How would disturbances and subsequent succession influence nutrient cycling and nutrient losses in an ecosystem? nutrient losses are in part related to uptake by plants
How would disturbances and subsequent succession influence nutrient cycling and nutrient losses in an ecosystem? nutrient losses are in part related to uptake by plants (see Figure 22.13) Uptake in turn is related to the rates of plant growth (NPP). As a result, the losses of nutrients during succession are related to patterns of plant growth. The lowest nutrient losses should correspond to the highest growth rates.
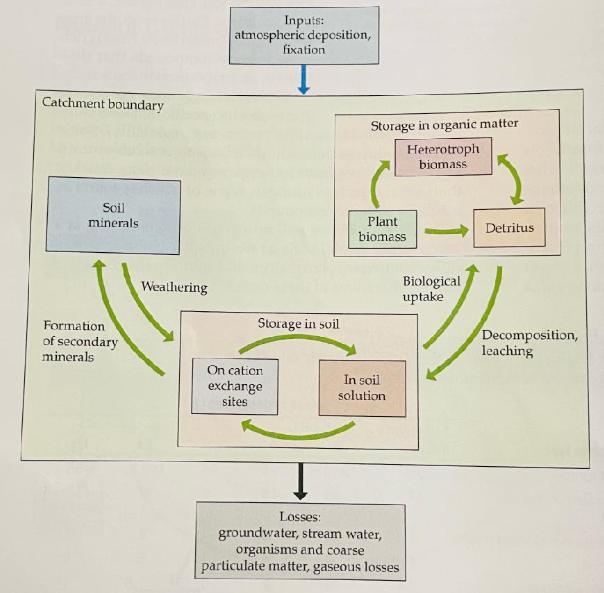
- Based on patterns of community replacement during succession, what pattern of nutrient loss from a catchment would you hypothesize following a disturbance in a forest? Consider how nutrients would change just after the disturbance, into the intermediate stages of succession, and finally into an old growth community made up of long-lived mature trees.
2. Would the patterns of nutrient loss that you hypothesized in Question 1 be the same for all nutrients? Would nutrients that limit NPP show the same patterns as nutrients that are not limiting to growth?
3. Peter Vitousek (1977) used a catchment approach to study nutrient retention by spruce-fir forests in the White Mountains of New Hampshire at different stages of secondary succession following logging. He measured nutrient loss in streams draining catchments of different successional stages. In order to evaluate the hypothesis that late successional communities would be more "leaky" than intermediate-stage communities, he examined the ratio of old-growth losses to losses during intermediate successional stages. He did this for several elements, some potentially more limiting to NPP than others. His results are shown in the table. (μeq/L, micro equivalents/liter). Do the data support Vitousek's hypothesis regarding changes in nutrient losses between intermediate and and late successional forest communities? How do the differences in the patterns of element losses relate to their importance to plant growth?
Mean growing-season stream water Concentrations (μeq/L) ±SE | |||
| Late Successional | Intermediate Successional | Ratio late: intermediate |
NO3¯ | 53 ± 5 | 8 ± 1.3 | 6.62 |
K+ | 13 ± 1 | 7 ± 0.5 | 1.81 |
Mg2+ | 40 ± 4.9 | 24 ± 1.6 | 1.66 |
Ca2+ | 56 ± 4.5 | 36 ± 2.5 | 1.56 |
Cl- | 15 ± 0.3 | 13 ± 0.3 | 1.16 |
Na+ | 29 ± 2.6 | 28 ± 0.9 | 1.03 |
Catchment boundary Soil minerals. Formation of secondary minerals Weathering Inputs: atmospheric deposition, On cation exchange sites fixation Storage in soil Storage in organic matter Heterotroph biomass Plant biomass In soil solution T Losses: groundwater, stream water, organisms and coarse particulate matter, gaseous losses ][ Biological uptake Detritus Decomposition, leaching
Step by Step Solution
3.49 Rating (149 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1
1 How would disturbances and subsequent succession influence nutrient cycling and nutrient losses in an ecosystem Disturbances can have a significant impact on nutrient cycling and nutrient losses in ...
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


