Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
#HW 2 #Due Date: 09/21/2018, 11:59PM ######################################## # # Name: # Collaboration Statement: # ######################################## def findNextOpr(txt): Takes a string and returns -1 if





#HW 2
#Due Date: 09/21/2018, 11:59PM
########################################
#
# Name:
# Collaboration Statement:
#
########################################
def findNextOpr(txt):
"""
Takes a string and returns -1 if there is no operator in txt, otherwise returns
the position of the leftmost operator. +, -, *, / are all the 4 operators
>>> findNextOpr(' 3* 4 - 5')
3
>>> findNextOpr('8 4 - 5')
6
>>> findNextOpr('89 4 5')
-1
"""
if len(txt)
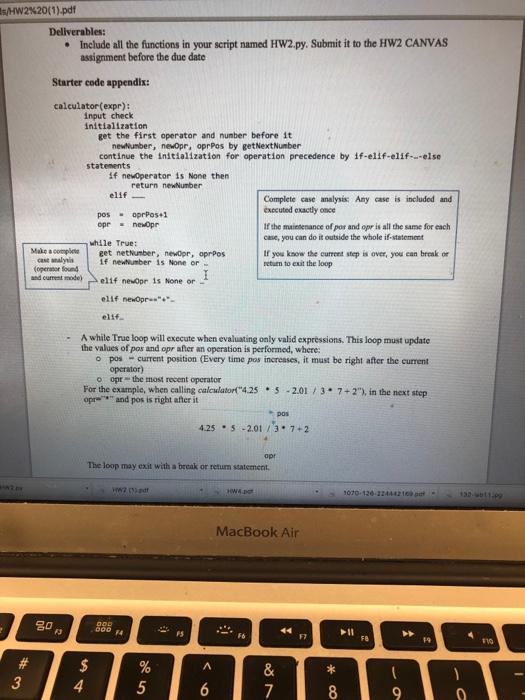
Goal: Write the function calculator(expr), where expr is a string. This function will compute the arithmetic expression given in expr. The arithmetic expression is a string of operands and operators that may include numeric values, four arithmetic operators (+, ,/, ") and extra spaces. An example of such expression is "-4.7552.03 7+ 2 Notes: For this assignment you can return an error message if 2 consecutive operators are found - 2 +-3 8' for example - In the starter code provided on CANVAS, there are 4 additional functions (partially written) that will help calculator(expr) to evaluate the expression. Try to understand al the variables given in the calculator(expr) code provided. Except for exeOpr, you must code the empty segments so the five functions work completely Function requirements: The function must return the computed value if expr is a correct formula, otherwise it must return an error message. When any function returns a numeric value, it must be float Do not use exec or eval function. You will not receive credit if your program uses any of the two functions anywhere The five functions provided in thd starter code must work Grading Notes: - calculator(expr) [60 pts]: The grading script will feed 4 randomly chosen test inputs, each for 15 points. One of them will be an input that should cause an error such as "4 /2 +5" or 2+ 3 5", whose expected returned value is an error message. . findNextOpr txt) [20 pts]: 2 randomly chosen test inputs checking the correet returned values. is Number(txt) [10 pts]: 2 randomly chosen test inputs checking the correct returned values. getNextNumber(expr, index) [10 pts]: 1 randomly chosen test input checking the correct returned value. Py HW2 (1) pdt Hw4.pdf 1070-126-224442169 pdf. 132-lab11 ip return "type error: findNextOpr"
# --- YOU CODE STARTS HERE
# --- CODE ENDS HERE
def isNumber(txt):
"""
Takes a string and returns True if txt is convertible to float, False otherwise
>>> isNumber('1 2 3')
False
>>> isNumber('- 156.3')
False
>>> isNumber('29.99999999')
True
>>> isNumber(' 5.9999 ')
True
"""
if not isinstance(txt, str):
return "type error: isNumber"
if len(txt)==0:
return False
# --- YOU CODE STARTS HERE
# --- CODE ENDS HERE
def getNextNumber(expr, pos):
"""
expr is a given arithmetic formula of type string
pos is the start position in expr
1st returned value = the next number (None if N/A)
2nd returned value = the next operator (None if N/A)
3rd retruned value = the next operator position (None if N/A)
>>> getNextNumber('8 + 5 -2',0)
(8.0, '+', 3)
>>> getNextNumber('8 + 5 -2',4)
(5.0, '-', 13)
>>> getNextNumber('4.5 + 3.15 / 5',0)
(4.5, '+', 4)
>>> getNextNumber('4.5 + 3.15 / 5',10)
(None, '/', 19)
"""
if len(expr)==0 or not isinstance(expr, str) or pos=len(expr) or not isinstance(pos, int):
return None, None, "type error: getNextNumber"
# --- YOU CODE STARTS HERE
# --- CODE ENDS HERE
def exeOpr(num1, opr, num2):
#This function is just an utility function for calculator(expr). It is skipping type check
if opr=="+":
return num1+num2
elif opr=="-":
return num1-num2
elif opr=="*":
return num1*num2
elif opr=="/":
return num1um2
else:
return "error in exeOpr"
def calculator(expr):
"""
Takes a string and returns the calculated result if the arithmethic expression is value,
and error message otherwise
>>> calculator(" -4 +3 -2")
-3.0
>>> calculator("-4 +3 -2 / 2")
-2.0
>>> calculator("-4 +3 - 8 / 2")
-5.0
>>> calculator(" -4 + 3 - 8 / 2")
-5.0
>>> calculator("23 / 12 - 223 + 5.25 * 4 * 3423")
71661.91666666667
>>> calculator("2 - 3*4")
-10.0
>>> calculator("4++ 3 +2")
'error message'
>>> calculator("4 3 +2")
'input error line B: calculator'
"""
if len(expr)
return "input error line A: calculator"
# Concatenate '0' at he beginning of the expression if it starts with a negative number to get '-' when calling getNextNumber
# "-2.0 + 3 * 4.0 becomes "0-2.0 + 3 * 4.0 .
expr=expr.strip()
if expr[0]=="-":
expr = "0 " + expr
newNumber, newOpr, oprPos = getNextNumber(expr, 0)
# Initialization. Holding two modes for operator precedence: "addition" and "multiplication"
if newNumber is None: #Line B
return "input error line B: calculator"
elif newOpr is None:
return newNumber
elif newOpr=="+" or newOpr=="-":
mode="add"
addResult=newNumber #value so far in the addition mode
elif newOpr=="*" or newOpr=="/":
mode="mul"
addResult=0
mulResult=newNumber #value so far in the mulplication mode
addLastOpr = "+"
pos=oprPos+1 #the new current position
opr=newOpr #the new current operator
#Calculation starts here, get next number-operator and perform case analysis. Conpute values using exeOpr
while True:
# --- YOU CODE STARTS HERE
# --- CODE ENDS HERE
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


