Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
I am lost throughout this lesson this is a problem he gave us to work and this is all the information i have for it.
I am lost throughout this lesson this is a problem he gave us to work and this is all the information i have for it. 



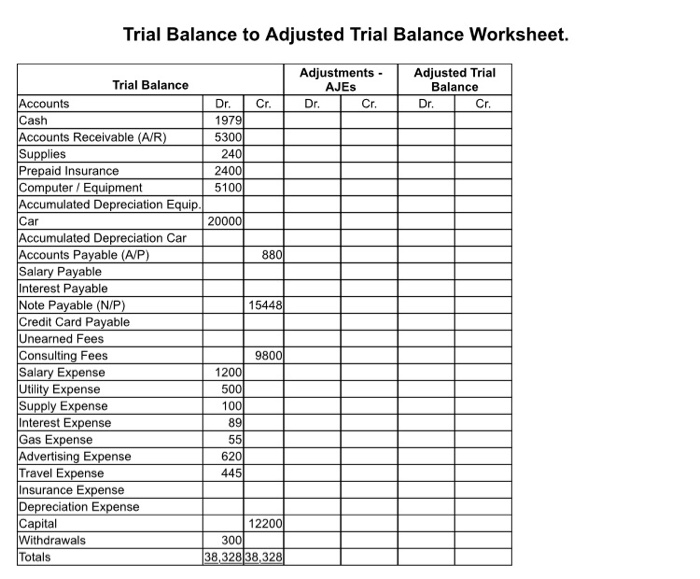

June 1 Jim began his business by transferring equipment valued at $4,200 into the business. He also placed $8,000 cash in a business checking account. He applied for and received a new credit card for the business. June 1 Jim purchased a car, costing $20,000 by paying $4,000 cash and signed a note for the balance with Biggs auto dealership. The note provides for a 10% APR interest cost. June 1 Jim purchased a new computer for $900 and supplies for $200, all on open account; payment terms 1/10, n/30. June 2 Jim filled bought gasoline for the car, $55. He put the purchase on the new credit card. June 3 Jim's first customer Larry Brown, prepays Jim to do a job search for him. Larry gives Jim $3,000 cash in advance. June 5 Jim receives $500 cash for a speaking engagement on the Triangle offence scheme. June 7 Jim hires a former player of his, "Hoops" Wilson as an assistant to work with him, to be paid $10 an hour. June 8 Jim put travel expenses for a motel room and food on the credit card, $445. June 9 Jim receives a bill for an ad he had placed in Coaches Anonymous magazine advertising Wooly Consulting. The ad ran last week. The bill is for $220, due in 10 days. There is an 18% APR interest charge on overdue accounts. June 10 Jim purchased office supplies at Staples for $140, paying cash. June 12 Jim purchased an insurance policy for 12 months' coverage on the car from NoState Insurance. He was required to pay a full year in advance, $2,400. June 13 Found Larry Brown a job with Tennessee State University. Hint: This event is related to the June 3 event above. June 13 Billed on account, two hockey coaches for consulting on how to beat the Canadians in the Olympic winter games, $2,000. June 14 Paid Hoops, the assistant for 40 hours' work. June 21 Made a $640 payment on the note signed for the car. This payment consists of both interest and principal. Hint: there has been 20 days since the loan began on June 1. Round the interest calculation result to the nearest dollar. June 21 Paid Hoops, the assistant for 40 hours' work. June 22 Received the utility bill for $280, however it is not due for 15 days. June 23 Received payment from one of the hockey coaches billed on June 13, $1,000. June 24 Found Bob Huggins a job with the West Virginia Hill Hoppers, billed him $4,300. June 25 Paid the bill for the computer purchased on June 1. Transactions continue on the next page........ Wooly Consulting transactions continued. June 28 Paid Hoops, the assistant for 40 hours' work. June 29 Purchased ads that will run immediately for $400 on open account in two magazines. June 30 Used $100 of the supplies previously purchased. June 30 Jim withdraws $300 cash to go play golf with. June 30 Received and immediately paid the telephone bill of $220. June 30 Paid off the balance on the credit card. June 30 Realized that he had not paid off the account for the ad on June 9. Sent in payment General Journal Date Account Debit Credit Adjusting Entry Events: 1. Jim recalls finishing up a job search for Mack Brown. He forgot to bill Mack the $980. 2. Hoops had worked 8 ($10/hr.) hours as of the end of June. He will not be paid until July 5. 3. An inspection of the insurance policy purchased from No State Insurance on June 12 indicates that it is a 12 month policy that included coverage for the entire month of June. Recall it was $2,400 for 12 months coverage. 4. Jim brought in the water bill for June, dated July 10 for $64. The bill is due upon receipt. 5. Jim counted the supplies remaining in the supply cabinet. The supply cabinet physical count reveals that there is only $80 of supplies remaining. 6. The last payment on the note was on June 21. As of June 30, 9 days of interest at 10%, has accrued but not yet been paid. (Round the result to the nearest dollar.) 7. The car is considered to have a useful life of 48 months with $3,920 salvage value. The computer and equipment is considered to have a 3 year life (36 months) with no salvage value. Round your calculation results to the nearest whole dollar. Assume Wooly had the asset for the entire month. Adjusting Entries Application Continued 1. What financial statements were affected by each entry? Number your answer to correspond to the number of the adjusting events above. 