Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
(i) Explain why carbon in steel makes martensite very hard, whereas it has a weak strengthening effect on austenite. [20%] (ii) The free energy
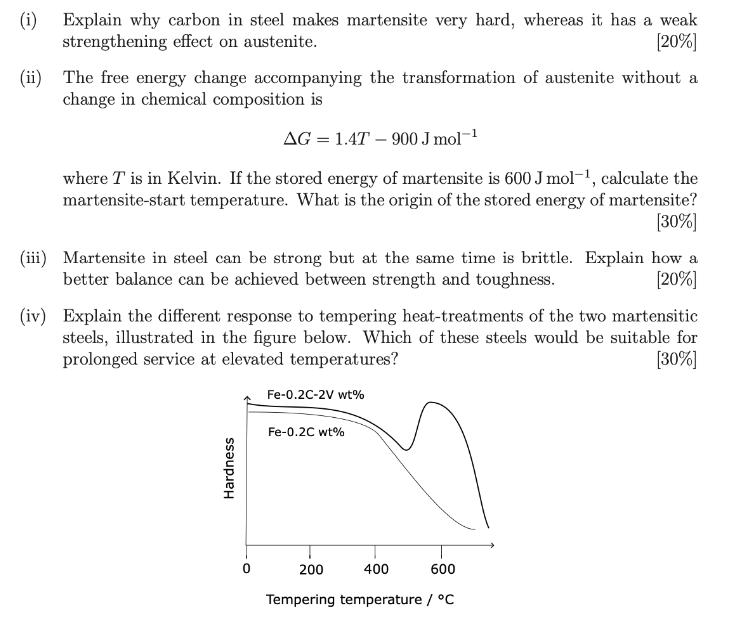
(i) Explain why carbon in steel makes martensite very hard, whereas it has a weak strengthening effect on austenite. [20%] (ii) The free energy change accompanying the transformation of austenite without a change in chemical composition is AG = 1.4T - 900 J mol where T is in Kelvin. If the stored energy of martensite is 600 J mol-1, calculate the martensite-start temperature. What is the origin of the stored energy of martensite? [30%] (iii) Martensite in steel can be strong but at the same time is brittle. Explain how a better balance can be achieved between strength and toughness. [20%] (iv) Explain the different response to tempering heat-treatments of the two martensitic steels, illustrated in the figure below. Which of these steels would be suitable for prolonged service at elevated temperatures? Fe-0.2C-2V wt% [30%] Hardness Fe-0.2C wt% 0 200 400 600 Tempering temperature / C
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


