 I don't understand it. The letter A only
I don't understand it. The letter A only
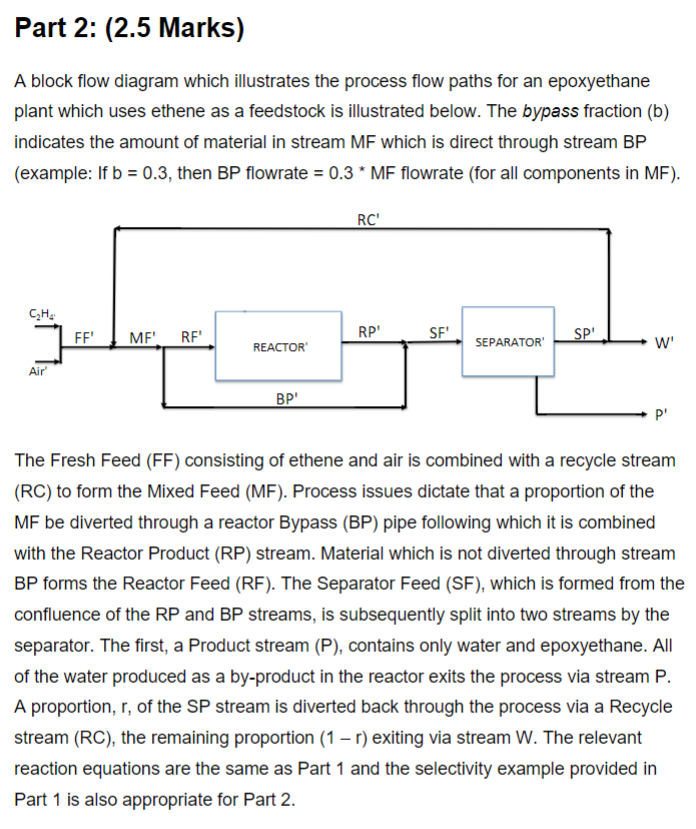
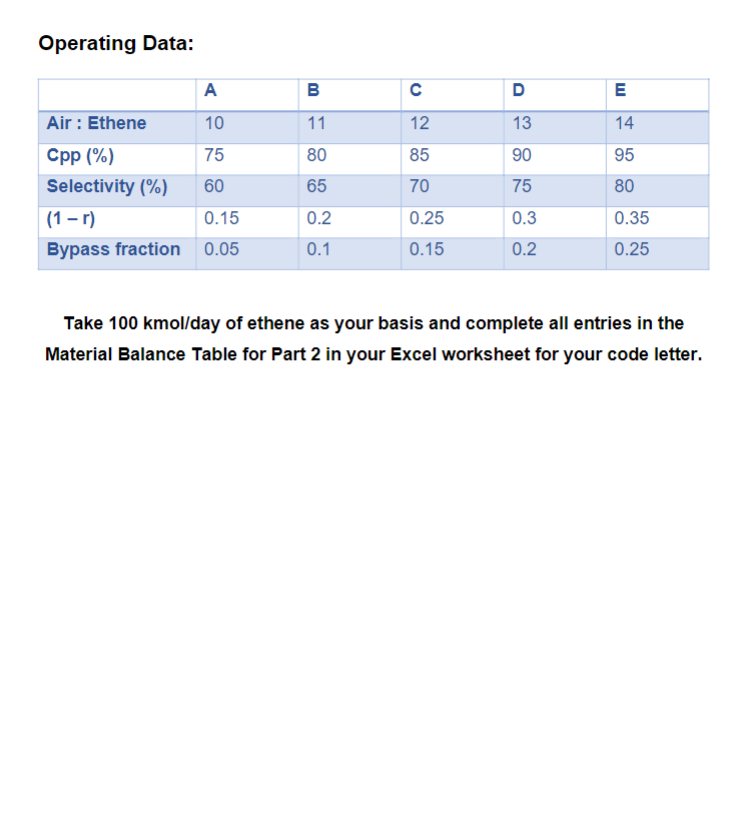
A block flow diagram which illustrates the process flow paths for an epoxyethane plant which uses ethene as a feedstock is illustrated below. The bypass fraction (b) indicates the amount of material in stream MF which is direct through stream BP (example: If b=0.3, then BP flowrate =0.3MF flowrate (for all components in MF). The Fresh Feed (FF) consisting of ethene and air is combined with a recycle stream (RC) to form the Mixed Feed (MF). Process issues dictate that a proportion of the MF be diverted through a reactor Bypass (BP) pipe following which it is combined with the Reactor Product (RP) stream. Material which is not diverted through stream BP forms the Reactor Feed (RF). The Separator Feed (SF), which is formed from the confluence of the RP and BP streams, is subsequently split into two streams by the separator. The first, a Product stream (P), contains only water and epoxyethane. All of the water produced as a by-product in the reactor exits the process via stream P. A proportion, r, of the SP stream is diverted back through the process via a Recycle stream (RC), the remaining proportion (1-r) exiting via stream W. The relevant reaction equations are the same as Part 1 and the selectivity example provided in Part 1 is also appropriate for Part 2. Operating Data: Take 100kmol/ day of ethene as your basis and complete all entries in the Material Balance Table for Part 2 in your Excel worksheet for your code letter. A block flow diagram which illustrates the process flow paths for an epoxyethane plant which uses ethene as a feedstock is illustrated below. The bypass fraction (b) indicates the amount of material in stream MF which is direct through stream BP (example: If b=0.3, then BP flowrate =0.3MF flowrate (for all components in MF). The Fresh Feed (FF) consisting of ethene and air is combined with a recycle stream (RC) to form the Mixed Feed (MF). Process issues dictate that a proportion of the MF be diverted through a reactor Bypass (BP) pipe following which it is combined with the Reactor Product (RP) stream. Material which is not diverted through stream BP forms the Reactor Feed (RF). The Separator Feed (SF), which is formed from the confluence of the RP and BP streams, is subsequently split into two streams by the separator. The first, a Product stream (P), contains only water and epoxyethane. All of the water produced as a by-product in the reactor exits the process via stream P. A proportion, r, of the SP stream is diverted back through the process via a Recycle stream (RC), the remaining proportion (1-r) exiting via stream W. The relevant reaction equations are the same as Part 1 and the selectivity example provided in Part 1 is also appropriate for Part 2. Operating Data: Take 100kmol/ day of ethene as your basis and complete all entries in the Material Balance Table for Part 2 in your Excel worksheet for your code letter

 I don't understand it. The letter A only
I don't understand it. The letter A only