2. Indicate whether the entry is an accrual adjusting entry, or a deferral adjusting entry. Event Financial Statements Affected Accrual or Deferral FooLON Trial Balance to Adjusted Trial Balance Worksheet. Adjustments - AJES Dr. Cr. Adjusted Trial Balance Dr. Cr. Trial Balance Accounts Dr. Cr. Cash 1979 Accounts Receivable (A/R) 5300 Supplies 240 Prepaid Insurance 24001 Computer / Equipment 5100 Accumulated Depreciation Equip. Car 20000 Accumulated Depreciation Car Accounts Payable (A/P) 880 Salary Payable Interest Payable Note Payable (N/P) 15448 Credit Card Payable Unearned Fees Consulting Fees 9800 Salary Expense 1200 Utility Expense Supply Expense 100 Interest Expense 89 Gas Expense Advertising Expense 620 Travel Expense 445 Insurance Expense Depreciation Expense Capital 12200 Withdrawals 3001 Totals 38,328 38,328 500 Adjusting Entries Exercise Step 1: Use the seven Adjusting Entry Accounting events on Module Homework 6-4 to complete seven adjusting entries on Module Homework 6-5. Complete this step in full before moving to Step 2 There are points attached for neatness, accuracy and following instructions: Skip a line between entries on page 6-5. Use pencil only. No pen. Date the entries using the appropriate dating method that should be used for recording AJES. Wooly Consulting was for the month of June. Use the provided Trial Balance to find any account balances needed for adjusting such as Prepaid Insurance and Supplies. Do not use an account that is not on the provided Trial Balance. Each item being depreciated has its very own A/D account, but you need use only one Depreciation Expense account. Unearned revenue is a category for various types of unearned revenue liabilities. You must specify the actual unearned revenue account. In this case it is Unearned Fees. Revenue is a category for various types of revenue. Recall that Consulting Fees is the revenue account for Wooly. Interest rate on the loan for the car was 10% APR. Recall Px Rx T = Interest Cost Watch for the rounding rules as provided. Step 2: Complete the table on the back of Module Homework 6-5 (pg. 6-6). Complete this step in full before moving to Step 3. Step 3: Post the AJEs you created on Module Homework 6-5 to the provided "Trial Balance to Adjusted Trial Balance Worksheet" on the other side of this page. Post the amounts to the appropriate "Adjustments - AJES" column. If an account was debited in the AJE, you would place it in the Dr. column of the work sheet for the given account. Step 4: On the "Trial Balance to Adjusted Trial Balance Worksheet" combine the 'Trial Balance amounts with the effects of the adjustments in the "Adjustments - AJE's" column and place the amounts in the appropriate "Adjusted Trial Balance" columns. Think in terms of how the T-account for the account would work here. June 1 Jim began his business by transferring equipment valued at $4,200 into the business. He also placed $8,000 cash in a business checking account. He applied for and received a new credit card for the business. June 1 Jim purchased a car, costing $20,000 by paying $4,000 cash and signed a note for the balance with Biggs auto dealership. The note provides for a 10% APR interest cost. June 1 Jim purchased a new computer for $900 and supplies for $200, all on open account; payment terms 1/10, n/30. June 2 Jim filled bought gasoline for the car, $55. He put the purchase on the new credit card. June 3 Jim's first customer Larry Brown, prepays Jim to do a job search for him. Larry gives Jim $3,000 cash in advance. June 5 Jim receives $500 cash for a speaking engagement on the Triangle offence scheme. June 7 Jim hires a former player of his, "Hoops" Wilson as an assistant to work with him, to be paid $10 an hour. June 8 Jim put travel expenses for a motel room and food on the credit card, $445. June 9 Jim receives a bill for an ad he had placed in Coaches Anonymous magazine advertising Wooly Consulting. The ad ran last week. The bill is for $220, due in 10 days. There is an 18% APR interest charge on overdue accounts. June 10 Jim purchased office supplies at Staples for $140, paying cash. June 12 Jim purchased an insurance policy for 12 months' coverage on the car from NoState Insurance. He was required to pay a full year in advance, $2,400. June 13 Found Larry Brown a job with Tennessee State University. Hint: This event is related to the June 3 event above. June 13 Billed on account, two hockey coaches for consulting on how to beat the Canadians in the Olympic winter games, $2,000. June 14 Paid Hoops, the assistant for 40 hours' work. June 21 Made a $640 payment on the note signed for the car. This payment consists of both interest and principal. Hint: there has been 20 days since the loan began on June 1. Round the interest calculation result to the nearest dollar. June 21 Paid Hoops, the assistant for 40 hours' work. June 22 Received the utility bill for $280, however it is not due for 15 days. June 23 Received payment from one of the hockey coaches billed on June 13, $1,000. June 24 Found Bob Huggins a job with the West Virginia Hill Hoppers, billed him $4,300. June 25 Paid the bill for the computer purchased on June 1. Transactions continue on the next page........ Wooly Consulting transactions continued. June 28 Paid Hoops, the assistant for 40 hours' work. June 29 Purchased ads that will run immediately for $400 on open account in two magazines. June 30 Used $100 of the supplies previously purchased. June 30 Jim withdraws $300 cash to go play golf with. June 30 Received and immediately paid the telephone bill of $220. June 30 Paid off the balance on the credit card. June 30 Realized that he had not paid off the account for the ad on June 9. Sent in payment General Journal Date Account Debit Credit Adjusting Entry Events: 1. Jim recalls finishing up a job search for Mack Brown. He forgot to bill Mack the $980. 2. Hoops had worked 8 ($10/hr.) hours as of the end of June. He will not be paid until July 5. 3. An inspection of the insurance policy purchased from No State Insurance on June 12 indicates that it is a 12 month policy that included coverage for the entire month of June. Recall it was $2,400 for 12 months coverage. 4. Jim brought in the water bill for June, dated July 10 for $64. The bill is due upon receipt. 5. Jim counted the supplies remaining in the supply cabinet. The supply cabinet physical count reveals that there is only $80 of supplies remaining. 6. The last payment on the note was on June 21. As of June 30, 9 days of interest at 10%, has accrued but not yet been paid. (Round the result to the nearest dollar.) 7. The car is considered to have a useful life of 48 months with $3,920 salvage value. The computer and equipment is considered to have a 3 year life (36 months) with no salvage value. Round your calculation results to the nearest whole dollar. Assume Wooly had the asset for the entire month. Adjusting Entries Application Continued 1. What financial statements were affected by each entry? Number your answer to correspond to the number of the adjusting events above. 2. Indicate whether the entry is an accrual adjusting entry, or a deferral adjusting entry. Event Financial Statements Affected Accrual or Deferral FooLON Trial Balance to Adjusted Trial Balance Worksheet. Adjustments - AJES Dr. Cr. Adjusted Trial Balance Dr. Cr. Trial Balance Accounts Dr. Cr. Cash 1979 Accounts Receivable (A/R) 5300 Supplies 240 Prepaid Insurance 24001 Computer / Equipment 5100 Accumulated Depreciation Equip. Car 20000 Accumulated Depreciation Car Accounts Payable (A/P) 880 Salary Payable Interest Payable Note Payable (N/P) 15448 Credit Card Payable Unearned Fees Consulting Fees 9800 Salary Expense 1200 Utility Expense Supply Expense 100 Interest Expense 89 Gas Expense Advertising Expense 620 Travel Expense 445 Insurance Expense Depreciation Expense Capital 12200 Withdrawals 3001 Totals 38,328 38,328 500 Adjusting Entries Exercise Step 1: Use the seven Adjusting Entry Accounting events on Module Homework 6-4 to complete seven adjusting entries on Module Homework 6-5. Complete this step in full before moving to Step 2 There are points attached for neatness, accuracy and following instructions: Skip a line between entries on page 6-5. Use pencil only. No pen. Date the entries using the appropriate dating method that should be used for recording AJES. Wooly Consulting was for the month of June. Use the provided Trial Balance to find any account balances needed for adjusting such as Prepaid Insurance and Supplies. Do not use an account that is not on the provided Trial Balance. Each item being depreciated has its very own A/D account, but you need use only one Depreciation Expense account. Unearned revenue is a category for various types of unearned revenue liabilities. You must specify the actual unearned revenue account. In this case it is Unearned Fees. Revenue is a category for various types of revenue. Recall that Consulting Fees is the revenue account for Wooly. Interest rate on the loan for the car was 10% APR. Recall Px Rx T = Interest Cost Watch for the rounding rules as provided. Step 2: Complete the table on the back of Module Homework 6-5 (pg. 6-6). Complete this step in full before moving to Step 3. Step 3: Post the AJEs you created on Module Homework 6-5 to the provided "Trial Balance to Adjusted Trial Balance Worksheet" on the other side of this page. Post the amounts to the appropriate "Adjustments - AJES" column. If an account was debited in the AJE, you would place it in the Dr. column of the work sheet for the given account. Step 4: On the "Trial Balance to Adjusted Trial Balance Worksheet" combine the 'Trial Balance amounts with the effects of the adjustments in the "Adjustments - AJE's" column and place the amounts in the appropriate "Adjusted Trial Balance" columns. Think in terms of how the T-account for the account would work here 






Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


