Question: I don't know where to start, please show me this step by step. //TODO is where I have to write code. Thank you. /** *
I don't know where to start, please show me this step by step.
//TODO is where I have to write code.
Thank you.
/** * Determine if a value is in the list * * @param target the value we are searching for * @param recursive whether we are doing the search recursively * @return true iff target is in the list */ public boolean contains(int target, boolean recursive) { if (target == Integer.MAX_VALUE) throw new RuntimeException("Maximum target exceeded."); if (target == Integer.MIN_VALUE) throw new RuntimeException("Minimum target exceeded."); if (recursive) { return recursiveSearch(first, target); } else { return iterativeSearch(first, target); } } /** * Search the list recursively * * @param node the node in the list where we are starting the search * @param target the value we are searching for * @return true iff value is in the list */ private static boolean recursiveSearch(Node node, int target) { // TODO: Implement this method return false; }
/** * Search the list using a loop instead of recursion * * @param node the first node in the list * @param target the value we are searching for * @return true iff value is in the list */ private static boolean iterativeSearch(Node node, int target) { // TODO: Implement this method return false; } /** * Print the list starting with the first node, by making calls to * the Node's toString() method */ public void printList() { // TODO: Implement this method }
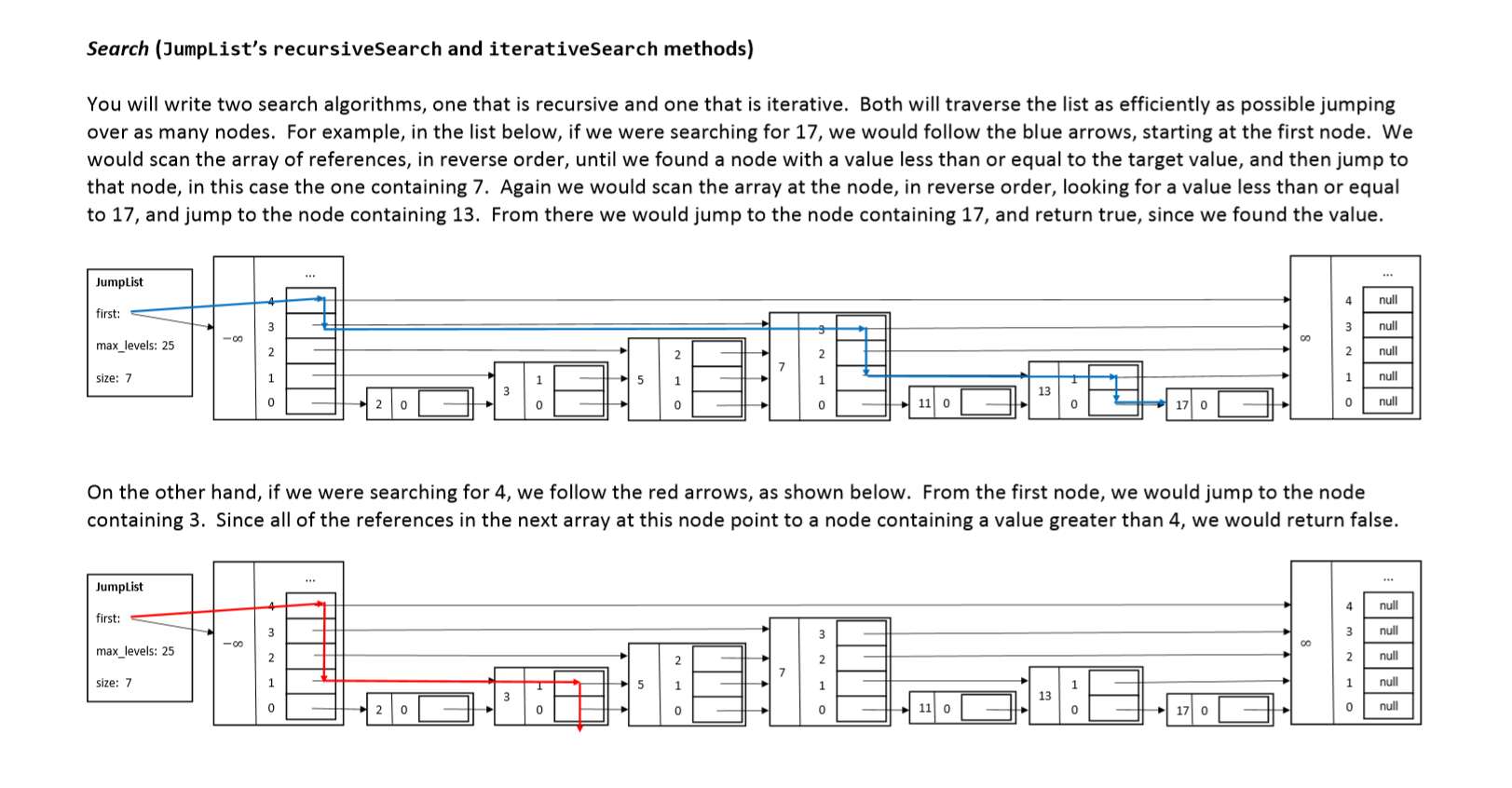
Search (JumpList's recursiveSearch and iterative Search methods) You will write two search algorithms, one that is recursive and one that is iterative. Both will traverse the list as efficiently as possible jumping over as many nodes. For example, in the list below, if we were searching for 17, we would follow the blue arrows, starting at the first node. We would scan the array of references, in reverse order, until we found a node with a value less than or equal to the target value, and then jump to that node, in this case the one containing 7. Again we would scan the array at the node, in reverse order, looking for a value less than or equal to 17, and jump to the node containing 13. From there we would jump to the node containing 17, and return true, since we found the value. JumpList null first: null 8 max_levels: 25 null po + mo size: 7 null null On the other hand, if we were searching for 4, we follow the red arrows, as shown below. From the first node, we would jump to the node containing 3. Since all of the references in the next array at this node point to a node containing a value greater than 4, we would return false. JumpList null first: null max_levels: 25 null size: 7 5 null null Search (JumpList's recursiveSearch and iterative Search methods) You will write two search algorithms, one that is recursive and one that is iterative. Both will traverse the list as efficiently as possible jumping over as many nodes. For example, in the list below, if we were searching for 17, we would follow the blue arrows, starting at the first node. We would scan the array of references, in reverse order, until we found a node with a value less than or equal to the target value, and then jump to that node, in this case the one containing 7. Again we would scan the array at the node, in reverse order, looking for a value less than or equal to 17, and jump to the node containing 13. From there we would jump to the node containing 17, and return true, since we found the value. JumpList null first: null 8 max_levels: 25 null po + mo size: 7 null null On the other hand, if we were searching for 4, we follow the red arrows, as shown below. From the first node, we would jump to the node containing 3. Since all of the references in the next array at this node point to a node containing a value greater than 4, we would return false. JumpList null first: null max_levels: 25 null size: 7 5 null null
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


