Question: (i) Define the decision variables (ii) Provide a verbal statement to define the objective function (iii) Provide verbal statements to describe the constraints (iv) Define



(i) Define the decision variables
(ii) Provide a verbal statement to define the objective function
(iii) Provide verbal statements to describe the constraints
(iv) Define a mathematic model to tackle the problem
PLEASE DO QUESTIONS IV IF YOURE ONLY GOING TO DO ONE
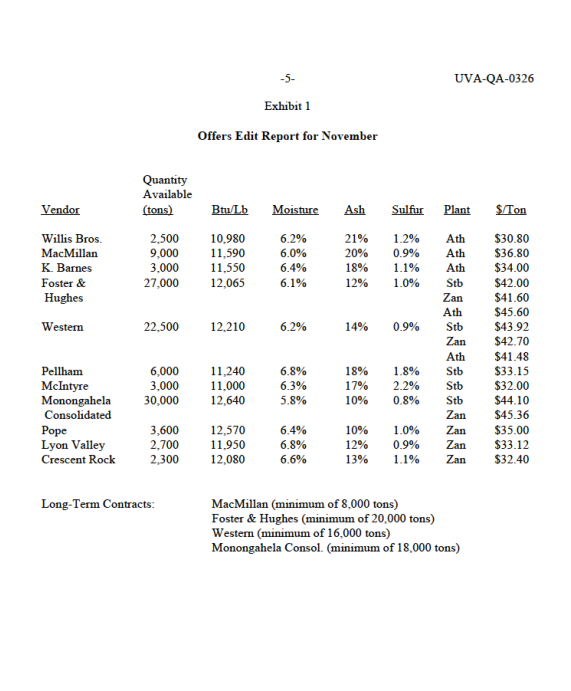
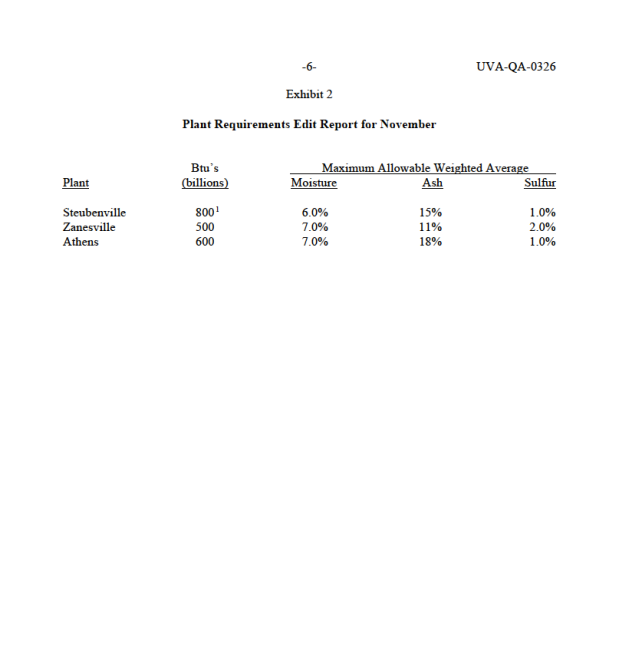
BUCKEYE POWER \& LIGHT COMPANY Don Peters was manager of the Production Fuels Department of Buckeye Power \& Light Company (BP\&L), a small utility in southeastern Ohio. BP\&L had three steam electric power plants-located in Athens, Zanesville, and Steubenville-whose primary energy source was coal. Each month, coal for those plants was purchased from a heterogeneous collection of vendors in Ohio, Pennsylvania, and West Virginia, ranging in size from small father-and-son operations to large mining companies. Peters was responsible for the monthly coal-procurement process, including how much to purchase from each vendor and which specific plant (or plants) each vendor should supply. In October 1986, Peters' immediate task was to determine November's coal-procurement schedule. BP\&L had recently retained the services of a consulting firm to analyze aspects of its operations, including the coal-procurement process. Peters hoped to use the opportunity of the consultant's analysis to rethink the entire procurement process. He also hoped the report would shed some light on two related issues that had been a source of controversy within the department. Coal Compared with oil, natural gas, and nuclear energy, coal was a relatively cheap source of fuel during the 1980 s. Coal is a combustible rock formed by the underground compression of partially decomposed plant matter over millions of years. There are four major types of coal, classified according to energy content: lignite (lowest energy content), sub-bituminous, bituminous (most widely used as a fuel source), and anthracite (highest energy content). Coal's energy content (or thermal value) is measured in British thermal units (Btu). (One Btu is the amount of heat needed to raise a pound of water one degree Fahrenheit.) Pure bituminous coal typically contains on the order of 15,000Btu per pound (Btu/lb). There are three major determinants of the quality of coal. One is total moisture content. There are two distinct types of moisture associated with coal. Free moisture lies on the surface of the coal. Its presence, which depends primarily on conditions in the mine and in transit, is an This case was prepared by Robert Carraway. It was written as a basis for class discussion rather than to illustrate effective or ineffective handling of an administrative situation. Copyright (c) 1986 by the University of Virginia Darden School Foundation, Charlottesville, VA. All rights reserved. To order copies, send an e-mail to sales@dardenpublishing.com. No part of this publication may be reproduced, stored in a retrieval system, used in a spreadsheet, or transmitted in any form or by any means - electronic, mechanical, photocopying, recording, or otherwise - without the permission of the Darden School Foundation. Rev. 12/93.0 2= UVA-QA-0326 important parameter in the design of coal-handling and -preparation equipment. Inherent moisture is trapped within the pores of the coal itself and is present even when the surface of the coal appears dry. Both types of moisture reduce energy content. A second determinant of coal quality is ash content. Ash is the incombustible residue that remains after the coal is burned. Like moisture, a high ash content increases shipping, handling, and preparation costs while reducing thermal value. Additional equipment and expense is required periodically to remove ash from a coal-fired furnace. Failure to do so adequately has a long-term impact on the life of a furnace. The third major determinant of quality is sulfur content. When coal is burned, sulfur oxides are released, creating pollution and contributing to the corrosion of vital plant parts. Some sulfur can be removed prior to burning by "washing" the coal. To further control pollution, "scrubbers" can be attached to smokestacks to filter out a substantial number of sulfur oxide particles. During the 1980 s, the maximum level of sulfur oxide pollution was regulated by law. Each coal-fired plant was thus forced to restrict the amount of sulfur in the coal it burned on the basis of the specific pollution-control equipment it was using. BP\&L's Coal-Procurement Process Each month, vendors