Question: How to answer question3? I have no idea on this one. y, W(x) xi i 8 8 o o o o o o o o
How to answer question3? I have no idea on this one.
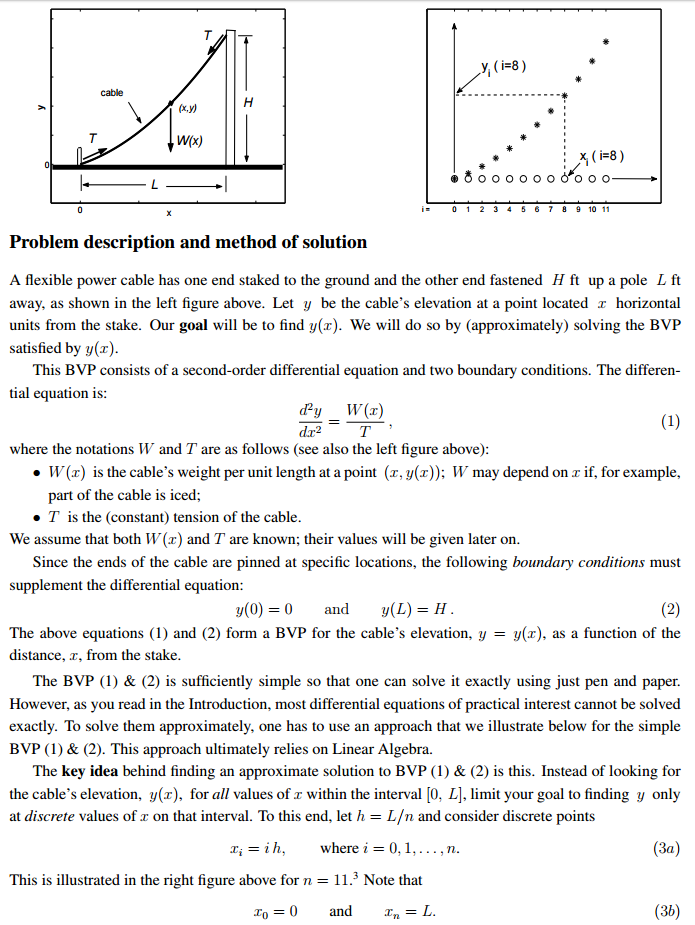



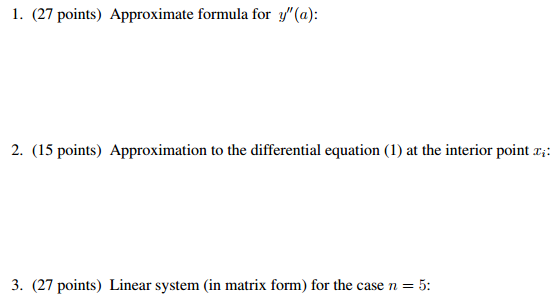
y, W(x) xi i 8 8 o o o o o o o o o 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Problem description and method of solution A flexible power cable has one end staked to the ground and the other end fastened H ft up a pole L ft away, as shown in the left figure above. Let y be the cable's elevation at a point located z horizontal units from the stake. Our goal will be to find y(z). We will do so by (approximately) solving the BVP atisfied by y(r) This BVP consists of a second-order differential equation and two boundary conditions. The differen tial equation is d2y W(z) (1) dac2 where the notations W and T are as follows (see also the left figure above): W (r) is the cable's weight per unit length at a point (z, y(z)); W may depend on if, for example part of the cable is iced T is the (constant) tension of the cable We assume that both W(ar) and T are known; their values will be given later on Since the ends of the cable are pinned at specific locations, the following boundary conditions must supplement the differential equation: y(0) 0 (2) and The above equations (1 and (2) form a BVP for the cable's elevation, y y(z), as a function of the distance, a. from the stake. The BVP (1) & (2) is sufficiently simple so that one can solve it exactly using just pen and paper However, as you read in the Introduction, most differential equations of practical interest cannot be solved exactly. To solve them approximately, one has to use an approach that we illustrate below for the simple BVP (1) & (2). This approach ultimately relies on Linear Algebra The key idea behind finding an approximate solution to BVP (1) & (2) is this. Instead of looking for the cable's elevation, y(z), for all values of a within the interval [0, L], limit your goal to finding y only at discrete values of r on that interval. To this end, let h L and consider discrete points (3a) i h where i 0,1 This is illustrated in the right figure above for n 11.3 Note that (3b) and y, W(x) xi i 8 8 o o o o o o o o o 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Problem description and method of solution A flexible power cable has one end staked to the ground and the other end fastened H ft up a pole L ft away, as shown in the left figure above. Let y be the cable's elevation at a point located z horizontal units from the stake. Our goal will be to find y(z). We will do so by (approximately) solving the BVP atisfied by y(r) This BVP consists of a second-order differential equation and two boundary conditions. The differen tial equation is d2y W(z) (1) dac2 where the notations W and T are as follows (see also the left figure above): W (r) is the cable's weight per unit length at a point (z, y(z)); W may depend on if, for example part of the cable is iced T is the (constant) tension of the cable We assume that both W(ar) and T are known; their values will be given later on Since the ends of the cable are pinned at specific locations, the following boundary conditions must supplement the differential equation: y(0) 0 (2) and The above equations (1 and (2) form a BVP for the cable's elevation, y y(z), as a function of the distance, a. from the stake. The BVP (1) & (2) is sufficiently simple so that one can solve it exactly using just pen and paper However, as you read in the Introduction, most differential equations of practical interest cannot be solved exactly. To solve them approximately, one has to use an approach that we illustrate below for the simple BVP (1) & (2). This approach ultimately relies on Linear Algebra The key idea behind finding an approximate solution to BVP (1) & (2) is this. Instead of looking for the cable's elevation, y(z), for all values of a within the interval [0, L], limit your goal to finding y only at discrete values of r on that interval. To this end, let h L and consider discrete points (3a) i h where i 0,1 This is illustrated in the right figure above for n 11.3 Note that (3b) and
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


