suisse 5 50% Deutsche Bank 4.50% Goldman Sachs ma Societe Generale 4.54% na 1001 na 1.20 10.90% 8.50% 6.90% 9.85% Industry Average 4.85% 1.10 9.04% As of March 2007 Appendix 7 Multiples analysis: comparable companies multiples Below, Exhibit 7.1 reports comparables companies trading multiples as of March 2007 EXHIBIT 7.1 Comparable companies trading multiples EV/EBITDA PIE (As from March Trading Market Enterprise 2007) Company Currency Cap (ml) Value FY2006 FY2007 FY2008 FY2006 FY2007 FY2008 Athletic Footwear Adidas EUR 8,478 10,718 9.1 78 175 12.7 JPY 281,748 281,938 100 204 189 162 K-Swiss USD 989 729 7.2 12.8 101 12.8 199 163 Nike USD 27,426 25,702 10.5 9.7 87 19.0 172 15.2 PPR - PUMA: A successful acquisition? 156 98 13.0 Asics Average 10.1 10.8 92 17.4 779 15.1 12.5 Outdoor and Activewear Billabong Columbia Sportswear Quicksilver AUD USD 3,508 2.338 3,761 2,122 147 104 10.6 8.5 21.9 193 187 17.1 15.9 15.2 USD 1.589 2,465 10.1 10.4 8.3 12.6 21.3 14.0 Average 11.7 10.8 19.6 190 15.0 Fashion brands Geox EUR EUR EUR 3,533 3,208 2.046 3,470 3,390 2,002 Hugo Boss Tod's Average Average fall comparables Puma 22.6 14.5 14.5 172 12.7 15.7 123 12.3 13.4 11.6 12.4 10.9 10.7 11.3 9.8 362 249 298 30.3 21.9 27.6 21.0 243 243 202 23.0 18.4 20.6 20.7 16.8 EUR 5,027 4,873 12.0 10.6 9.5 19.1 14.7 Source: Company reports and market data



 information provided in Appendix 5-7 to come up with DCF and relative valuation of Puma.
information provided in Appendix 5-7 to come up with DCF and relative valuation of Puma.