interested in supplying one or more of BP\&L's coal-fired power plants completed an offer sheet specifying the amount of coal they had to sell along with its quality and price. Quality was expressed in terms of Btu/lb and moisture, ash, and sulfur content. Vendors were asked to quote a per ton price, transportation included, for each power plant they were willing and able to supply. The Production Fuels department took all offers, adjusted them for past performance (particularly the amount of coal available for purchase, which was often overstated and had to be adjusted downward), and summarized the results in a document called the offers edit report (Exhibit 1). At the same time, each of the three coal-fired power plants submitted its requirements for the upcoming month. Corporate policy dictated that a plant have sufficient Btu's on hand each month to satisfy 120% of expected demand. Exactly how many Btu's to order for the upcoming month depended on both the estimated ending inventory of coal in the current month (stated in terms of Btu's) and the expected demand during the upcoming month. Each plant also provided minimum acceptable quality standards for moisture, ash, and sulfur content. Each of those was stated in terms of a weighted average of all coal delivered to the plant in the month. For example, 1,000 tons of coal with 2% sulfur content and 500 tons of coal with 1% sulfur content would produce an overall 1.67% sulfur-content level; this number was not allowed to exceed the sulfur standard. The sulfur standards were set by law; moisture and ash standards were left to the discretion of the individual plant managers, who were familiar with the costs associated with handling the increased levels of moisture and ash at their respective plants. The Production Fuels Department was responsible for taking the offers edit report and the plant requirements, summarized in the plant requirements edit report (Exhibit 2), and arriving at an overall coal-procurement plan. Peters, as manager of the department, had the flexibility to negotiate with both vendors and plant managers to strike a better overall deal for the company. For example, he could negotiate price reductions and/or quantity increases with vendors. Similarly, he could make plant managers aware of particularly restrictive quality requirements and negotiate to have them relaxed. Ultimately. Peters was responsible for approving the overall coal-procurement plan. Recently, the Production Fuels Department had been struggling with two issues related to the coal-procurement process: long-term contracts and safety-stock levels. Long-Term Contracts Because of a utility's need to have a guaranteed source of fuel, long-term contracts with coal vendors were a long-standing industry practice. A long-term contract with a vendor obligated the utility to buy a minimum amount of coal each month from that vendor at the contract-specified price. The balance of the utility's needs were met by purchasing additional coal on the spot market. Prior to 1973 , BP\&L had purchased approximately 65% of its coal on long-term contract. The energy crisis of the 1970 s and resulting surge in demand for coal and coal prices had precipitated an upward trend in that figure. By 1986, BP\&L was purchasing 80% of its coal on long-term contract (vendors in late 1986 with whom BP\&L had long-term contracts and the contract amounts are indicated in Exhibit 1). As the energy crisis eased, however, the availability of coal became less of a concern. Moreover, by 1986 prices on the spot market were running about $6 per ton less than long-term contract prices. Many people in the Production Fuels department thought that the percentage of coal purchased on long-term contract should be reduced, perhaps back to the 65% level. Peters estimated that returning to the 65% figure would allow BP\&L to reduce the amount of coal purchased on long-term contract by 12,000 tons. If such a reduction were to be made, it was not clear to Peters which of the current long-term contracts should be reduced and/or eliminated. 20% Safety Stock Running out of coal forced a utility to purchase energy from a neighboring utility at a premium price. In August, for example, BP\&L had sold 10 billion surplus Btu's on an emergency basis to a utility in western Pennsylvania for $20,000. A rash of such purchases by Offers Edit Report for November Long-Term Contracts: MacMillan (minimum of 8,000 tons) Foster \& Hughes (minimum of 20,000 tons) Western (minimum of 16,000 tons) Monongahela Consol. (minimum of 18,000 tons) 6 UVA-QA-0326 Exhibit 2 Plant Requirements Edit Report for NovemberStep by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


