i am not sure my answer please help me!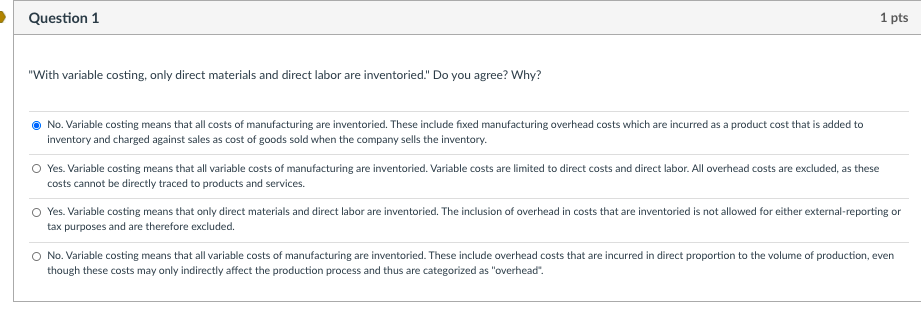
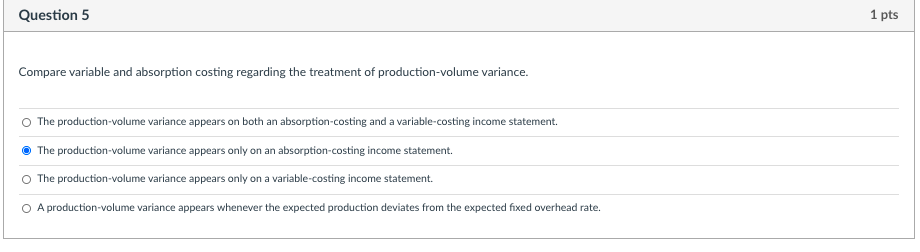
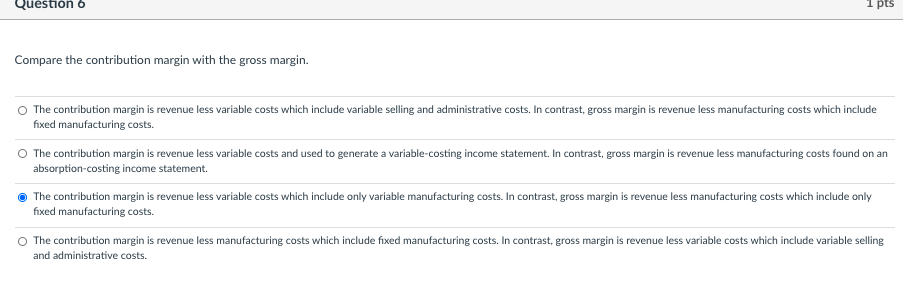
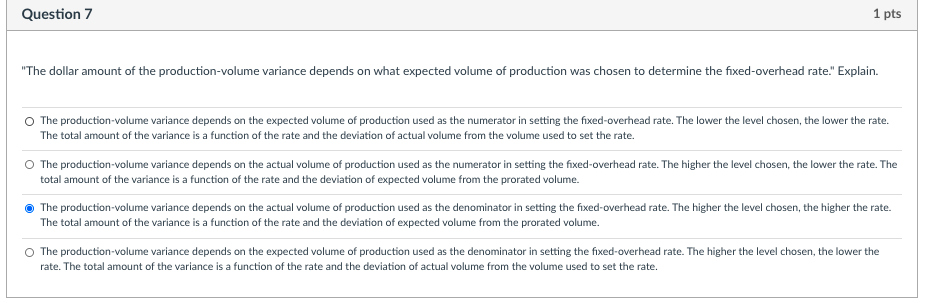
Question 1 1 pts "With variable costing, only direct materials and direct labor are inventoried." Do you agree? Why? No. Variable costing means that all costs of manufacturing are inventoried. These include fixed manufacturing overhead costs which are incurred as a product cost that is added to inventory and charged against sales as cost of goods sold when the company sells the inventory. Yes. Variable costing means that all variable costs of manufacturing are inventoried. Variable costs are limited to direct costs and direct labor. All overhead costs are excluded, as these costs cannot be directly traced to products and services. Yes. Variable costing means that only direct materials and direct labor are inventoried. The inclusion of overhead in costs that are inventoried is not allowed for either external-reporting or tax purposes and are therefore excluded. No. Variable costing means that all variable costs of manufacturing are inventoried. These include overhead costs that are incurred in direct proportion to the volume of production, even though these costs may only indirectly affect the production process and thus are categorized as "overhead". Question 5 1 pts Compare variable and absorption costing regarding the treatment of production-volume variance. The production-volume variance appears on both an absorption-costing and a variable-costing income statement. The production-volume variance appears only on an absorption-costing income statement. The production-volume variance appears only on a variable-costing income statement. A production-volume variance appears whenever the expected production deviates from the expected fixed overhead rate. Question 6 1 pts Compare the contribution margin with the gross margin. The contribution margin is revenue less variable costs which include variable selling and administrative costs. In contrast, gross margin is revenue less manufacturing costs which include fixed manufacturing costs. The contribution margin is revenue less variable costs and used to generate a variable-costing income statement. In contrast, gross margin is revenue less manufacturing costs found on an absorption-costing income statement. The contribution margin is revenue less variable costs which include only variable manufacturing costs. In contrast, gross margin is revenue less manufacturing costs which include only fixed manufacturing costs. The contribution margin is revenue less manufacturing costs which include fixed manufacturing costs. In contrast, gross margin is revenue less variable costs which include variable selling and administrative costs. Question 7 1 pts "The dollar amount of the production-volume variance depends on what expected volume of production was chosen to determine the fixed-overhead rate." Explain. The production-volume variance depends on the expected volume of production used as the numerator in setting the fixed-overhead rate. The lower the level chosen, the lower the rate. The total amount of the variance is a function of the rate and the deviation of actual volume from the volume used to set the rate. The production-volume variance depends on the actual volume of production used as the numerator in setting the fixed-overhead rate. The higher the level chosen, the lower the rate. The total amount of the variance is a function of the rate and the deviation of expected volume from the prorated volume. The production-volume variance depends on the actual volume of production used as the denominator in setting the fixed-overhead rate. The higher the level chosen, the higher the rate. The total amount of the variance is a function of the rate and the deviation of expected volume from the prorated volume. The production-volume variance depends on the expected volume of production used as the denominator in setting the fixed-overhead rate. The higher the level chosen, the lower the rate. The total amount of the variance is a function of the rate and the deviation of actual volume from the volume used to set the rate










